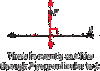Chapter 3 Review Flashcards
(30 cards)
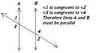
parallel lines
coplanar lines that do not intersect
Example: AB || MN
*Arrows are used to indicate that lines are parallel.

skew lines
lines that do not intersect and are not coplanar
EX. Lines n1 and n2 are skew.
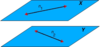
parallel planes
planes that do not intersect
EX. Planes X and Y are parallel

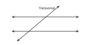
transversal
a line that intersects two or more coplanar lines at two different points
interior angles
angles that lie between two transversals that intersect the same line
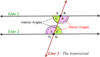
exterior angles
an angle that lies in the region that is not between two transversals that intersect the same line
consecutive interior angles
interior angles that lie on the same side of the transversal

alternate interior angles
nonadjacent interior angles that lie on the opposite sides of a transversal

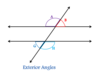
alternate exterior angles
nonadjacent exterior angles that lie on the opposite sides of a transversal

corresponding angles
angles tha tlie on the same side of a transversal and on the same same sides of the intersecting lines
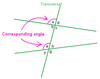
Postulate 3.1: Corresponding Angles Postulate
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then each pair of corresponding angles is congruent.

Theorem 3.1: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then each pari of alternate interior angles is congruent.

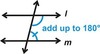
Theorem 3.2: Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then each pair of consecutive interior angles is supplementary.
Theorem 3.3: Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then each pair of alternate exterior angles is congruent.
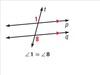
Theorem 3.4: Perpendicular Transversal Theorem
In a plane, if a line is perpendicular to one of two parallel lines, then it is perpendicular to the other.

slope
the ratio of change along the y-axis to the change along the x-axis between two points on a line
slope formula
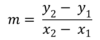
Postulate 3.2: Slopes of Parallel Lines
Two nonvertical lines have the same slope if and only if they are parallel. All vertical lines are parallel.
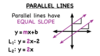
Postulate 3.3: Slopes of Perpendicular Lines
Two nonvertical lines are perpendicular if and only if the product of their slopes is - 1. Vertical and horizontal lines are perpendicular.
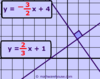
slope-intercept form
y =mx + b
(m = slope; b = y-intercept)
point-slope form
y - y1 = m (x - x1)
(m = slope; (x1,x2) = any point on the line)
Postulate 3.4: Converse of Corresponding Angles Postulate
If two lines are cut by a transversal so that corresponding angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel.
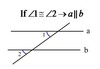
Postulate 3.5: Parallel Postulate
If given a line and a point not on the line, then there exists exactly one line through the point that is parallel to the given line.

Theorem 3.5: Alternate Exterior Angles Converse
If two lines in a plane are cut by a transversal so that a pair of alternate exterior angles is congruent, then the two lines are parallel.