Clinical anatomy of the spine Flashcards


What kind of joints are facet joints?
Synovial
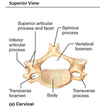
What is unique about C1 (atlas) vertebra?
Has no vertebral body
What is the first palpable vertebra?
C7 (vertebra prominens)
What makes rotational head movements possible?
The odontoid process (dens) of C2 acts as a pivot within C1 allowing rotational movements





What are the extrinsic muscles of the spine?
Trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major/minor, levator scapularis
What are the deep muscles of the spine?
Erector spinae
Regarding the spinal cord:
a) what is it?
b) where does it exit the skull?
c) where does it terminate?
a) inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata
b) foramen magnum
c) the cauda equina at L2


How are a) ascending and b) descending (i.e. motor) signals transmitted through the spinal cord at the level of the vertebrae?
a) ascending fibres enter via the dorsal root, into the posterior horn of the grey matter and into ascending sensory tracts
b) motor signals enter the anterior horn of the grey matter and exit via the ventral root, into the spinal nerve and onto the muscle of action
What happens after the ventral and dorsal roots combine to become the spinal nerve root?
Divide into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) rami; posterior rami serve the muscles of the back and the thin strip of sensation in the centre of the back, anterior rami serve everything else
What forms the intervertebral foramen?
The superior and inferior notches of the two adjacent vertebral pedicles
The cauda equina is composed of which nerve roots?
L2-S5 and the coccygeal nerve
What is mechanical back pain and what is it typically caused by?
Relapsing and remitting back pain with no neurological symptoms or “red flags”.
Typical causes- obesity, poor posture, poor lifting technique, facet joint OA, spondylosis
What is spondylosis?
Loss of water content in discs with age; leading to increased pressure on facet joints and secondary OA
How is mechanical back pain treated, and what should patients be encouraged to do?
Analgesia and physio; patients should be encouraged to maintain normal function (bed rest leads to stiffness and spasm)
What is a typical history of discogenic back pain?
Acute onset of pain, usually after lifting a heavy object, characteristically worse on coughing
Where is the commonest site for disc prolapse impingement?
Sciatic nerve (L4, L5 and S1) roots
How does sciatica present?
Neuralgic pain or tingling radiating down the back of the thigh to below the knee
How is disc prolapse typically treated?
Analgesia, maintain mobility
Drugs for neuropathic pain e.g. Gabapentin, amitriptylline may be useful
What can OA of facet joints lead to? How might this be treated?
Bony entrapment of exiting nerve roots. Surgical decompression


