congenital cards Flashcards

norwood -
small aorta is attached to pulmonary artery

stages of hypoplastic left heart surgery
- Norwood to make megatrunk with unobstructed outflow
*with Blalock-Taussig shunt (artery to artery shunt: right subclavian artery to right PA)
*or Sano (modification of Norwood) to increase shunting
- Bi-directional Glenn
- Fontan

Norwood
goal: all systemic flow from RV - neoaorta constructed via side-to-side anastomosis of MPA and hypoplastic aorta - Blalock-Taussig shunt to divert some flow to lungs (systemic-pulmonary shunt)
Blalock-Taussig shunt
done in conjunction with the Norwood
BTS is a synthetic graft from Right Subclavian Artery to Right Pulmonary Artery
also…if PDA is present that is taken down to prevent overshunting to the lungs

Sano shunt
right pulmonary artery –> right ventricle

Bi-directional Glenn
SVC –> RPA (bi-directional because RPA left open to allow blood to flow into both lungs

Fontan
3rd stage in hypoplastic left ventricle surgery
passive blood flow into the lungs.
1) ASD is closed
2) shunt between IVC and left pulmonary artery

Blalock-Taussig shunt
done in the stage 1 norwood for hypoplastic left heart



to prevent overshunting (pulmonary edema), what step needs to be done during the Blalock Taussig shunt?
take down a PDA if present to prevent over shunting
complications of a BT shunt
- subclavian steal syndrome
- possible over shunting and pulmonary edema (worse if you don’t take down a PDA)



bi-directional Glenn
SVC –> PA
vein to artey



L-transposition
arch is on the left


D-transposition
arch is on the right

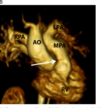

most likely procedure(s) performed

stenning or mustard


tricuspid atresia

Jatene - arterial switch for D type transposition


D- transposition


unroofed coronary sinus


Ebstein anomaly - atrialized right ventricle






