Digestive System Flashcards
The digestive system includes…
- Oral Cavity
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
- Rectum
- Anal Canal
The oral cavity includes…
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary Glands
The intestinal area also include…
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
Digestive processes
- Propulsion/Motility
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Elimination
Propulsion
- Peristalsis
- Swallowing
Digestion
Mechanical
-Chewing
-Churning (stomach)
-Segmentation
Chemical
Identify 1-4
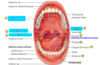
1- Hard palate
2- Palatoglossal arch
3- Palatopharyngeal arch
4- Soft palate
Identify 1-6
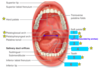
1- Uvula
2- Fauces
3- Tongue
4- Lingual frenulum
5- Gingivae
6- Vestibule
Identify 1-8

1- Vestibule
2- Gingiva
3- Hard palate
4- Palatoglossal arch
5- Soft palate
6- Uvula
7- Fauces
8- Palatopharyngeal arch
Teeth
The hardest substance in the body (made with calcium phosphate)
Contains pulp
Pulp consists of…
nerves, blood vessels and soft connective tissue
Identify 1-7

1- enamel
2- gingiva
3- dentin
4 - pulp cavity
5- root canal
6- cementum
7- periodontal ligaments
Identify 1-3

1- Crown
2- Neck
3- Root
How many teeth do children have? Adults?
20
32
1-4 bitches

1- (3) molars
2- (2) bicuspids
3- (1) cuspid
4- (2) incisors
Papillae - what are they? located where?
where taste buds are located
on tongue
Label 1-3

1- sublingual salivary gland
2- submandibular salivary gland
3- parotid salivary gland
Saliva has what in it to help with digestion?
Mucins, electrolytes, antibodies, enzymes
What enzymes are in saliva? What do they do?
Salivary amylase- begins chemical digestion of complex carbohydrates
lingual lipase- begins chemical digestion of triglcerides
1-5 :)

1- mucosa
2- submucosa
3- muscularis externa
4- serosa
5- lumen
Label the parts of the mucosa

1- epithelium
2- lamina propria
3- muscularis mucosae
1-4 (parts of the muscularis externa)

1- longitudinal
2- circular
3- longitudinal
4- circular
what are the circled things called and what layer are they in?

- glands in submucosa
- submucosa
1-4 of serosa

1- epithelium / visceral peritoneum
2- connective tissue
3- epithelium / visceral peritoneum
4- connective tissue
what is the esophagus?
A muscular tube leading from the mouth to the stomach. DOES NOT contribute to digestion on its own (all about propulsion/motility)
What is the esophagus involved in?
movement of food mass - involves waves of muscular contraction called peristalsis
1-4 What is this a picture of?

1- mucosa
2- submucosa
3- muscularis externa
4- adventitia (fibrous connective tissue)
esophagus
How is the entrance and exit of stuff regulated by the esophagus?
Sphincters
Upper esophageal sphincter
Lower esophageal sphincter
What is GERD
when the lower esophageal sphincter doesn’t close all of the way and stomach acid comes back up into esophagus
What are mesenteries?
folds of the peritoneum that support and stabilize organs, hold fat, and provide a route for blood vessels

what is the greater omentum?
a large superficial mesentery that hangs down over many abdominal organs like an apron
Label F,C,B,P

F- fundus
C- cardia
B- body
P- pylorus
Label 1-5

1- longitudinal muscle
2- circular muscle
3- oblique muscle
4- lesser curvature
5- greater curvature

Label 1-3

1- lower esophageal sphincter
2- pyloric sphincter
3- rugae
1-4

1- mucosa
2- submucosa
3- muscularis externa
4- serosa
1-4 b words

1- gastric pit
2- epithelium
3- lamina propria
4- gastric gland
what do secretions mix together to make?
Chyme
1-4

1- surface mucus cells
2- parietal cells
3- chief cells
4- enteroendocrine cells
what do surface mucus cells do?
secrete a think alkaline mucus that protects the mucosa from the acidic environment inside the stomach
what do parietal cells do?
Secrete hydrochloric acid (kills
microorganisms in swallowed food,
denatures proteins) and intrinsic intrinsic
factor (necessary for the absorption
of Vitamin B12 in the small
intestines)
what do chief cells do?
Secrete pepsinogen, a precursor to
the enzyme pepsin –> breaks proteins
down into smaller pieces
what do enteroendocrine cells do?
Secrete gastrin, somatostatin, histamine and several other paracrine and endocrine hormones
What are the digestive functions of the stomach?
Chemical breakdown of proteins begins
- HCl acid denatures (unravels) long proteins
- Pepsin chops ‘em into smaller pieces
Almost no absorption of nutrients occurs in the stomach
- No major organic molecules absorbed across the mucosal epithelium
- Some drugs absorbed –> aspirin
- Alcohol is absorbed to some extent
What are peptic ulcers?
Erosion of mucosal lining in the esophagus, stomach or duodenum
Most cases involve H.pylori bacteria
• Causes chronic inflammation of the mucosa
• Compromises integrity of natural defenses (esp.
mucus production)
Small intestine - how long? diameter? sections?
20 feet
1-1.5 inches
3 sections
- doudenum
- jejunum
- ileum
1-3 please :)
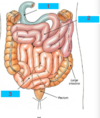
1- duodenum
2- jejunum
3- ileum
Duodenum - Length? Purpose?
about 10in-1ft
“mixing bowl” –> where chyme is mixed with pancreatic secretions and bile from liver
label 1

circular fold
Jejunum - Length? Purpose?
about 7.5-8ft
where final chemical digestion and most absorption of organic nutrients (carbs, fat, protein) occurs
what are these folds?

Plicae
Label 1-2

1- mucosa
2- villi
Label 1-4
(this is a picture of a single villus of the jejunum)

1- goblet cell
2- epithelium (cells have microvilli - creates “brush border”)
3- lacteal
4- capillary network
Ileum - Length? Purpose?
about 11ft
continued absorption of stuff not absorbed in the jejunum
specific absorption of Vit.B12
has Peyer’s patches
Large intestine - Length? How many sections? What are they called?
5ft long 3in diameter
4
cecum, colon (4 sub sections), rectum, and anal canal
label 1-3 What part of the large intestine is this?

1- ileocecal valve
2- cecum
3- vermiform appendix
cecum
Label the 4 parts of the colon

1- ascending colon
2- transverse colon
3- descending colon
4- sigmoid colon
1 and 2

1- Haustrum
2- tenia coli
Is the mucosal layer of the large intestine folded?
NO
Main functions of the large intestine?
-Reabsorb water, compact unusable material in fecal matter
-Absorb some vitamins made by bacteria living in large intestines
• Vit K
• Biotin
• Vit B5
-Conversion of organic wastes
• Bilirubin (from breakdown of RBC’s) stercobilins and urobilins
• Protein leftovers ammonia, indole/skatole, hydrogen sulfide
-Storage of fecal matter until defecation
What are the two structures here?

Rectum and anal canal
Accessory organs of intestines
Create secretions that are dumped into the intestines
include
- pancreas
- liver
- gallbladder
What do cells of pancreatic acini do?
make enzymes and buffers
Dumps them into duodenum via pancreatic duct
What do cells of pancreatic islets do?
make hormones insulin and glucagon that regulates blood glucose levels
label 1-3
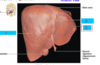
1- right lobe of liver
2- falciform ligament
3- left lobe of liver
1-5

1- caudate lobe
2- left lobe
3- porta hepatis (containing hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein)
4- quadrate lobe
5- right lobe
what are the functional unit of the liver?
Lobules

1-5

1- portal triad
2- bile duct
3- portal venule
4- portal arteriole
5- central vein
Liver functions
Metabolic regulation
• major control point for determining nutrient content of circulating blood
Hematological regulation
• has a number of immunological and blood-related functions
Bile production
• important for the process of fat digestion
1-4

1- left and right hepatic ducts
2- cystic duct
3- common hepatic duct
4- common bile duct
What is cholelothiasis?
Gallstones


