Clinical Neuro/ Collapse Flashcards
Sudden death

DDX individual animal sudden death

Haemorrhage




Peracute toxaemia

Trauma

Iatrogenic causes of sudden death

Sudden death in groups of animals

Electrocution
* Mains electricity
- Especially around sheds, pole and water
- Kills people too

Anaphylaxis

Nutritional poisonings







Cyanide – sudden death in a herd

Blue Green Algae herd sudden death

OPs and Monensin poisoning?

Urea– sudden death

Nutritional deficiencies that cause sudden death

Infectious agents that result in sudden death

Blackleg

Black disease

Anthrax

Summary sudden death

Down cow? Downer cow? Downer cow syndrome?

Sternal recumbency

Lateral recumbency

Aetiology musculoskeletal? Toxaemia? Metabolic? Misc?

Assessment of the Down Cow

Exam of the down cow


Prop up cows that are in lateral recumbency!


Clues from the posture


Hyper-alert and aggressive
Presentation– musculoskeletal? Acute systemic/toxic? metabolic?

Prolonged recumbency?

Differentiate Down cows into?

Musculoskeletal down cows?

Lifting cows for examination
Musculoskeletal assessment– back examination?

Lumbosacral ligament examination?

Limb examination?

* Limb assessment (in lateral or hanging)
- manipulate each limb
– ability to extend and flex to full extent
– abduct in normal range
– crepitus or laxity in hip/stifle
– Crepitus or laxity in hip/stifle
– cruciate rupture (pain on stifle flexion)
– palpate full leg for heat/swelling


Gastrocnemius rupture
Femoral n. ? Sciatic n.? Obturator n.?

Assessing nerve and motor function


Diagnosis of limb fractures and dislocations? Spinal fractures?



Picture.. but also downer cow syndrome?




Prognosis of Radial n. paralysis

Calving paralysis prognosis

Femoral n. injuries

Prognosis of: Obturator n. injury? Lumbosacral injury? Non-responsive milk fever? Radial n. injury?

Poor prognostic signs

Treatment of downer cows

Important points sudden death


Brown MM

Causes of recumbency–> MTMM
Musculoskeletal issues
Toxaemia
Metabolic
Miscellaneous (e.g. parturition, exhaustion)



Grass tetany (hypomagnesium)

Preg Toxaemia
The problem occurs because a certain amount of
glucose is needed by the liver to enable it to
utilise the
incoming
fat. If the fat is coming in
faster than the liver can make glucose, such as
when the animal has very little quality feed, the
fat starts to build up in the liver. The liver
becomes enlarged, pale and
fatty, and ketones
build up to excessive levels in the blood, and
start to affect the brain. Brain function is affected
and the animal stops eating. This process is not
easy to reverse.
Treatment:
IV fluids, C-section, or induction of calving
Sometimes injections of glucose,
calcium
borogluconate and magnesium salts under the
skin are used, but these are far more likely to be
effective if given intravenously by a veterinarian.
Oral treatments of propylene glycol and
electrolytes are also useful to treat mild cases.

Down cow? Downer cow? Downer cow syndrome? Springer? Close up?

Downer cows
Most conditions occur close to calving
Most conditions are influenced by pre-calving nutrition
** Nutrition around calving– transition period is 4 weeks before to 4 weeks after calving…. this period is a major focus for farmers, vets, and advisors

Pre-calving nutrition



Aims of transition

Transition diets

Hypocalcaemia
Parturient hypocalcaemia- metabolic disease with paresis & hypocalcaemia
- Weakness, recumbency, depression of consciousness, can be fatal
* Common disease of dairy cattle (can occur in beef cows)
- Called severe problem if > 3% of the herd, or cows <5 yo affected
* Sudden increase in Ca requirement with onset of lactation
- Colostrum 2.3 g Ca/kg; Milk 12 g Ca/kg
- Onset of lactation increases Ca requirement by 2-4 fold
* Subclinical hypocalcaemia is very common

Calcium- regulation

DCAD

Risk factors for milk fever

Clinical signs of milk fever

Stage 1 and Stage 2 Milk Fever

Stage 3 Milk Fever

DDX Milk Fever

What is wrong with the three stages of Milk Fever?

S/c treatment for hypocalcaemia?

Treatment i/v for hypocalcaemia?

Prevention of hypocalcaemia

Non-parturient hypocalcaemia

Feeding the close-up cows- summary?

Grass Tetany

Risk factors Grass Tetany

Clinical signs of Grass Tetany

Diagnosis of Grass Tetany



Grass Tetany Treatment

Control of Grass Tetany

Disorders of Energy Metabolism
Gluconeogenesis- converts non carbohydrates (pyruvate) to glucose
Glycolysis- converts glucose to pyruvate; gluconeogenesis upside down
Citric Acid (Krebs) cycle- Generates energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbs, fats, and proteins into CO2 and water; generates some amino acids and things

Energy metabolism in the ruminant
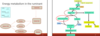
Hepatic lipidosis– herd diagnosis

4 Syndromes of Energy Metabolism

Preg Toxaemia


Treatment of preg toxaemia

Protein- Energy Malnutrition

Treatment of Protein- Energy Malnutrition

Fatty Liver/ Fat Cow Syndrome
Excessively fat dairy cows just after calving
Something stops them eating
Metabolic crisis and fatty liver

Ketosis

Downer cows
Other causes of recumbency
Any severe toxaemia
dehydration
anemia
Neurological disease
Terminal disease
Bovine ephemeral fever

Listeriosis and downer cows

Nitrate/ Nitrite Poisoning

Sources of nitrites

Diagnosis nitrite


Treatment of nitrite

Distance exam


Neuro/ musculoskeletal exam on the 5 station exam

DDX cardinal sign is recumbency

Prognosis and treatment of a recumbent cow

Abbreviated clinical exam


Neurological diseases of cattle- history, observation, clinical exam


Neuro eye tests

Neuro face and mouth tests and head
- ear, cheek, lip, and nostril– position and movement
- response to sound
- head tilt and balance
- head nodding

Exam procedures neuro cow

Manifestations of neuro dysfunction

Changes in mental state

Examples of involuntary movements

Paralysis

Incoordination

Abnormalities of sensation

Lead poisoning

Acute lead poisoning v. subacute lead poisoning

Diagnosis of lead poisoning

Treatment of lead poisoning


Polioencephalomalacia

Diagnosis of polioencephalomalacia

Treatment of polioencephalomalacia


Nervous coccidiosis

Treatment of nervous coccidiosis

Meningoencephalitis

Hypovitaminosis A


Tetanus

Treatment of Tetanus

Listeriosis

Treatment of Listeriosis

Brain abscess

Rabies

BSE

Botulism


Paspalum staggers

Perennial Ryegrass staggers





Periodic spasticity

Elso Heel

Cranial and Spinal Trauma

Peripheral nerve trauma

Meningitis in calves

Citrullinaemia

Inherited congenital myoclonus- in calves

Maple Syrup Urine Disease

Cerebellar Defects

Vertebral Body Abscess

Alpha Mannosidosis



