Chemotherapy Flashcards
Radical vs primary
Radical = curative intent
Primary = alone for cure
Neo-adjuvant/ adjuvant/ chemoradiation
Neo-adjuvant = before an operation Adjuvant = after an operation Chemoradiation = with radiotherapy
Palliative vs high dose - what is given in high dose to help?
Palliative = incurably advanced disease
High dose = with bone marrow transplant of stem cell support
What are the consequences of chemo targeted at cells with low rate of renewal?
SE can increase over time eg cardiomyopathy, neuropathy, deafness
Carboplatin = more you have it, more likely you are to have a reaction
How to manage N+V with chemo?
Prevent with ondansetron + dexamethasone IV
Post dose = metoclopramide, dexamethasone
Beware effects of steroids on blood sugars
How many cancer patients require chemo?
60-70%
What is the mechanism of action of chemo?
Usually targets DNA
Toxic towards actively proliferating cells
What cancers are treated with neo-adjuvant chemo?
Used in osteosarcoma
Breast cancer

When is prophylactic chemo used + give an example?
Before overt malignancy appears eg tamoxifen used for in-situ breast cancer before invasive cancer is recognised
Which cells in the body are usually affected by chemo + what occurs?
Haematopoietic stem cells
Lining of GI tract
Causes myelosuppression + mucositis

How long is the average course of chemo?
6 sessions in 6 months
What supportive care can be given during high dose treatment?
Bone marrow support with growth factors of blood stem cells/ bone marrow
What cancers are treated with high dose chemo?
Hodgkins + Ewings Sarcoma
When is chemo given intravesically?
For superficial bladder cancer

When is chemo given intraperitoneally?
Tumours that have spread trans-coelomically (ovarian)

When is chemo given intra-arterially?
For tumours with well-defined bloody supply eg hepatic artery infusion for liver mets
How is chemo dose calculated + what are the exceptions to this rule?
Using body surface area (BSA) Formula of DuBois + DuBois Carboplatin is calculated according to renal function Trastuzumab is calculated on body weight alone
SE of chemo
N+V, GI side effects, GU - nephrotoxicity + bladder toxicity, hepatic toxicity
Skin + soft tissue toxicity - hand foot syndrome, extravasation, photosensitivity
Lethargy + myalgia, myelosuppression, alopecia
Peripheral neuropathy
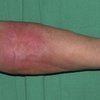
Why does chemo cause myelosuppression?
Kills haematopoietic progenitor cells
Leads to leucopenia + thrombocytopenia
What is the nadir?
Lowest point of neutrophil drop (drops 10-14 days after chemo)

What are the GI SE with chemo + why do they happen?
Oral mucositis = reflects damage to epithelium
Diarrhoea due to colitis or small bowel mucosal inflammation
Constipation due to dehydration = can develop into paralytic ileus caused by autonomic neuropathy

How is alopecia caused + what can be done about it?
Due to damage to rapidly dividing cells in hair follicle
Use of cold cap to reduce blood flow to scalp
What neurological SE are there?
Peripheral + autonomic neuropathy
CNS toxicity
Ototoxicity - cochlear damage causing high tone hearing loss
What is extravasation?
Highly vesicant drugs cause tissue damage




