19 Kidney Blood Nerve Flashcards
3 natural sites of constriction for the ureter
beginning: where renal pelvis becomes ureter middle: where the ureter crosses the pelvic inlet at the bifurcation of the common iliac vessels end: where the ureter enters the urinary bladder
What vertebral level should the hilus of the kidney be located?
L1
Name a condition that lowers the vertebral level of the hilus of the kidney and why/how it does that?
horseshoe kidney can cause the relationship of the renal pelvis to the vertebra to be around L3; this is because by definition, the horseshoe kidney occurs when the inferior poles of the kidneys are fused; their traditional ascent is stopped by the inferior mesenteric artery
What is #1 and what can it be caused by
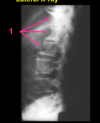
anteiror notching of vertebral bodies caused by an aortic aneurism
an aortic aneurism is a bulging of the aorta that can also cause compression of the intervertebral discs
What are these scans showing?

An aortic aneurism
What provides sympathetic innervation to the celiac plexus?
thoracic splanchnic nerves, which are pre ganglionic
What provides parasympathetic innervation to the celiac plexus?
posterior vagal trunk, which are pre ganglionic and synapse in the walls of the target organs
What provides sympathetic innervation to the superior mesenteric plexus?
Thoracic splanchnic nerves, which are pre ganglinonic
What provides parasympathetic innervation to the superior mesenteric plexus?
posterior vagal trunk, which synapses in the walls of target orbans
What nerves provide sympathetic innervationto the inferior mesenteric plexus?
lumbar splanchnic nerves, which are pre ganglionic
What nerves provide parasympathetic innervation to the inferior mesenteric plexus?
pelvic splanchnics, which are preganglionic and synapse in the walls of target organs
Spinal segments for the pelvic splanchnics?
S2-S4
Origin of thoracic duct?
cisterna chyli


