FGT 1 Flashcards
Pics (22 cards)

multinucleated squamous cells containing eosinophilic to basophilic viral inclusions with a “ground-glass” appearance
The cell in the center shows HSV cytopathic effect
clinical findings

yellow, frothy vaginal discharge, vulvovaginal discomfort, dysuria, and dyspareunia
vaginal and cervical mucosa - fiery-red appearance, with marked dilatation of cervical mucosal vessels “strawberry cervix.”
Risk factors
Clinical findings
Saline microscopy shows what?

Risk factors: diabetes mellitus, antibiotics, pregnancy, OCPs
Findings: Pruritic vaginitis with a white or thick (“cottage cheese”) discharge and fiery red vaginal mucosa
Saline microscopy shows yeasts and pseudohyphae
Disease?
Define disease

“Violin-string” adhesions of chronic Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
a type of perihepatitis that causes liver capsular infection without infecting the hepatic parenchyma or pelvis
Disease
Define disease
What kind of epithelium
Clincal signs
Tx
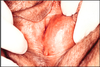
Bartholin cyst/bartholin duct abcess
obstruction of the Bartholin gland duct by an inflammatory process
transitional or squamous epithelium
pain and local discomfort
excised or opened permanently (marsupialization)
Disease
Microscopic findings
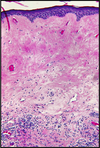
Lichen Sclerosus
marked thinning of the epidermis
degeneration of the basal cells
hyperkeratosis
sclerotic changes of the superficial dermis
bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate in the underlying dermis
Describe picture
Disease predisposes risk to?
Associated with which HLA?
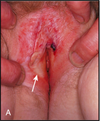
Lichen sclerosis. The vulva shows a parchment-like appearance
increased risk of SCC
HLA - DQ7
Disease/why do you get it
Gross findings
Microscopic findings

Squamous cell hyperplasia due to rubbing vulvar mucosa in response to pruritus
Gross: White plaques (leukoplakia)
Microscopic findings: thickening of the epidermis (acanthosis), hyperkeratosis
Describe picture
Disease
Etiology
C/F (mc site)

Papillary, exophytic, treelike cores of stroma covered by thickened squamous epithelium
Condyloma Acuminatum
low oncogenic risk HPVs- 6 and 11
C/F: benign genital warts (•vulvar, perineal, and perianal)
Describe picture

HPV cytopathic effect (koilocytic atypia) characterized by atypical, enlarged, hyperchromatic nuclei with perinuclear halos
What disease is related to infection with high risk HPVs- especially HPV 16?
Precursor lesion
Basaloid and warty carcinomas
Precursor lesion: classic vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN)
Describe picture
Associated w/ what disease

marked atypia of the basal layer of the squamous epithelium and normal-appearing differentiation of the more superficial layers (Differentiated VIN)
Keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma (a/w long-standing lichen sclerosus or squamous cell hyperplasia)
Describe picture
Associated w/ what disease

epidermal thickening, nuclear atypia, increased mitoses, and lack of cellular maturation (Classic VIN)
Basaloid and warty carcinomas
Describe picture
Disease
Morphology

Basaloid vulvar carcinoma (HPV positive), composed of small, immature (basaloid) cells. This invasive tumor has an area of central necrosis.
Basaloid carcinoma
nests and cords of small, tightly packed cells that lack maturation and resemble the basal layer of the normal epithelium
+/- foci of central necrosis
Describe picture
Disease
Morphology

Well-differentiated, keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva (HPV negative)
Invasive keratinzing squamous cell carcinomas
nests and tongues of malignant squamous epithelium
prominent central keratin pearls
Describe picture
Disease (mc sites)
Morphology

Benign papillary projections covered with columnar secretory epithelium and underlying myoepithelial cells
Papillary Hidradenoma (labia majora/interlabial folds)
sharply circumscribed nodule
Describe picture
Disease
Morpohology

The epidermis is infiltrated by large cells with pale-pink cytoplasm that are spreading along the basal portion of the squamous epithelium
Extramammary Paget Disease
intraepithelial proliferation of malignant cells.
pruritic, red, crusted, maplike area - labia majora.
Characteristics of paget cells
larger than surrounding keratinocytes
Single/ small clusters within epidermis
pale cytoplasm containing mucopolysaccharide
PAS /Alcian blue/ Mucicarmine +
Cytokeratin 7 +
spread laterally within the epidermis
Disease (mc sites)
Differentiating features (3)
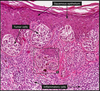
Malignant melanoma (Labia majora/minor, clitoris)
S-100 protein + on IHC
Cytokeratin -ve
Lack of muco-polysaccharides (Both are present in Paget disease)
Disease
Cause of disease
Precursor lesion
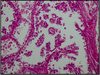
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
intrauterine exposure to DES
Precursor lesion: Vaginal adenosis
Disease
Microscopic findings
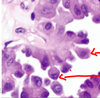
Clear cell adenocarcinoma
M/E:
Cells are large and have distinct cell membranes; moderate to abundant clear cytoplasm
cuboidal and sometimes hobnail type with nuclei protruding into the lumen
Nuclei are round to irregular, hyperchromatic with conspicuous nucleoli
Disease
Tumor cell origin
Gross
Microscopic

Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (sarcoma botryoides) mc age < 5 years
malignant embryonal rhabdomyoblasts
Gross: polypoid, rounded, bulky masses, grapelike
M/E:
Small tumor cells with oval nuclei
Small protrusions of cytoplasm from one end-tennis racket
Loose fibromyxomatous stroma


