Coxal articulation Flashcards
1
Q
Coxal articulation
A
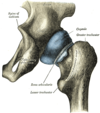
- Joint surfaces are the facies lunata acetabuli (rest of acetabulum is covered by a pilar of adipose tissue - pulvinar acetabuli) and caput femoris
- Joint pit is deepened by the labrum acetabulare
- Lig. transversum acetabuli crosses the acetabular notch, and converts it into a foramen through which the nutrient vessels enter the joint
- It also prevents inferior displacement of head of femur
2
Q
Joint capsule of the coxal articulation
A
- Is strong and attached to the acetabular margin, reaching the intertrochanteric line on the femur and dorsally reaching the centre of collum femoris (fossa trochanterica lies extraarticularly)
- Is reinforced by several strong ligaments
- Lig. iliofemorale descends from the anterior inferior iliac spine to the intertrochanteric line
- Lig. pubofemorale descends from the cranial margin of the superior ramus of the pubic bone to the anterior inferior side of the joint capsule
- Lig. ischiofemorale begins at the dorsal acetabular margin and grows together with the dorsal part of the joint capsule, and then diminishes on its cranial side
3
Q
Zona orbicularis of the coxal art.
A
- is a ligament encircling the neck of the femur formed by the circular fibers of ligamentum ischiofemorale and ligamentum pubofemorale
4
Q
Ligamentum capitis femoris
A
- Runs from fovea capitis femoris, leaves the joint capsule below the ligamentum transversum acetabuli and attached by two bands, one into either side of the acetabular notch
5
Q
Bursa iliopectinea
A
- A synovial bursa located below the m.iliopsoas on the anterior side of the join capsule
6
Q
Movement of the coxal joint
A
- It is a typical restricted spherical joint (enarthrosis)
- Moves in three axes: extension/flexion, abduction/adduction and femoral supination/pronatioin
- Ligaments of the joint are stretched during extension and therefore limit its extent
- The middle position is reached when the joint is in flexion with light abduction and external rotation


