Exam 1 Biochemistry Thread Flashcards
(137 cards)
Gibbs free energy (G)
The potential energy of a chemical reaction or system with the capacity to do work.
High Energy Bond
Any bond that releases > -7 kcal/mol upon dissociation.
Gibbs Free Energy Equation
The change in free energy of a system (∆G) at constant pressure and temperature.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
∆G ⇒ change in free energy
∆H ⇒ change in enthalpy
∆S ⇒ change in entropy
T ⇒ absolute temperature in Kelvin
Reaction Spontaneity
∆G > 0 ⇒ Reaction proceeds in the reverse direction (endergonic)
∆G = 0 ⇒ equilibrium
∆G < 0 ⇒ Reaction proceeds in the forward direction (exergonic)
Equilibrium Constant
(K or Keq)
Defined as the ratio of the concentration of products to concentration of reactants.
A + B ↔︎ C + D

Free Energy Change
The free energy change for a reaction (∆G) is given by:
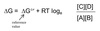
Standard Free Energy
At Equilibrium
∆G = 0.
Concentrations of reactants and products are at equilibrium values.
Standard free energey change is related to the equilirium constant (Keq).

Reaction Kinetics
Rate of ractions determined by the rate constants (k) and concentrations of reactants.
Equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backwards reaction.

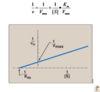
∆G Trends
As we approach equilibrium:
Keq gets bigger because [products] > [reactants]
∆G gets smaller
More negative K ⇒ more positive ∆G.
D & L
Isomers
D & L isomers are enantiomers.
D if OH on the farthest chiral C is on the right
L if OH on the farthest chiral C is on the left
D form in the body.

α and β
Isomers
α and β isomers are the result of ring formation ⇒ anomers
Fischer projections:
alpha ⇒ OH on the same side as oxygen ring
beta ⇒ opposite side
Hayworth projections:
alpha = trans
beta = cis

Fisher to Hayworth
Projections
right side ⇒ up
left side ⇒ down

Anomeric C
The anomeric C is linked to two oxygens.
C#1 → anomeric C in aldoses
C#2 → anomeric C in ketoses
Epimers
Isomers that differ in the position of OH at only one carbon.
Considered diasteriomers.

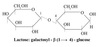
Galactose
C4 epimer of glucose.

Mannose
C2 epimer of glucose

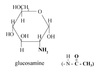
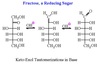
Reducing Sugar
Anomeric C has available OH.
All monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
Ketose must tautomerize to an aldose first.
Keto-Enol Tautomerization
Sugars freely interconvert between the keto and aldo forms in solution.
Catalyzed by base.
Mutarotation
Cyclic sugars undergo epimerization between the alpha and beta anomeric forms in solution.
Forms a racemic mixture ⇒ racemization.
Shows mutarotation of plane polarized light.
Glucose Test
Urine test for glucose:
Glucose oxidase used to oxidize glucose to gluco-lactone and H2O2.
Peroxidase used to visualize the H2O2.
Clinitest
Uses Benedict’s reagent (copper reduction) to test for the presence of reducing sugars in urine.
Monosaccharide Reactions
Oxidation of terminal OH group

Monosaccharide Reactions:
Reduction of Carbonyl C
Yields new OH and creates a polyol.

Monosaccharide Reactions:
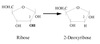
Reduction of OH
Reduction of OH on C#2 yields a deoxy sugar