Dislipidemia Flashcards
(71 cards)
Dyslipidemias include?
High LDL
Low HDL
High TG
Chylomicrons?
- Transport fatty acids and cholesterol from the intestine to the liver
- TG rich
- Clears from the blood stream within 12 hours
Lipoprotein Analysis should be done when patient has?
Fasted for 9-12 hours
Along with age and family history risk factors for CHD include?
Hypertension or on HTN meds
Low HDL
male- <40mg/d
FM- <50 mg/dl
C-reactive protein or CRP is what type of marker?
What are the ACC/AHA guidelines?
Inflammatory marker
hsCRP
< 1 mg/l= low risk
1-3= moderate
>3 is high risk
Normal levels of Lp (a) are?
How can it be treated?
< 30 or 75 nmol/L
Niacin, Estrogens, PCSK9-I
Vit D insuffieciency is linked to?
CHD and total mortality
Combined cholesterolemia is?
High TG and Cholesterol
Mixed Dyslipidemia is?
High TG and low HDL
What are the two types of Familial Hypercholesterolemia?
Heterozygous
Homozygous
What are the secondary causes of Hypercholesterolemia?
- DM
- Obese
- Alcohol
- Hypothyroidism
- HIV
- Liver impairment
- CKD
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
- Autoimmune dissorders
LDL-C
Desirable?
very high
<100
>190
TG levels?
Normal?
very high?
<150
>= 500
Non HDL Cholesterol
Desirable?
Very high
<130
>= 220
Drug induced Dyslipidemia?
Thiazides
BBs
Estrogens
Atypical
Steroids
Cyclosporine
Protease inhibitors
Retinoids
- ^LDL and TGs
- Decrease HDL, ^ TGs
- ^HDL and TGs, decrease LDL
- decrease HDL ^TGs
- ^LDL and TGs
- ^LDL and TGs
- ^LDL and TGs, Decrease HDL
- ^LDL and TGs, decrease HDL
The 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline Key Points?
- Encourage adherence of a heart healthy lifestyle
- Statins are recommended for adults in groups demonstrated to benefit
- Engage in Clinic patient discussion before initiating statin therapy
- Initiate the appropriate intensity of statin therapy to reduce ASCVD risk
- Used Pooled cohort equation for estimating 10-ASCVD risk
- Evidence is inadequate to support specific LDL ot non HDL goals
- Nonstatin drug therapy may be considered in selected individuals
NHLBI
Recommendations based on RCT evidence
Less expert opinion than in prior guidelines
The changes from ATP-III
- Dont focus on specific LDL or non HDL goals
- Obtain a lipid panel to monitor adherence
- Use medications proven to reduce ASCVD risk
- Moderate to high intensity statin
- Four Statin-Benefit groups
- Risk decisions in primary prevention
- Optimal lifestyle
- Clinic patietn discussion-shared decision making
What is the first statin benefit group?
Clinical ASCVD
- MI, Angina, Revascularization
- Stroke
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
2nd Statin benefit group?
LDL-C >= 190 and >= 21 years
3rd statin benefit group?
DM: Age 40-75 years, LDL-C 70-189 mg/dL
4th statin benefit group
Primary Prevention
- Risk calculator >= 7.5% 10 year
- No DM
- Age 40-75
- LDL-C 70-189 mg/dL
Summary of statin initiation recommendation to Reduce ASCVD risk
Is the patient older than 21 and have ASCVD?
If so is the patient older than 75?
if older than 21 and less than 75 initiate high-intensity statin therapy
Patient is greater than 75 or not a canidate for High-intensity initiate moderate intensity
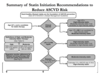
Summary of statin initiation recommendation to Reduce ASCVD risk
Does the patient not have ASCVD?
Then if patient has a LDL >=190 initiate high intensity therpay
If it is not that high but the patient has DM with an LDL 70-189 age 40-75 Initiate moderate statin
But if the patient calculated risk is >=7.5% then initiate high intensity therapy




