Chapter 1 Review Flashcards
Undefined terms
Can only be explained using examples and descriptions (ie. point, line, plane)
Point
A location.
Has neither shape nor size.
Named by a capital letter.
Example: point A
• A
Plane
A flat surface made up of points that extends infinitely in all directions. There is exactly one plane through any three points not on the same line.
Named: Plane m, plane ABC

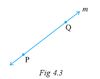
Line
Made up of points and has no thickness or width. There is exactly one line through any two points.
Named: line m, line PQ
Collinear
Points that lie on the same line
Coplanar
points that lie on teh same plane
intersection
the point or set of points shared by two or more geometric figures
P represents the intersection

defined terms
Explained using undefined terms and/or other defined terms
space
a boundless, three-dimensional set of all point; can contain lines and planes
line segment
part of a line that can be measured using two endpoints
between
Point M is between points P and Q if and only if P, Q, and M are collinear and PM + MQ = PQ

congruent segments
segments that have the same measure

distance between points
the length between two points as measured by the absolute value of the difference between their coordinates
Formula d = | b - a |

Distance formula (in a coordinate plane)

irrational number
A number that cannot be expressed as a repeating decimal.
Midpoint
the point halfway between the endpoints of a segment
Midpiont formula (in a coordinate plane)
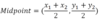
Midpoint formula
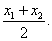
segment bisector
any segment, line, or plane that intersects a segment at its midpoint
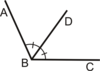
ray
a part of a line that has one endpoint and extends indefinitely in one direction
Named by stating the endpoint first and then any other point on the ray
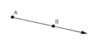
opposite rays
two rays that share the same endpoint, go in opposite directions, and are collinear
EX. BA and BC are opposite rays

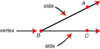
angle
formed by two noncollinear rays that have a common endpoint

sides
the rays that form an angle
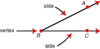
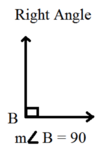
vertex
the common endpoint of an angle