Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Flashcards
Spirometry results in obstructive diseases
low FVC
very low FEV1
low FEV1:FVC
(all three must be present)
Total lung capacity in obstructive diseases
increases
Chronic bronchitis lasts for how long
3+ months of coughing over a minimum of 2+ years
Histological findings of chronic bonchitis
hypertrophy of bronchial mucinous glands
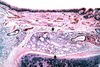
Most prominent feature of chronic bronchitis
large amounts of mucous production
Mucus in chronic bronchitis
goes up: cough it up
goes down: plugs bronchioles
“Blue bloaters”
chronic bronchitis
cyanosis, due to mucus plugs
increase pCO2 and decrease pO2
Infection in chronic bronchitis
more likely
infections love to hide behind plugged tubes
plugged with mucus
Cor pulmonale
right heart failure
after right ventricular hypertrophy
due to pulmonary HTN
Reid index
used to determine thickness of mucus glands in chronic bronchitis
if >50% → chronic bronchitis
normal < 40%
Basic pathophysiology of emphysema
- loss of elastic recoil of alveoli
- air way collapse
*bronchioles normally have alveoli on them and their elastic recoil keeps the bronchioles open
*when they are consolidated, they don’t hold up as well and the bronchioles collapse under the vaccum-type pressure
*obstruction of the airway
How are the alveoli damaged in emphysema
usually there is a balance of
proteases ⇔ anti-proteases
proteases clean up debris that ends up in the alveoli
anti-proteases inactivate these so things don’t get out of hand
by increasing particulate matter (smoking) or losing antiproteases (A1AT deficiency)
macrophages go crazy either way and destroy the alveoli
⇒ emphysema
α1 anti-trypsin
tell me about it
A1AT synthesized in liver
put in blood, travels to lungs to act as anti-protease and keep balance in macrophages
proteases ⇔ anti-proteases
Problems in A1AT deficiency
liver cirrhosis
⇒ buildup of A1AT in liver, where it is synthesized
⇒ pink, PAS+ granules
emphysema
Type of emphysema seen in smoking
centriacinar emphysema
b/c damage most where convection ends (bronchioles)
upper lobs preferentially
smoke → up
Type of emphysema found in A1AT deficiency
panacinar emphysema
all over
because deficiency is all over
“Pink puffer”
emphysema
pursed lips to build back pressure
Genes in A1AT deficiency
PiM is normal
PiZ is pathologic
homozygous = bad
heterozygous = not as bad
Why total lung capacity increases in emphysema
loss of lung elasticity
lung doesn’t pull in like it wants to collapse as much
chest wall still wants to expand it
Hypoxemia in emphysema
loss of capillaries in alveolar walls
alveolar destruction
CD4+ involved in asthma
Th2 cells
IL-4: IgE class-switching
IL-5: eosinophil recruitment
IL-10: stimulates Th2 cells over Th1
Late phase of asthma
Major Basic Protein
damages alveoli
Crystals in asthma sputum
Charcot-Leyden crystals
Someone coughs this up and gives it to you

Charot-Leyden crystals
Major Basic Protein cystals
asthma


