Development of Orofacial Structures Flashcards
(42 cards)
FNP NCC come from where
NCC to arch 1 come from
forebrain and midbrain
midbrain and hindbrain
Neurocranium vs viscerocranisum
neurocranisum is brain case, viscerocranium is face, jaw and larynx
Skull
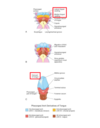
Endochondral ossification creates?
Intramembranous ossification creates?
red=mesoderm blue is NC
Enochondral ossification:
- neurocranium
occipital: meso
Body of sphenoid: meso
ethmoid: NC
petrous/mastoid parts of temp: meso
-viscerocranium
ossicles of the ear NC
Intramembranous ossification flat bones
Neurocranium
parietal meso, Frontal NC
viscerocranium
squamous temporal, maxillary, zygomatic all NC

Congenital abnormalities
Premature closure of sutures
- what is plagiocephaly?
- what isoxycephaly or brachycephaly?
- what is scaphocephaly
scaphocephaly elongates head in A/P direction
oxycephaly leads to prominent forehead
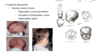
Derivatives of:
- Mandibular prominence
- Maxillary prominence
- Frontonasal prominence

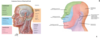
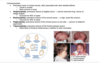
Characteristics of frontonasal dysplasia and embryologic mechanism of defects
accounted for by lack of migration or fusion of medial nasal prominence. problem w/ frontal nasal prominence or more specifically medial nasal prominences.


A. problem w/ fusion of medial nasal prominence
B. mandibular prominences did not completely fuse
C. nasal lacrimal duct didnt form. both of them, maxillary prominence didnt fuse w/ intermaxillary segment, and maxillary prominence didnt fuse w/ lateral nasal prominence. facial cleft
D. maxillary and mandibular didnt fuse “enough”
E. Overfusion of maxillary and mandibular, one nostral is overfusion of medial nasal prominence
F. medial nasal prominence didn’t completely fuse
Critical weeks for palate formation? overall weeks for palate formation?
-secondary palate gives rise to what?
is derived from what?
critical is 6-9

Week 7

Facial Primordia:
- how many
- when?
- separated from cavity of primordial pharynx by what? what happens to it?

Facial development occurs during which weeks?
- FNP surrounds what part of the forebrain?
- FNP is from NCC of what parts of brain
FNP surrounds ventrolateral part of forebrain
- frontal portion will form the forehead, nasal portion forms rostral boundary of stomodeum/nose.
- FNP is NCC from forebrain and midbrain
PA1 splits into what?
- what contributes their NCCs?
- boundaries of stomodeum?

First things that form in the face
-whats happening 3rd and 4th week: what disintegrates, what extends and fuses toward midline?

whats happening by end of 4th week on inferolateral parts of FNP?
- what produces MNP/LMP?
- nasal pits come from? what do nasal pits form?

Formation/ Morphological changes of nasal pits

- which way do maxillary prominences grow?
- what does the nasolacrimal groove separate?
- by end of sixth week what has merged and what has formed

Between 7-10th weeks what happens to MNP, MXP, LNPs?
- results in?
- what forms the intermaxillary segment?

- what structures form from maxillary prominence?
- mesoderm in PA2 forms what?
- mesoderm in PA1 forms?
- innervation of both

Nasal Cavities:
- what causes nasal pits to deepen, what does this form?
- what does the oronasal membrane separate and when does it rupture?

- primary chonae, secondary
- olfactory epithelium comes from

Palatogenesis:
- during which weeks, which weeks critical
- what is merging
- what is primary palate
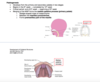
- what is the definitive palate?
- when does secondary palate develop and from what?
- palatal shelves and importance of tongue movement
- when do palatal shelves become horizontal

Final palate:
- what forms the premaxillary part of maxilla
- what forms hard palate
- soft palate formed by
- Nasopalatine canal persists as what in adult