Electron Transport Pathway Flashcards
(65 cards)
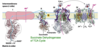
Where do the electrons come from that enter the electron transport chain
Stored in NADH and FADH2 produced during glycolysis, acetyl-CoA formation, and the TCA cycle.
What parts of the ETC are exergonic? Endergonic?
The electrons are passed along in a series of exergonic redox reactions, their energy is used in the endergonic process of ATP formation in the process of oxidative phosphorylation
Which enzymes generate NADH and FADH2?
Enzymes that generate NADH and FADH2 are all Dehydrogenases
2 NADH:
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
α-ketogluterate Dehydrogenase
Malate Dehydrogenase
2 FADH2:
Succinate Dehydrogenase
How many sets of ETC enzymes and ATP synthase molecules does a mitochondria in the liver have?
10,000
What physical property does the mitochondrial outer membrane have?
It is permiable to small molecules and ions
What physical properties does the mitochondrial inner membrane have?
It is impermiable to most small molecules and ions, including H+
Contains:
- electron carrier complexes I-IV
- ADP-ATP translocase
- ATP synthase (F0F1)
- Other membrane transporters
What physical properties does the mitochondrial matix have?
Contains:
- pyruvate
- TCA cycle enzymes
- fatty acid β-oxidation enzymes
- amino acid oxidation enzymes
- DNA, ribosomes
- Many other enzymes
- ATP, ADP, Pi, Mg2+, Ca2+, K+
- Many soluble metabolic intermediates
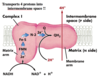
Enzyme complex I
Name
Mass
Number of Subunits
Prosthetic Group(s)
H+ pumped
Enzyme complex I
Name: NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase
Mass: 850 kDa
Number of Subunits: 43 (14 in bacteria)
Prosthetic Groups: FMN, Fe-S
accepts electrons from NADH, produces ubiquinone, transports 4 H+
Enzyme complex II
Name
Mass
Number of Subunits
Prosthetic Group(s)
H+ pumped
Enzyme complex II
Name: Succinate-ubiquinone reductase
Mass: 140 kDa
Number of Subunits: 4
Prosthetic Groups: FAD, Fe-S
accepts electrons from FADH2, produces ubiquinone also known as succinate dehydrogensae from the TCA cycle
Transfers 0 H+
Enzyme complex III
Name
Mass
Number of Subunits
Prosthetic Group(s)
H+ pumped
Enzyme complex III
Name: Ubiquinone: cytochrome c oxidoreductase
Mass: 250 kDa
Number of Subunits: 11
Prosthetic Groups: Henes, Fe-S
accepts electrons from reduced ubiquinone and passes them to cytochrome c , transports 4 H+
Enzyme complex IV
Name
Mass
Number of Subunits
Prosthetic Group(s)
H+ pumped
Enzyme complex IV
Name: Cytochrome oxidase
Mass: 160 kDa
Number of Subunits: 13 (3-4 in bacteria)
Prosthetic Groups: Heme, CuA, CuB
accepts electrons from cytochrome c and uses them to reduce O2, producing water , transports 2 H+
Cytochrome c
Mass
Number of Subunits
Prosthetic Group(s)
H+ pumped
Cytochrome c
Mass: 13 kDa
Number of Subunits: 1
Prosthetic Group: Heme
NOT A PUMP! A lipid-soluble intramembrane transporter
P side
Side of inner membrane facing intermembrane space between inner and outer mitochondrial membrane
N side
Matrix side of inner membrane
Which TCA cycle enzyme is embedded in the ETC? Where is it?
Succinate dehydrogenase, embedded in N side (matrix side) of complex II
Coenzyme Q is also called?
Ubiquinone
Complex I name and function
Which enzyme complexes transport H+?
Complex I, Complex III, Complex IV

How do electrons flow through electron transport?
Electrons flow:
I to III to IV
– or –
II to III to IV

Complex I detail
- Passes electrons from NADH to CoQ.
- Contains over 40 different polypeptide chains (7 are encoded by mitochondrial genes).
- Contains one flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and 6-7 iron-sulfur clusters.
- NADH binding site is on the matrix side
- Non-covalently bound FMN accepts two electrons from NADH
- Several iron-sulfur centers pass one electron at a time toward ubiquinone (CoQ) binding site
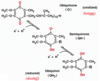
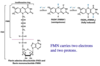
FMN structure
Which way do electrons flow from atom to atom as measured by standard reduction potential?
- If a compound has a large positive Reduction Potential (E’° in volts),
it will accept electrons from compounds with lower R.P.
- electrons flow from negative to positive
- analagous to ∆G°’
How does reduction potential factor in to the ETC?
The more positive the standard potential, the greater the affinity for electrons.
To have sequential transfer of electrons, carriers must transfer electrons to carriers with higher standard potential
The further down the chain, the greater the RP

How are proton pumps powered by the ETC?
As electrons are passed through and between complexes, they move to positions of lower free energy. The energy released is used to pump protons, which in turn drive ATP synthesis.