Clinical Exam 14-1 Flashcards
why should hand be slightly arched (cuffed) for a PA wrist?
to reduce OID of carpals
(T/F) X-table lat sternum is usually done when the pt can’t stand for a routine lat XR
T
recommended obliquity for RAO sternum for asthenic type pt?
20º
term for leakage of contrast media from a vein into the surrounding tissue
extravasation
mA technique for large plaster cast
+ mAs 100%
which AP XR of shoulder & prox humerus is created by placing affected palm of hand against the thigh?
neutral rotation
most common type of aseptic or ischemic necrosis. Lesions typically involve only one hip (head and neck of femur)
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
why is the RAO sternum preferred to the LAO pos?
the RAO projects the sternum over the heart shadow
trapezoid aka
lesser multangular
which foot pos will best show the lat (3rd) cuneiform?
AP obl w med. rotation
what AP XRs are taken for NT shoulder
AP int & AP ext

P/C
how long is the small instestines?
15-18 ft
a NON vis. post. fat pad on a well-exposed, correctly positioned lat elbow generally suggests
neg study for injury
how many total bones in the foot?
26
XR of an AP knee shows rotation w almost total superimposition of the fibular head & prox. tib. what must tech do to correct this pos error?
rotate knee medially
(T/F) an RPO of the SI joints demonstrates the L SI joint open
T
how much of the small intestines is the ileum
3/5
CR angle for scapular-Y XR?
none
(T/F) xiphoid process located at level of T7/T8
F (T9-T10)
when doing a dist. femur XR the knee joint should be ___” above the bottom of the cassette
2”
which of the malleoli is part of the dist. tib?
med.
AP pelvis shows that the R iliac wing is foreshortened. what pos error occurred?
L rotation
(T/F) routine XRs for sternum are the LAO & R/L lat
F (RAO)
is a separation of the AC joint is suspected, what is performed to confirm the separation?
AP 15º cephalic angle
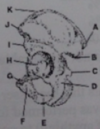
What is C?

coronoid process
min # projections generally required for hand
3
which XRs best demonstrates path involving the 1st CMC joint
AP thumb, modified Robert’s method
(T/F) a R/L marker may be taped over the area of interest to indicate location of T to ribs
F
what anatomical part are you showing if you perform a Grashey view?
glenoid cavity
kV technique for fiberglass cast
+ 3-4 kV
3 parts of small intestine
duodenum, jejunum & ileum
dist. phalynx fx from ball strinking the end of extended finger; DIP partially flexed w avulsion fx
Baseball/Mallet fx
when a pt signs a consent form, legally the pt: - must have exam - has no grounds to sue for malpractice - may still claim that they were not properly informed of the risk of procedure - may be able to request another doc to perform the study
may still claim that they were not properly informed of the risk of the procedure
pt enters ER w possible R AC joint separation. R clavicle & AC joint exams are ordered, the clavicle is taken 1st, and a small linear fx of the mid shaft of the clavicle is discovered. what should tech do in this situation?
consult w ED physician before continuing w AC joint study
preferred SID for finger?
40”
which of the following occurs in many pt’s and is defined as an expected outcome to the introduction of contrast? - moderate itching/sneezing - some metallic taste in mouth & temp hot flash - mild condition of urticaria (hives) - all of the above
some metallic taste in mouth & temp hot flash
where is CR for PA hand
3rd MCP joint
what structure connects the ant. aspect of the ribs to the sternum?
costocartilage
the thumb is naturally in a _______ pos in a PA XR of hand
45º obl
pt to ER for possible perf ulcer. what XRs should be done?
UGI w gastroview
pos that fills the stomach & C-loop of duodenum w Ba?
RAO
which is NOT true about an AP humerus for adult? - use 14 x 17” IR - place epicondyles II to IR - pronate hand - use min of 40” SID
pronate hand
XR of ant obl scapular Y reveals that the scapula is slightly rotated (vertebral & axillary borders not superimposed). Axillary border is more lat. compared w vertebral border. what should be done for repeat?
+ thorax rotation
XR of lat sternum shows that the pt’s ribs are superimposed over the sternum. what needs to be done to correct this?
ensure pt not rotated
routine for IVP?
scout KUB, nephrogram, AP KUB, RPO KUB, LPO KUB, & post void
rapid injection of contrast into vascular system called
bolus injection
may be used to detect pleural effusion (fluid within pleural space) or for guidance when a needle is inserted to aspirate the fluid (thoracentesis)
sonography (U/S)
most common aseptic/ischemic necrosis; lesions typically involve one hip
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
extending the ankle joint or pointing the foot/toes downward is called?
plantar flexion
What is H?

Olecranon
who should be asked to help hold an uncooperative pt?
family member wearing an apron
when performing routine lat knee, the CR is angled how many ºs?
5º cephalic
most commonly fx’ed carpal bone
scaphoid
what is the correct course of action for the tech when, during an injection of contrast, a pt experiences a side effect of mild hot flashes & some metallic taste in his mouth?
reassure pt & contin injection & imaging sequence, while carefully observing the pt for a possible more severe reaction to follow
where are the 3 possible veins for venipuncture located?
in the antecubital fossa
What is A?
med. epicondyle
how many carpals in the hand?
8
from a pronated pos, which of the following is required for a PA obl XR of the 4th digit of hand
45º lat rotation
when ankle is rotated 15-20º internally, this XR is known as the?
Mortise
XR of an AP axial clavicle shows that the clavicle is w/in the mid aspect of the lung apices. what should tech do to correct this?
increase the cephalic CR angle
min # projections generally required for humerus
2
XR of an LPO SI joints shows that the ilium is superimposed over the involved joint. what pos error has occurred?
excessive rotation/obliquity
term that describes the act of voiding under voluntary control
urination
situation: male pt comes in for a VCUG. which XR/pos would be performed for this procedure? - 30º RPO - erect lat - recumbent lat - erect PA
30º RPO
acromion is located on what bone?
scapula
kV technique for small plaster cast
+ 5-7 kV
routines for ankle?
AP, int obl, lat
situation: during single-contrast Ba enema, radiologist suspects a possible defect w/in the R colic flexure. what pos best shows this region of the colon?
LPO
(T/F) an LPO of SI joints will show the L SI joint open
F (R)
peristalsis describes?
normal contractive waves of the digestive system
situation: while attempting to insert an enema tip into the rectum, the tech experiences resistance. what is the tech’s next step?
have radiologist insert it using fluoro guidance
(T/F) the tech should rotate the feet inward if a fx or dislocation is suspected to get rid of the lesser trochanters
F
chronic inflammation of the intestinal wall that results in bowel obstruction in at least half of affected patients. The cause is unknown
Chron’s disease
uses the Salter-Harris classification
Epiphyseal fx
when performing axial view of the Calcaneus the CR is angled how many degrees cephalic to the long axis of the foot?
40
mAs technique for fiberglass cast
+ mAs 25%
ideal kV range for a double-contrast Ba enema is
90-100
(T/F) post. dislocation of the shoulder occurs more frequently than an ant. dislocation
F
a PA scaphoid shows extensive overlap of the dist. scaphoid & adjacent carpals. what lead to this problem?
insufficient ulnar flexion
scapula articulates w?
clavicle & humerus
air-filled “coiled spring” appearance
intussusception
(T/F) avg kVp range for routine elbow is 85-90 kVp
F
when performing the lower leg one should include the _____ joint & ______ joint
ankle, knee
what CR angle is used for AP obl foot?
CR perp to IR
range from sprains to fracture-dislocations of the bases of the first and second metatarsals
Lisfranc joint injuries
intra-articular fx of radial styloid process
Hutchinson’s/Chauffeur’s fx
which carpal articulates w the radius?
scaphoid
where should the CR enter for an AP XR of the 1st toe?
IP joint
how should pt be positioned in order to show the glenoid fossa in profile?
rotate pt 45º toward affected side
what do you do to technique factors for volvulus?
-
the int. prominence/ridge where the trachea bifurcates into the R/L bronchi is called?
carina
pt w pneumothorax should have horizontal beam lateral decubitus XR with the affected side ________
up
primary disadvantage of AP CXR?
+ mag. of heart
which shoulder XR best shows the scapulohumeral joint space?
grashey
pt enters ER w T to pelvis. pt’s main complaint is about her L hip. which of the following XRs should be taken 1st to R/O fx/dislocation?
axiolateral (inferorsuperior) XR of L hip
involves inflammation of the bone and cartilage of the anterior proximal tibia, is most common in boys 10 to 15 years old
Osgood-Schlatter disease
which of the following bony structures CANNOT be palpated? - ischial spine - ASIS - ischial tuberosity - symphysis pubis
ischial spine
where would the IP joint be found in the foot?
btw the phalanges of the 1st digit
What is E?

Capitulum
(T/F) amount of rotation for RAO sternum depends on the size of the thoracic cavity
T
CR centering for nephrotomogram
midway btw iliac crest & xiphoid process
what are the 2 PA methods of doing the tangential view of the patella?
Hughston & Settegast
when performing obl elbows, med/lat rotation should be how many degrees?
45
longitudinal fx @ base of 1st MC w fx line entering the CMC
Bennett’s fx
which of the following will show the intercondyloid fossa? 1. Beclere 2. Settegast 3. Camp-Coventry
1 & 3 only
aka degenterative joint disease (DJD)
osteoarthritis
as a general guideline where should the top of the CW imaging plate or cassette be placed for an AP pelvis XR
1-3” above the iliac crest
(T/F) when doing a special tangential view of ribs, the tech is interested on the upside from the IR when the pt is obl
T
situation: pt comes to rad dept for double-contrast Ba enema. pt cannot lie on her side during the study. which XR should replace the lat rectum XR?
ventral decub
lat scapula requires CR to?
med. border
an AP elbow shows that there is complete separation of the prox radius/ulna. what pos. error has occurred?
excessive lat rotation
situation: a pt enters ER w blunt T to sternum. pt is in great pn and cannot lie prone or stand erect. which routines would be best for the sternum?
LPO & horizontal beam lat XRs
which shoulder XR shows the lesser tubercle?
AP int
what would be the best arm pos for a good AP scapula
abduction
pt enters ER w multiple injuries. doc concerned about a dislocation of the L prox humerus. pt unable to stand. what routine is advised to best show this condition? (Other than AP Scapular Y)
AP & Neer XRs
what 2 bony landmarks are palpated for positioning of the elbow
humeral epicondyles
(T/F) LAO sternum provides the best frontal image of the sternum w min. amount of distortion
F (RAO)