Electophoresis Flashcards
Principle of electrophoresis
most frequency used in clincal practice, represents a method of seperartion of charged particles based on their different movement when they are placed in an electrical filed.
Charged particles move toword the opossite charged electrode:
- cations (positively charged particles) move to the catode (negatively charged electrode
- anions (negatively charged particles) move to the anode (positively charged electrode)
The rate of migration in electrophoresis depends on:
- the size of the particles (bigger particles move slower)
- the shape of the particels
- the net charge of the particles (more negatively charged ions move quicker)
- the mass of the particles
- electrical force applied on the charged particles
- the characteristics of the supporting medium and the properties of the buffer
supporting material: filter paper or sheets (Blatt) of plastik like cellulose acetate membranes, polyacrylamide, starch, agar or agarose gels)
properties of the buffer: pH, ionic strength, compositon
Immunglobulin G (IgG)
- is the prototype of the immunglobuline family
- the most abudant antibody in plasma (represents about 75% of total immunglobuline in serum)
- major antibody of the secondary immunse response (the synthesis takes a longer period than that of IgM)
- can cross the placenta (major protective antibody in newborns)
Immunglobulin M (IgM)
- is the first immunglobulin produced in response to an antigen
Immunglobulin A (IgA)
- is the major antibody in external secretions like salvia, tears, sweat, bronchial mucus intestinal mucus
Immunglobulin D (IgD)
- has an unknwon function
Immunglobulin E (IgE)
- plays am important role in allergic reactions
Total serum protein in g/dl + seperated in albumin and globulin
Total serum protein: 6 - 8 g/dl;
albumin: 4,5 - 5 g/dl
globulin: 1,5 - 2,5 g/dl

Pathological modification is case of
acute inflammation
↑ α1-globulins
↑ α2-globulins

Pathological modifications in case of
chronic inflammation
↑ γ-globulins

Pathological modifications in case of
multiple myeloma
↑ Total proteins
↑ γ-globulins

Pathological conditions in case of
hepatic cirrhosis
↓ Total proteins
↓ Albumin
↑ β-globulins
↑ γ-globulins

Patological modifications in the case of
nephrotic syndrome
↓ Total proteins
↓ Albumin
↑ α2-globulins
↑ β-globulins
↓ γ-globulins (in severe forms)

Pathological modifications in the case of
hypogammaglobulinemia
↓Totalproteins
↓ γ-globulins

Choose the correct answer: In acute inflammation are increased:
a. α1- and γ-globulins;
b. α2- and γ-globulins;
c. β- and γ-globulins;
d. γ-globulins;
e. α1- and α2-globulins
e. α1- and α2-globulins
Complete the blank spaces with one of the following words: increased, decreased, unmodified.
In nephrotic syndrome:
albumin is…..,
α1-globulins are…..,
α2-globulins are…..,
β- globulins are…..
γ-globulins are…..
decreased
unmodified
increased
increased
decreased
Specify the name of the disease you suppose to be corresponding to the following results of protein electrophoresis. Explain your answer.
Albumin: 45%
α1-Globulins: 5%
α2-Globulins: 8%
β-Globulins: 17%
γ-Globulins: 25%
Total serum proteins: 5.4g/dl
Hepatic cirrhosis
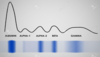
Normal aspect of human serum electrophoresis

Albumin
- the major protein fraction in serum (represent 52-59% of total serum proteins)
- synthesized by the liver as a single polypeptide chain (with 585 amino acids and MW of 65000 daltons)
- role: maintaning the osmotic pressure of the blood and to transport small molecules like ions (Ca, Cu, heavy metals), bilirubin, fatty acids, hormons, certain drugs (salicylates like aspirin and dicoumarol)
Globulin
- divided into four fractions:
albumin, alpha1 (α1), alpha2 (α2), beta (β) and gamma (γ) globulins
each fraction contains different proteins with specific function
α1-Globulins

α2-Globulins

β-Globulins

γ-Globulins
● Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
● Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
● Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
● Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
● Immunoglobulin D (IgD)