Exam 4 Flashcards
(40 cards)
How many naturall occuring isotopes are there?
300
Alpha Radiaton
parent nuclide release to daughter nuclei
42He
Nuclear equation represents…
changes that occur during radioactivity and other nuclear processes
Nuclide
specific isotope in nuclear chemistry
Parent nuclide
origninal atom
Daughter Nuclide
Balanced Nuclear Equations
sum of the atomic numbers
Alpha Radiation
has the most ionizing power, but the least penetrating power
Beta radiation
occurs when a unstable nucleaus emits an electron, as the emission occurs a nuetron turns into a proton
0-1e
Gamma Radiation
different from alpha or beta radiation, Gamma radiation is not matter but electromagnetic radiation
00y
Beta particle symbol
0-1e
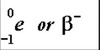
Gamma Rays
lowest ionizing power but highest penetrating power
Electron Capture
electron in the 1s shell is captured by the nucleus and a proton is converted to a nuetron
Beta particles
intermediate ionizing power
intermediate penetrating power
Half-life
times it takes for half of the parent nuclides in a radioactive sample to decay to the daughter nuclides
Acid-Base Buffers
solution that lessens the impact of pH from the addition of acid or base
conjugate acid-base pair
both species are appreciable quantities in solution
Carbon-14
constantly formed in the upper atmosphere by the nuetron bombardment of nitrogen
continuous formation of carbon-14 in the atmosphere and its continuous decay back to nitrogen-14 produce a nearly constant equilibrium concentration of atmospheric carbon-14
carbon-14 half life
5730 years
geiger counter
cathode and anode tube with voltage souce and amplifier to mueasure radiation
units of radiation intensity
1 becquerel(Bq)= 1 dep(disintegration per second)
1 curie(Ci)= 3.7x1010 dps
intensity of radiation
inversly proportional to the square of distance from the source
radiation dosimetry
all radiaton is not the same in terms of its cell damaging effects. the damage depends on the ionizing power, the intensity and the length of exposure
units of dose
Roentgen


