CONDITIONS to KNOW Flashcards
(400 cards)
shock
inaqequate perfusion
dyspnea
shortness of breath
hypercarbia
increase co2 in blood
intrapulmonary shunting
blood returning to left side of heart unoxygenated
arterial air embolism
air in pulmonary vasculature

cardiogenic shock
heart fails to pump——> pulmonary edema
pulmonary edema
backup of blood into the lungs because left cant remove as fast as right gives (from cardiogenic shock)
fluid in alveolar sacs
s/s= dyspnea, rapid shallow breaths, sudden attack of rresp distress, coughing, cold sweats, tachycardia, cool cyanotic skin
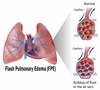
edema
too much fluid in tissues leads to swelling
pericardial effusion
collection of fluid between pericardial sac and myocardium
can lead to cardiac tamponade

cardiac tamponade
fluid in pericardial sac creates extreme pressure that doesn’t allow adequate filling of heart

obstructive shock
mechanical obstruction prevents aquate blood to fill chambers of heart
pulmonary embolism
blood clot formed in vein breaks off and lodges in pulmonary artery
no gas exchange in blocked area
s/s= cyanosis, dyspnea, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypoxia, chest pain, hemotypsis

distributive shock
widespread dilation of vessels, blood pools, less perfusion
septic shock
severe infection: toxin damages cellular wall= increased permeability
neurogenic shock
spinal cord injury damages nervous system that contracts/dilates vessels= vessels dilate
absence of sweating, normal HR during hypertension, normal skin
anaphylactic shock
person reacts violently to a substance they have been sensitized to, dilation
s/s= urticaria, angioedema, wheezing, hypotension, n/v, ab cramps
cyanosis is late sign
psychogenic shock
sudden nervous system reaction, temporary dilation, syncope
hypovolemic shock
inadequate amount of fluid in system
anemia
hypoxic tissues
hemorrhage
bleeding
hemoptysis
cough up red blood
hematoma
mass of blood collected in the tissue beneath skin

hematuria
red blood in urine
hematemesis
vomiting blood