CPA 1.3: LAB Ribs Flashcards
Upper Ribs 1-2 EVALUATION
*** primarily bucket handle
Patient supine or seated. Examiner at head of table or behind patient. To evaluate bucket handle motion of rib 1, place thumbs posteriorly on the angle of rib 1. Place index fingers in the supraclavicular fossa anterior to the trapezius, over the superior lateral aspect of rib 1. Instruct patient to inhale and exhale and monitor motion through respiration.

Middle ribs 3-6 EVALUATION
Primarily bucket handle motion
Patient supine. Examiner places two fingers just lateral to the sternum on the costal cartilage of each rib set. Monitor the relative cephalad or caudal relation of the pair and, on the symptomatic side, determine whether that rib is more prominent or less prominent or superiorly or inferiorly positioned. The examiner then monitors the ribs through inhalation and exhalation. Next, palpate ribs 4-6 at their costochondral ends with the thumbs and at their midaxillary lines with the fingertips. Repeat this process for each set of ribs.

Lower ribs 7-10 EVALUATION
Rib 7: Primarily pump handle
Ribs 8-10: Primarily bucket handle
Patient supine. Examiner stands to the side of patient. Using thumbs, palpate rib 7 bilaterally at its costochondral articulation for pump handle motion. Contact ribs 8-10 at the midaxillary line with the fingertips for bucket handle motion. Monitor through respiration.

Floating ribs 11 and 12 EVALUATION
Caliper
Patient prone. Examiner at side of table and uses thumbs to palpate the posterior aspect and 2nd and 3rdfingers to palpate the lateral and anterior aspects of ribs 11 and 12 bilaterally. Monitor through respiration.
**Restriction of motion is influenced by quadratus lumborum

Diagnosis of elevated first rib
Position
Patient: seated
Doctor: standing behind patient
Hand Position
- Thumbs palpate posterolateral body of the first rib lateral to the costotransverse articulation
- Index fingers palpate anterior infraclavicular space
Technique
- Induce a caudad force alternately on each rib
- Monitor relative cephalad or caudad position of the pair
- Assess for prominence, pain and spring with downward pressure

Describe what happens in inhalation and exhalition in evaluation and diagnosis
INHALATION
If one rib stops moving before the other rib during exhalation, that rib has an exhalation restriction, therefore an inhalation dysfunction
*Moves into inhalation position, restricted to exhalation position
The most inferior (bottom) rib in a group of ribs is the key rib to target treatment.
“BITE”
EXHALATION
If one rib stops moving before the other rib during inhalation, that rib has an inhalation restriction, therefore an exhalation dysfunction.
*Moves into exhalation position, restricted to inhalation position
The most superior (top) rib in a group of ribs is the key rib to target treatment.
“BITE”
Rib 1 inhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine
Doctor: sitting at head of table
Hand Position
- Thumb ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib placed on anteromedial aspect of dysfunctional rib
- Contralateral hand maneuvers the head into flexion, sidebent towards and rotated away from dysfunctional rib
Technique
- Follow rib down and forward into exhalation
- As patient inhales, resist the motion of the dysfunctional rib
Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is maximally improved

Ribs 2-6 inhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine with dysfunctional rib resting on doctor’s knee, sidebend towards dysfunctional rib
Doctor: standing with flexed knee ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib on the table
Hand Position
-Web of ipsilateral thumb-index finger is placed in the intercostal space superior to the dysfunctional rib
Technique
- During exhalation: doctor exaggerates the motion
- During inhalation: doctor resists the motion
- Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is maximally improved

Ribs 7-10 inhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine with ipsilateral shoulder adducted (abduction is shown only to illustrate proper hand placement)
Doctor: stands on side of dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
-Ipsilateral thumb and index finger on superior surface of dysfunctional rib
Technique
- Sidebend to the level of dysfunctional rib
- During exhalation: doctor exaggerates the motion
- During inhalation: doctor resists the motion
- Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is maximally improved

Ribs 11-12 inhalation treatment
Position
Patient: prone with legs sidebent 15-20° towards the dysfunction (decrease tension on quad. lumborum m.)
Doctor: stands opposite the dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
–Cephalad hand – hypothenar eminence medial and inferior to the angle of the dysfunctional rib
–Caudad hand – grasps ASIS ipsilateral to dysfunction to shorten quadratus lumborum
Technique
- Apply sustained lateral and cephalad traction to dysfunctional rib
- During exhalation: doctor exaggerates the motion
- During inhalation: doctor resists the motion
- Repeat 3-5 times or until motion is maximally improved

Ribs 1-2 exhalation treatments
Position
Patient: supine, head rotated 30° away from dysfunctional rib with dorsum of ipsilateral wrist on forehead
Doctor: stands contralateral to dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
–Cephalad hand – placed on top of patients hand on forehead
–Caudad hand – grasps the superior angle of the dysfunctional rib
Technique
- While applying caudad, lateral traction with caudal hand instruct the patient to flex the head and neck (while maintaining rotation) and apply counterforce
- Maintain isometric contraction 3-5 seconds then have patient relax
- Increase caudad, lateral traction and repeat steps of muscle energy

Ribs 3-5 Exhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine with arm ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib fully flexed
Doctor: contralateral to dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
–Cephalad hand – rests on patients arm
–Caudad hand – grasps the superior angle of the dysfunctional rib
Technique
- While applying caudad, lateral traction on the affected rib with the caudad hand, instruct patient to push elbow against doctors cephalad hand while applying a counterforce
- Maintain isometric contraction 3-5 seconds then have patient relax
- Increase caudad, lateral traction and repeat steps of muscle energy
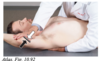
Ribs 6-8 exhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine with ipsilateral shoulder flexed to 90°
Doctor: ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
Cephalad hand – grasps the superior angle of the dysfunctional rib
Caudad hand – maneuvers elbow
Technique
- While exerting caudad, lateral traction with cephalad hand, instruct patient to push elbow towards the ceiling (scapular protraction) and apply counterforce
- Maintain isometric contraction 3-5 seconds then have patient relax
- Increase caudad, lateral traction and repeat steps of MET

Ribs 9-10 exhalation treatment
Position
Patient: supine with arm on dysfunctional side abducted
Doctor: ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
Cephalad hand – abducts ipsilateral shoulder to 90° and stabilizes elbow
Caudad hand – grasps the superior angle of the dysfunctional rib
Technique
- Instruct patient to push their elbow caudally (into adduction) and apply counterforce
- Maintain isometric contraction 3-5 seconds then have patient relax
- Increase caudad, lateral traction and repeat steps of MET

Ribs 11-12 exhalation treatment
Position
Patient: prone with legs sidebent 15-20° away from dysfunction (increase tension on ipsilateral quadratus lumborum)
Doctor: stands contralateral to dysfunctional rib
Hand Position
Cephalad hand – stabilizes rib superior to the dysfunctional rib
Caudad hand – grasps iliac crest ipsilateral to dysfunctional rib (increase tension on ipsilateral quadratus lumborum)
Technique
- Cephalad hand exerts cephalad pressure while patient pulls iliac crest ipsilateral to the dysfunction towards the ipsilateral shoulder while physician applies counterforce
- Maintain isometric contraction 3-5 seconds then have patient relax
- Increase caudad, lateral traction and repeat steps of MET



