ECG Physiology and Anatomy Flashcards
where does the coronary sinus drain into?
right atrium
where does the coronary sinus fill from? what type of blood?
cardiac veins deoxygenated
what are the order of the layers of the heart?
peri epi myo
where do coronary arteries sit?
deep to epi, embedded in muscle
what do coronary arteries supply?
epi and myo
the closure of what valves produce S1?
tricuspid (R side) mitral (L side)
the closure of what valves produce S2?
pulmonary (R side) aortic (L side)
label


label


what are the bifurcations of the aorta?
ascending aorta
R common carotid
L common carotid
subclavian artery
what are the bifurcations of the SVC?
subclavian vein
IJV
BCV
what brings oxygenated blood to the heart?
what takes away deoxygenated blood from the heart?
pulmonary veins
pulmonary arteries
where is the SA node?
RA
what type of cells are in the SA node?
pacemaker cells
how does excitation spread from SA node?
where to?
cell to cell conduction via gap junctions
AV node -> atria -> ventricles
what causes pacemaker potential?
decreased K efflux
increased Na influx
in pacemaker cells, what causes AP depolarisation?
increased Ca influx
in pacemaker cells, what causes AP repolarisation?
increased K efflux
in ventricular muscle cells, what causes depolarisation?
increased Na influx
in ventricular muscle cells, what causes the plateau?
increased Ca influx
decreased Na influx
in ventricular muscle cells, what causes repolarisation?
decreased Ca influx
increased K efflux
label
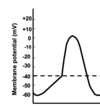

label




