Dermatology COPY Flashcards
Define Macule
Non palpable
Well circumscribed change in skin color
Less than 1 cm
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Macule
(labial melanotic macule)
Define Patch
nonpalpable
well circumscribed change in skin color
Larger than 1 cm
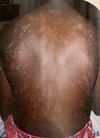
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Patch
(Speckled Nevus)
Define Plaque
Palpable
Elevated
Solid skin lesion
Greater than 1 cm
Define Papule
Palpable
Elevated
Solid skin lesion
Less than 1 cm
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Papule
(Spitz nevus)
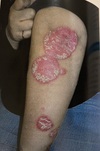
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Plaque
(Psoriatic plaque)
Define Wheal
Transient
Smooth papule or plaque
Seen in urticaria
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Wheal
(Urticaria)
Define Vesicle
Small
Fluid containing blister
Less than 1 cm
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Vesicles
(Herpes Zoster)
Define Bulla
Large
Fluid containing blister
Greater than 1 cm
Define Pustule
Vesicle containing pus
Define Nodule
Solid
Non-superficial skin mass
1-2 cm
Define Tumor
Solid skin mass
Greater than 2 cm
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Bulla
(Bullous Pemphigoid)
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Pustules
(Pustular psoriasis)
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Nodule
(Large pigmented dermatofibroma)
What is the primary morphology of this lesion?

Tumor
(Melanoma)
Define Scale
Flaking off of the stratum corneum
Define Crust
Dried exudate
Define Excoriation
Linear skin damage
Due to scratching or scraping
Define Lichenification
Skin thickening
Prominent skin lines
Due to repeated rubbing or scratching