Chapter 5 - Several Useful Discrete Distributions Flashcards
(11 cards)
__ __ __ take on only a finite or countable infinite number of values.
Discrete random variables
Three discrete probability distributions serve as models for a large number of practical applications:
Binomial Random Variable
Possion Random Variable
Hypergeometric Random Variable
1) The experiment consists of __ __ __.
2) Each trial results in one of two outcomes, __ or __.
3) The probability of success on a single trial is __ and remains __ from trial to trial. The probability of failure is q = 1 – p.
4) The trials are __.
5) We are interested in x, the number of __ in n trials.
1) n identical trials.
2) success (S) or failure (F).
3) p, constant
4) independent
5) successes
The Binomial Probability Distribution For a binomial experiment with n trials and probability p of success on a given trial, the probability of k successes in n trials is

The Mean and Standard Deviation For a binomial experiment with n trials and probability p of success on a given trial, the measures of center and spread are:

You can use the __ __ __ to find probabilities for selected binomial distributions.
cumulative probability tables
a model for data that represent the number of occurrences of a specified event in a given unit of time or space
Poisson Random Variable
x is the number of events that occur in a period of time or space during which an average of m such events can be expected to occur. The probability of k occurrences of this event is
Mean = ?
Standard Deviation =?
Mean: µ
Standard Deviation: σ = √µ

The Hypergeometric Probability Distribution
The probability of exactly k successes in n trials is:
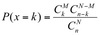
Mean and Variance
The mean and variance of the hypergeometric random variable x resemble the mean and variance of the binomial random variable:

Binomial Probabilities can be approximated with Poisson Probabilties when?
np < 7 using µ = np


