CR Flashcards
(25 cards)
Name the heart tube sections and what they become in the adult heart

A - Truncus arteriosus ⇒ Proximal aorta and pulmonary artery
B - Bulbis Cordis ⇒ Ventricular outflow tracts and right ventricle
C - Primitive Ventricle ⇒ Left ventricle
D - Primitive Atria ⇒ Left and right atria
E - Sinus Venosus ⇒ Sinus venarum (the smooth muscle of the right atrium) and coronary sinus
What are the cyanotic and acyanotic conditions of the heart
Cyanotic:
- Tetralogy of fallot
- Tricuspid Atresia - no tricuspid forms (blood moves through fossa ovalis)
- Transposition of Great Vessels
- Truncus Arteriosus - single trunk leaving the heart (combination of aorta and pulmonary)
Acyanotic:
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular spetal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Coarctation of the aorta
What are the 5 leukoctye types, their characteristics and their function
Neutrophils - first responder of immune cells
Basophils - Release histamine and mount a non-specific immune response
Eosinophils - fight parasites but also provoke allergy symptoms
Lymphocytes - B and T cells that defend against specific invaders
Monocytes - Clean up dead cells

What does the right coronary artery supply in the heart
Sinoatrial node
Atrioventricular node
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Apex
Posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum
What findings are seen in a Chest X-ray of someone with heart failure
ABCDE
- Alveolar Oedema (‘Bat wing sign’)
- B lines (Kerly)
- Cardiomegaly (increased cardiothoracic ratio)8*
- Dilation of upper lobe vessels
- Effusions (Pleural)
* measured accurately on a posterior-anterior view chest X-ray
Name the areas of the JVP waveform

- A wave: Atrial contraction
- X1 descent: Atrial relaxation
- C wave: Closure of the tricuspid valve and ventricular contraction
- X2 descent: End of right ventricular contraction, initial phase of atrial filling
- V wave: Atrial filling (tricuspid valve is still closed)
- Y descent: Atrial emptying due to opening of the tricuspid valve and ventricular filling
Name the parts of the wave

- A - Total Lung Volume (TLV)
- B - Tidal Volume
- C - Inspiratory Capacity
- D - Functional Residual Capacity
- E - Expiratory Reserve Volume
- F - Vital Capacity
- G - Residual Volume
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (not labelled) - Volume of additional air that can be inhaled
Symptoms and Signs of Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia
Including:
- Hb
- MCV
- LDH
- Unconjugated bilirubin
- Haptoglobin
Symptoms:
- Splenomegaly
- Butterfly rash
- Pale
Signs:
- Hb - Low
- MCV - Normal
- LDH - High
- Unconjugated bilirubin - High
- Haptoglobin - Low
Name the stages of heart formation (cardiogenesis)
1) The heart is one of the earliest differentiating organs and first appears as blood islands - groups of haemangioblasts and myoblasts - derived from the cardiogenic mesoderm at 18 days gestation.
2) At 20 days gestation, the blood islands begin to coalesce to form the right and left endocardial tubes.
3) The left and right endocardial tubes then undergo a process called lateral folding, forming the primitive heart tube by 21 days gestation.
4) The primitive heart tube undergoes cardiac looping from day 23 to 35, twisting the primitive ventricle and atria into the final positions adopted by the adult heart.
5) Simultaneously, atrial septation begins by day 28 from endocardial cushions of the atrioventricular canal.
6) Ventricular septation begins by the end of the 4th week and is completed by the 8th week.
7) Outflow tract separation, whereby the truncus arteriosus is divided into the proximal aorta and pulmonary artery, occurs in the 5th week of gestation.
What would iron deficiency show as in a blood smear
Microcytic and hypochromic red blood cells (which stain poorly).
Poikilocytosis (variation in shape) and anisocytosis (variation in size).
Increased number of platelets
Abnormally shaped red cells (e.g. target cells and pencil cells).
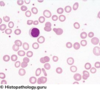
What would B12 deficiency show in a blood smear
Abnormally large nucleated red cell precursors (megaloblasts)
Hypersegmented neutrophils
Anisocytosis
Poikilocytosis
The RBCs in addition to being large, also show oval morphology
Defective DNA synthesis may also result in fragmentation of nuclear DNA known as Howell-Jolly bodies.
What response fails that allows Millary TB to form
Failure of CD4 T cells to coordinate the cell mediated response to mycobacterium tuberculosis
What organisms can cause Tuberculosis
(5-18 year olds)
Bacteria:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Viruses:
- Type A influenza
- Respiratory syncytial virus
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus
Is sickle cell anemia autsomal dominant or autosomal recessive
Autosomal recessive
What are the X-ray characteristic of COPD
hyperinflation of the lungs
flattened hemidiaphragms
narrow mediastinum
At what vertebral level is the carina (bifurcation of the trachea) positioned
T4/5
What nerve innervates the infrahyoid muscles
Ansa cervicalis
What does partial occlusion cause on an ECG
T-wave inversion, ST depression, pathological Q waves
Is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis resitrictive or obstructive
Restrictive
What pathology is shown here

Tubercolosis
What does atrial fibrillation increase the chance of
Stroke
What are the nasal conchae lined with
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Is COPD obstructive or restrictive
Obstructive
Is asthma obstructive or restrictive
Obstructive


