Conference Lab 1: Introduction and Back Flashcards
High yield conference 1 topics
CNS
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral
group or bundle of nerve fibers outside CNS
two general kinds of nerve terminals?
cutaneous (Sensory) and muscular (motor)
What kind of root has only sensory info?
Dorsal
What kind of root has only motor info?
Ventral
What nerve types or areas have both sensory and motor info?
spinal nerves, dorsal and ventral rami
Somatic
muscle; body wall and extremities
Visceral
organs, glands, vessels
Dorsal root
sensory info, afferent fibers
Ventral root
motor info, efferent fibers
Afferent
Away from body, back to brain; carries sensory info
Efferent
Towards the body, away from brain; carries motor info
Dermatome
portion of the skin innervated by the particular spinal nerve
What should you keep in mind when testing a dermatome?
boundaries between one dermatome and another are not exact ; to test go right in the middle of the dermatome!!
Cutaneous branches
BOTH dorsal and ventral rami
Facet joints
joints between the articular processes of adjoining vertebrae
Where (relative to vertebra) are intervertebral discs found?
in between the BODIES of vertebrae
Where (relative to vertebra) are intervertebral discs found?
in between the BODIES of vertebrae
anatomical definition of the origin and insertion of a muscle
origin is more proximal insertion is more distal
forces that normally produce muscle on a joint
gravity and muscle contraction
the force that causes a specific desired motion
PRIMARY MOVER, agonist
a muscle that causes a motion opposite to the desired motion
antagonist
What are the functions of synergistic muscles ?
stabilize other joints and neutralize undesirable motions
What do we call the basic functional units that make up each muscle ?
motor units
Motor unit
single motor neuron and the muscle fibers that it supplies
the three types of muscle contraction
Shortening (isotonic or concentric) contraction Static or isometric contraction Lengthening (isotonic or eccentric) contraction
nerve fiber
axon and supporting cells
cranial nerve
A peripheral nerve arising from the brain
spinal nerve
A peripheral nerve arising from the spinal cord
How is a gross spinal nerve formed?
Dorsal and ventral roots emerging from each segment of the spinal cord combine to form a spinal nerve
How long is a typical spinal nerve?
1cm
How does a typical spinal nerve terminate?
Divides into dorsal and ventral ramus
What are the two general kinds of terminal branches of peripheral nerves that are derived from the rami ?
Muscular Cutaneous
Where are the nerve cell bodies located for afferent nerve fibers?
in the dorsal root ganglion
Where are the nerve cell bodies located for efferent nerve fibers ?
in the spinal cord gray matter
Four basic functional fiber types are found in a typical spinal nerve
Somatic efferent Visceral efferent Somatic afferent Visceral afferent
What are dermatomes supplied by?
each dermatome is supplied by both the dorsal and ventral ramus of its spinal nerve
If there is back pain in back pain localized to the area between the spinous processes of T11 and L3 on the patients right side, what DERMATOMES does this correspond to?
T11-L2 This was determined by figuring out which nerves come out between the indicated vertebrae and then corresponding that to the dermatomes (i.e. between T11 and T12, T12 and L1…)
What do the dorsal rami innervate?
Deep back muscles (erector spinae) skin of medial 2/3 of back posterior ligaments of the spine facet joints
What are the posterior ligaments of the spine?
They are innervated by DORSAL RAMI Include supraspinous, interspinous ligaments and ligamentum flavum
ligamentum flavum
ligaments between lamina
three types of muscle contraction
shortening (concentric, isotonic) lengthening (eccentric) static (isometric)
Lateral bending of the spine
Ipsilateral = shorten Contralateral = lengthen *muscles on left and right are doing opposite things = antagonist muscle groups
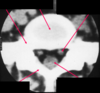

foraminal stenosis
narrowing of the space in the vertebral foramen; can be caused by hypertrophy (enlargement) of facet joint and/or vertebral body
Name a disease that can cause facet joint hyertrophy
osteoarthritis; formation of osteocyte will cause stenosis


