Chapter 7 Endocrine system Flashcards
(23 cards)
What to finish!!!!!!!!!!!
slide # 8 and 11
What is the endocrine system?
Made up of endocrine cells, tissues, organs and the hormones they produce
What are hormones and target cells?
- Hormone
- Chemical messenger or signal molecule that helps maintain homeostasis
- Act to regulate target cell’s activity
- Hormones secreted into interstitial fluid and diffuse into blood where they are transported to distant targets
- Bind to target cell receptors to initiate response
- -Exert effect at very low concentrations
- -Half-life indicates how long will be active in body - Target cell
- Cell that contains a receptor for the hormone
- Hormones only affect target cells
- Target cells have 2,000-100,000 receptors for a given hormone
What is the difference between the nervous system and Endocrine system in regards to communication, speed, duration, and target cells?
- Nervous system:
-Communicates by sending electrical impulses to neurotransmitters which releases hormones or chemicales.
-Impulses are sent quickly to target cells.
-The duration is also quick and does not last long.
-the targets of the nervous system are muscle cells, neurons or glands - Endocrine system:
-Communicates via hormones and chemicals
-Speed of endocirne is usuallly slow except in the case of adrenaline
-The duration varies at it may last seconds, days, or hours.
-Endocrine acts on almost all cells using a specific hormone to target a compatable cell
.

What are the twelve glands we need to know?
- Adrenal Gland
- Heart
- Hypothalamus
- Islets of Langerhans (spleen)
- Kidneys
- ovaries
- parathyroid gland
- Pineal gland
- Pituitary anterior
- Pituitary posterior
- Testes
- Thryoid gland
What are the twelve glands and what do they release?
- Adrenal gland = epinephrine
- Heart = atrial natriuretic hormone
- Islets of Langerhans (Pancreas) = Insulin, glucogon
- Kidneys = erythropoietin
- Ovaries = estrogen, progesterone
- Parathyroid gland = parathyroid hormone
- Pineal gland = melatonin
- Pituitary anterior = trophic hormones
- Pituitary posterior = antidiuretic hormones, oxytocin
- Testes = testosterone
- Thyroid gland = thyroxine, calcitonine
What are the classifications of hormones?
- Amines derived from an amino acid
- Ex: epinephrine - Proteins are chains of amino acids
- Ex; protein, insulin - Steroids are lipids derived from cholesterol
- Ex: testosterone
What is the peptide hormone synthesis? Explain its process.

What is the difference between water and lipid soluble hormones?
- Water soluble hormones
- Hydrophilic and Lipophobic
- Cannot pass through plasma -membranes
- Receptors on outside surface of cells and trigger a response inside the cell - Lipid soluble hormones
- lipophilic and hydrophobic
- Can enter target cells directly
- Receptors usually on the inside of cells and trigger a response inside the cell
Can hydrophilic hormones cross cell membranes? If not then how?
-Amines and protein hormones cannot cross cell membrane, so bind to receptors on cell surface
-Often make use of a 2nd messenger mechanism to pass signal to inside of target cell:
Ex: Tyrosine kinase

What is Steroid hormone action?

What are the different ways of hormone interaction?
- Synergistic - work together to produce an effect
- Permissive - one hormone makes the target cell more responsive to second hormone
- Antagonistic – hormones oppose each other

What is the hypothalamus and what does it do?
- Integration between nervous and endocrine systems
- Hypothalamus controls activity of pituitary gland
Releases hormones that act on anterior pituitary
Produces hormones stored & released from posterior pituitary

What does the anterior pituitary do?
Anterior pituitary releases 6 “trophic” hormones that act on other endocrine glands to stimulate growth, development and release of hormones

What are adrenal glands and what do they do?
- Sit above kidneys and function as 2 glands
- Outer glandular cortex secretes steroid hormones
- Inner neural medulla secretes epinephrine

What is the thryoid gland and what does it do?
- Located just below the larynx
- Follicular cell hormones increase body metabolism
- Regulate BMR & oxygen use
- Parafollicular cells produce Calcitonin:
-Lowers blood calcium
-Inhibits breakdown of calcium from bone /deposits on bone
-Stimulates kidneys to excrete calcium

What is the parathyroid gland and what does it do?
- Embedded back of thyroid gland
- Secrete parathyroid hormone
-Hormone promotes rise in blood Ca2+ by acting on bones, kidneys, intestine

What is the pancreas and what does it do?
- Acts as both endocrine and exocrine glands
-Endocrine cells located in islets of Langerhans - Antagonistic hormones regulate blood sugar
-Glucagon (alpha cells) increase glucose levels
-Insulin (beta cells) lower glucose levels

How does insulin work?
Binds to receptors on target cells
-Vesicles with GLUT 4 carrier proteins bind to membrane
-Glucose diffuses through GLUT 4 channels
-Occurs in adipose, muscle, and the liver
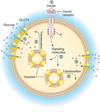
What is the Endocrine reflex pathway?
- Stimulus
- Sensor
- Input signal
- Integrating Center
- Output signal (hormone in blood)
- Targets
- Response

What is the pineal gland and what does it do?
- Located on roof of third ventricle in the brain
- Secretes melatonin – regulate circadian rhythms


