Chapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides & Proteins Flashcards
residue
reflects the loss of the elements of water when one amino acid is joined to another
hydrolyzed
broken down
All 20 of the common amino acids are _____-amino acids. They have a _____ group and an _____ group bonded to the same carbon atom (the _____ carbon). They differ from each other in their _____ _____, or ______ groups, which vary in structure, size, and electric charge and and influence the solubility of the amino acids in _____. This structure is common to all but one of the α-amino acids. (_____, a cyclic amino acid)

- α
- carboxyl
- amino
- side chains
- R
- water
- Proline
For all the common amino acids except _____,
the α carbon is bonded to four different groups: (______). The α-carbon atom is thus a _____ center. Thefour different groups can occupy _____ unique spatial arrangements; thus amino acids have two possible _____. Since they are nonsuperposable mirror images of each other they are _____. In glycine, the R group is another _____ atom
- glycine
- carboxyl group
- amino group
- R group
- hydrogen atom
- chiral
- two
- stereoisomers
- enantiomers
- hydrogen
The absolute configurations of simple sugars and amino acids are specified by the _____ _____ system, based on the absolute configuration of the three-carbon sugar _____. L and D refer only to the _____ _____ of the four substituents around the chiral carbon, not to _____ properties of the molecule.
- D, L
- glyceraldehyde
- absolute configuration
- optical

For all chiral compounds, stereoisomers having a configuration related to that of L-glyceraldehyde are designated L, and stereoisomers related to D-glyceraldehyde are designated D. The functional groups of the amino acids are matched with those of glyceraldehyde by aligning those that can be interconverted by simple,_____ _____ chemical reactions. Then L-Amino acids are those with the α-amino group on the _____, and D-amino acids have the α-amino group on the _____. Explain…
- one-step
- left
- right
- In these perspective formulas
- C are lined up vertically, w/chiral atom in the center
- C are numbered beginning with the terminal aldehyde or carboxyl carbon, 1 to 3 from top to bottom
- R group is always below the α carbon
- L-Amino acids have the α-amino group on the left
- D-amino acids have the α-amino group on the right

Nearly all biological compounds with a chiral center
occur naturally in only one _____ form, either D or L. The amino acid residues in protein molecules are exclusively _____ _____. _____-Amino acid residues have been found in only a few, generally small peptides, including some peptides of bacterial cell walls and certain peptide antibiotics.
- stereoisomeric
- L stereoisomers
- D
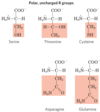
amino acids can be grouped into five main classes based on the properties of their _____ groups, particularly their ______, or tendency to interact with _____ at biological _____.
- R
- polarity
- water
- pH (near pH 7.0)
A few amino acids are somewhat difficult to characterize or do not fit perfectly in any one group, particularly _____, ______ and _____. Their assignments to particular groupings are the results of considered judgments rather than absolutes.
- glycine
- histidine
- cysteine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
______ has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive ______ structure. The secondary amino (imino) group is held in a _____ ______ that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing it
- Proline
- cyclic
- rigid conformation

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
_____, one of the two sulfur containing amino acids, has a slightly nonpolar ______ group in its side chain
- Methionine
- thioether

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
_____ has the simplest structure. Although it is most easily grouped with the nonpolar amino acids, its very _____ _____ _____ makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions
- Glycine
- small side chain

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
chains of _____, _____, _____, _____ tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of _____ _____.
- alanine
- valine
- leucine
- isoleucine
- hydrophobic interactions

Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups
- nonpolar
- hydrophobic

Glycine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Alanine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Proline
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Valine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Leucine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Isoleucine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Methionine
Nonpolar, Aliphatic R Groups

Aromatic R Groups
_____, _____, and _____, with their aromatic side chains, are relatively nonpolar (hydrophobic).
- Phenylalanine
- tyrosine
- tryptophan

Aromatic R Groups
The _____ group of tyrosine can form hydrogen bonds, and it is an important functional group in some enzymes
- tyrosine

Aromatic R Groups
Tyrosine and tryptophan are significantly more polar than phenylalanine, because of the tyrosine _____ group and the _____ of the tryptophan indole ring.
- hydroxyl
- nitrogen

Aromatic R Groups
Tryptophan and tyrosine, and to a much lesser extent phenylalanine, absorb _____ ______. This accounts for the characteristic strong absorbance of light by most proteins at a wavelength of ______ nm
- ultraviolet light
- 280

Aromatic R Groups
Tyrosine and tryptophan are significantly more polar than phenylalanine, because of the tyrosine _____ group and the _____ of the tryptophan indole ring.
- hydroxyl
- nitrogen

Tryptophan
Aromatic R Groups

Tyrosine
Aromatic R Groups

Phenylalanine
Aromatic R Groups

Polar, Uncharged R Groups
Asparagine and glutamine are the amides of two other amino acids also found in proteins—______ and _____, respectively—to which asparagine and glutamine are easily hydrolyzed by acid or base
- aspartate
- glutamate

Polar, Uncharged R Groups
Cysteine is readily oxidized to form a covalently linked dimeric amino acid called _____. Two cysteine molecules are joined by a ______ bond. The residues are strongly hydrophobic (_____). ______ bonds between Cys residues stabilize the structures of many proteins.

- cystine
- disulfide
- nonpolar
- Disulfide

Polar, Uncharged R Groups
The polarity of serine and threonine is contributed by their_____ groups, and that of asparagine and glutamine by their _____ groups. Cysteine is an outlier here because its polarity, contributed by its _____ group, is quite modest. Cysteine is a weak acid and can make weak hydrogen bonds with ______ or _____.
- hydroxyl
- amide
- sulfhydryl
- oxygen
- nitrogen
Polar, Uncharged R Groups
more soluble in water (hydrophilic), than those of the nonpolar amino acids, because they contain functional groups that form hydrogen bonds with water. This class of amino acids includes _____, _____, ______, _____ and _____. The polarity of serine and threonine is contributed by their hydroxyl groups, and that of asparagine and glutamine by their amide groups. Cysteine is an outlier here because its polarity, contributed by its sulfhydryl group, is quite modest. Cysteine is a weak acid and can make weak hydrogen bonds with oxygen or nitrogen.
- serine
- threonine
- cysteine
- asparagine
- glutamine

Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups
The most hydrophilic amino acid R groups are those that are either _____ or _____ charged
- positively
- negatively
Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups
The amino acids in which the R groups have significant positive charge at pH 7.0 are _____, which has a second primary amino group at the ε position on its aliphatic chain; _____, which has a positively charged guanidinium group; and _____, which has an aromatic imidazole group.
- lysine
- arginine
- histidine

Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups
As the only common amino acid having an ionizable side chain with pKa near neutrality, ______ may be _____ _____ (protonated form) or ______ at pH 7.0. His residues facilitate many enzyme-catalyzed reactions by serving as proton donors/acceptors.
- histidine
- positively charged
- uncharged

Glutamine
Polar, Uncharged R Groups

Asparagine
Polar, Uncharged R Groups

Cysteine
Polar, Uncharged R Groups

Threonine
Polar, Uncharged R Groups

Serine
Polar, Uncharged R Groups

Histidine
Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups

Arginine
Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups

Lysine
Positively Charged (Basic) R Groups

Negatively Charged (Acidic) R Groups
The two amino acids having R groups with a net negative charge at pH 7.0 are _____ and _____, each of which has a second _____ group.
- aspartate
- glutamate
- carboxyl

Glutamate
Negatively Charged (Acidic) R Groups

Aspartate
Negatively Charged (Acidic) R Groups

In addition to the 20 common amino acids, proteins may contain residues created by modification of _____ ______ already incorporated into a polypeptide. _____ is a special case. This rare amino acid residue is introduced during _____ _____ rather than created through a postsynthetic modification.
- common residues
- Selenocysteine
- protein synthesis
The amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids, along
with the ionizable R groups of some amino acids, function as _____ _____ and _____. When an amino acid lacking an ionizable R group is dissolved in water at neutral pH, it exists in solution as the dipolar ion, or _____ which can act as either an _____ or a _____
- weak acids
- bases
- zwitterion
- acid
- base
amphoteric / ampholytes
compound that is able to react both as a base and as an acid

Lecture
Acid-base titration involves the gradual addition or removal of _____
protons
Lecture
Titration of an amino acid
First stage:
- The ______ group of glycine loses its proton
- At the midpoint of this stage, equimolar concentrations of the proton-donor (_____) and proton-acceptor (_____) species are present
- a point of inflection is reached at this midpoint where the pH is equal to the pKa of the protonated group being titrated: both pH & pKa = 2.34
- As titration proceeds, another point of inflection is reached at pH 5.97 where removal of the first proton is complete and removal of the second begins
- —COOH
- +H3N—CH2—COOH-
- +H3N—CH2—COO-

Lecture
pH and pKa are simply convenient notations for _____ _____ and the _____ _____ for ionization, respectively. The pKa is a measure of the tendency of a group to give up a _____ , with that tendency decreasing _____ as the pKa _____ by one unit.
- proton concentration
- equilibrium constant
- proton
- tenfold
- increases
Lecture
Titration of an amino acid
Second stage:
- The second stage of the titration corresponds to the removal of a proton from the _____ rgroup
- titration is essentially complete at a pH of about 12 at which point the predominant form of glycine is ______
- —NH+3
- H2N—CH2—COO-
Lecture
From the titration curve of glycine we can derive several important pieces of information:
- a quantitative measure of the pKa of each of the two ionizing groups
- that the pKa of any functional group is greatly affected by its chemical environment
- the number of regions of buffering power
- relatively flat portion of the curve, extending for approximately 1 pH unit on either side of the first and second pKa of 2.34
- electric charge of amino acide
Lecture
titration curves predict the relationship between amino acid’s _____ _____ and the _____ of the solution. using the glycine titration example, at pH 5.97, the point of inflection between the two stages in its titration curve, glycine is present predominantly as its _____ form, fully _____ but with no net electric charge, its _____ ______

- net charge
- pH
- dipolar
- ionized
- isoelectric point

Lecture
isoelectric point, isoelectric pH or pI
- The characteristic pH at which the net electric charge of a molecule is zero
- the arithmetic mean of a molecule’s pKa values

Lecture
A molecule has a net ______ charge at any pH above its pI and will thus move toward the positive electrode (the _____) when placed in an electric field. At any pH _____ its pI, a molecule has a net positive charge and will move toward the negative electrode (the _____). The farther the pH solution is from its isoelectric point, the greater the _____ _____ _____ of its molecules.
- negative
- anode
- below
- cathode
- net electric charge
all amino acids with a single α-amino group, a single α-carboxyl group, and an R group that does not ionize have titration curves resembling that of _____ in ____ stages
- glycine
- two
amino acids with an ionizable R group have more complex titration curves, with _____ stages corresponding to the three possible _____ steps; thus they have three _____ values. The additional stage for the titration of the ionizable R group merges to some extent with that for the titration of the _____ group, the titration of the _____ group, or ______
- three
- ionization
- pKa
- α-carboxyl
- α-amino
- both
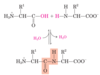
Two amino acid molecules can be covalently joined through a substituted amide linkage, termed a ____ _____, to yield a dipeptide
peptide bond
- a dipeptide bond formed by removal of the elements of water (_____) from the ______ group of one amino acid and the ______ group of another
- It is an example of a ______ reaction
- Under standard biochemical conditions, the equilibrium for the reaction favors the amino acids over the dipeptide becase ….
- To make the reaction thermodynamically more favorable, the carboxyl group must be …
- dehydration
- α-carboxyl
- α-amino
- condensation
- Amino groups are good nucleophiles, but the hydroxyl group is a poor leaving group and is not readily displaced
- chemically modified or activated so that the hydroxyl group can be more readily eliminated
oligopeptide
When a few amino acids are joined
polypeptide
When many amino acids are joined
polypeptides generally have molecular weights below ______, and those called proteins have _____ molecular weights.
- 10,000
- higher
an amino acid unit in a peptide is often called a ______ which is the part left over after losing the elements of ______ —a hydrogen atom from its _____ ______ and the _____ moiety from its carboxyl group
- residue
- water
- amino group
- hydroxyl
In a peptide, the amino acid residue at the end with a free α-amino group is the amino-terminal (or _____) residue, placed on the _____ side; the residue at the other end, which has a free carboxyl group, is the carboxylterminal (______) residue, placed on the _____ side
- N-terminal
- left
- C-terminal
- right
hydrolysis of a peptide bond is an _____ reaction, it occurs only slowly because it has a _____ _____ ______ . As a result, the peptide bonds in proteins are quite _____, with an average half-life of about _____ years
- exergonic
- high activation energy
- stable
- 7
Peptides contain only ____ free α-amino group and _____ free α-carboxyl group, at opposite ends of the chain, these groups _____ as they do in free amino acids, although the ionization constants are different because an oppositely charged group is no longer
- one
- one
- ionize
The α-amino and α-carboxyl groups of all nonterminal amino acids are _____ joined in the peptide bonds, which do not _____. However, the _____ _____ of some amino acids can.
- covalently
- ionize
- R
Thus the acid-base behavior of a peptide can be predicted from its
- free α-amino and α-carboxyl groups
- combined with the nature and number of its ionizable R groups
Like free amino acids, peptides have characteristic _____ _____ and a characteristic _____ ______
- titration curves
- isoelectric pH
the ______ value for an ionizable _____ _____ can change somewhat when an amino acid becomes a residue in a peptide
- pKa
- R group
multisubunit proteins
have two or more polypeptides associated noncovalently
The individual polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein may be identical or different. If at least two are identical the protein is said to be _____, and the identical units (consisting of one or more polypeptide chains) are referred to as _____
- oligomeric
- protomers
Lecture
- We can calculate the approximate number of amino acid residues in a simple protein containing no other chemical constituents by dividing its molecular weight by _____
- average molecular weight of the 20 common amino acids is about _____, the smaller amino acids predominate so the average molecular weight of protein amino acids is nearer to _____. Because a molecule of water (Mr 18) is removed to create each peptide bond, the average molecular weight of an amino acid residue in a protein is calculated
- 110
- 138
- 128
- 128 - 18 = 110
Many proteins, for example the enzymes ribonuclease A and chymotrypsin, contain only amino acid residues and no other chemical constituents; these are considered _____ _____
simple proteins
conjugated proteins
proteins that contain permanently associated chemical components in addition to amino acids
prosthetic group
- The non–amino acid part of a conjugated protein
- Conjugated proteins are classified on the basis of the chemical nature of the prosthetic group
- for example, lipoproteins contain lipids, glycoproteins contain sugar groups, and metalloproteins contain a specific metal
dialysis
- a procedure that separates proteins from small solutes
- partially purified extract is placed in a bag or tube made of a semipermeable membrane
- bag/tube iis suspended in a much larger volume of buffered solution
- membrane allows exchange of salt and buffer but not proteins
- large proteins are kept within the bag/tube while concentration of other solutes change and come into equilibrium with the solution outside the membrane
The second step in any protein purification procedure is to subject the ____ _____ to treatments that separate the proteins into different fractions based on a _____ such as size or charge, a process referred to as ______
- crude extract
- property
- fractionation
Early fractionation steps in a purification utilize differences in protein solubility, which is a complex function of
- pH
- temperature
- salt concentration
- other factors
Lecture
name methods for fractionating proteins
salting out
- The solubility of proteins is lowered in the presence of some salts, an effect called “salting out.”
- addition of certain salts in the right amount can selectively precipitate some proteins, while others remain in solution
- Ammonium sulfate is often used to salt out proteins
- The proteins precipitated are removed from those remaining in solution by low-speed centrifugation
Column chromatography
- uses a solid, porous material (matrix) supported inside a column made of plastic or glass
- protein sample to be separated is layered on top of the column
- A solution (mobile phase) flows through protein sample and percolates into the solid matrix (stationary phase)
- solution that passes out of the column at the bottom (the effluent) is constantly replaced by solution supplied from a reservoir at the top
- protein sample forms a band within the mobile phase as proteins migrate through the column
- some proteins are retarded to different degrees by their different interactions with the matrix material
- Individual types of proteins gradually separate from each other
- Separation/resolution improves as the length of the column increases
- each individual protein band broadens with time due to diffusional spreading, a process that decreases resolution

Ion-exchange chromatography
- Protein mixture is added to column containing cation or anion exchangers
- Proteins move through the column at rates determined by their net charge at the pH being used
- With cation exchangers, proteins with a more negative net charge move faster and elute earlier
- With anion exchangers, proteins with a more positive net charge move faster and elute earlier
- Separation can be optimized by gradually changing the pH and/or salt concentration of the mobile phase
- The affinity of each protein for the charged groups on the column is affected by the pH (which determines the ionization state of the molecule) and the concentration of competing free salt ions in the surrounding solution

Size-exclusion chromatography / gel filtration
- separates proteins according to size
- large proteins emerge from the column sooner than small ones—a somewhat counterintuitive result
- solid phase consists of cross-linked polymer beads with engineered pores or cavities of a particular size
- Large proteins cannot enter the cavities and so take a shorter/rapid path around the beads
- Small proteins enter the cavities and are slowed by their more labyrinthine path through the column
- can also be used to approximate the size of a protein

Affinity chromatography
- separates proteins by their binding affinity
- beads in the column have a covalently attached chemical group called a ligand—a group or molecule that binds to a macromolecule such as a protein
- When a protein mixture is added to the column, any protein with affinity for this ligand binds to the beads, and its migration through the matrix is retarded
- After proteins that do not bind are washed through the column, the bound protein is eluted by a solution containing either a high concentration of salt or free ligand
- Salt weakens the binding of the protein to the immobilized ligand
- Free ligand competes with the ligand attached to the beads, releasing the protein from the matrix
- protein product that elutes from the column is often bound to the ligand used to elute it
A biochemist wants to separate two peptides by ionexchange chromatography. At the pH of the mobile phase to be used on the column, one peptide (A) has a net charge of 23, due to the presence of more Glu and Asp residues than Arg, Lys, and His residues. Peptide B has a net charge of 11. Which peptide would elute first from a cation-exchange resin? Which would elute first from an anion-exchange resin?
A cation-exchange resin has negative charges and binds positively charged molecules, retarding their progress through the column. Peptide B, with its net positive charge, will interact more strongly than peptide A with the cation-exchange resin, and thus peptide A will elute first. On the anion-exchange resin, peptide B will elute first. Peptide A, being negatively charged, will be retarded by its interaction with the positively charged resin.
HPLC, or high-performance liquid chromatography.
- enhances Chromatographic methods
- uses high-pressure pumps that speed the movement of the protein molecules down the column
- uses higher-quality chromatographic materials that can withstand the crushing force of the pressurized flow
- By reducing the transit time on the column, limits diffusional spreading of protein bands and thus greatly improve resolution
electrophoretic methods often adversely affect the _____ and thus the ______ of proteins
- structure
- function
electrophoresis
w/detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
- A protein will bind about 1.4 times its weight of SDS, nearly one molecule of SDS for each amino acid residue
- SDS contributes a large net negative charge, rendering charge of the protein insignificant and conferring on each protein a similar charge-to-mass ratio
- it unfolds proteins, so most SDS-bound proteins assume a similar rodlike shape
- Electrophoresis separates proteins almost exclusively on mass (molecular weight), with smaller polypeptides migrating more rapidly
- After electrophoresis, the proteins are visualized by adding a dye such as Coomassie blue, which binds to proteins
- progress of protein purification procedure can be monitored as the number of protein bands visible on the gel decreases after each new fractionation step
- When compared to proteins of known molecular weight, the position of an unidentified protein can provide a good approximation of its molecular weight
- If the protein has two or more different subunits, the subunits are generally separated by the SDS and a separate band appears for each.
Isoelectric focusing
- determines the isoelectric point (pI) of a protein
- A pH gradient is established by allowing a mixture of low molecular weight organic acids and bases to distribute themselves in an electric field generated across the gel
- When a protein mixture is applied, each protein migrates until it reaches the pH that matches its pI
two-dimensional electrophoresis
- Combining isoelectric focusing and SDS electrophoresis sequentially
- permits the resolution of complex mixtures of proteins
- separates proteins of identical molecular weight that differin pI, or proteins with similar pI values but different molecular weights
By international agreement, 1.0 unit of enzyme activity for most enzymes is defined as the amount of enzyme causing transformation of _____ ______ of substrate to product per minute at ______ under optimal conditions of measurement
- 1.0 µmol
- 25ºC
activity
total units of enzyme in a solution
specific activity
- the number of enzyme units per milligram of total protein
- measure of enzyme purity
- increases during purification of an enzyme and becomes maximal and constant when the enzyme is pure
Activity versus specific activity
- difference between these terms can be illustrated by considering two flasks containing marbles
- flasks contain the same number of red marbles but different numbers of marbles of other colors
- If the marbles represent proteins, both flasks contain the same activity of the protein represented by the red marbles
- The second flask, however, has the higher specific activity because red marbles represent a higher fraction of the total

A protein is generally considered pure when further purification steps fail to ______ specific activity and when only a single protein species can be _____ (for example, by electrophoresis).
- increase
- detected
Proteins are separated and purified on the basis of differences in their properties. Proteins can be selectively precipitated by changes in _____ or ______, and particularly by the addition of certain ______. A wide range of chromatographic procedures makes use of differences in ______, _____ ______, _____, and other properties. These include _____-_____, _____-______, ______, and high-performance _____ ______.
- pH
- temperature
- salts
- size
- binding affinities
- charge
- ion-exchange
- size-exclusion
- affinity
- liquid chromatography
Electrophoresis separates proteins on the basis of _____ or _____. ______ _____ electrophoresis and _____ ______ can be used separately or in combination for higher resolution.
- mass
- charge
- SDS gel
- isoelectric focusing
All purification procedures require a method for quantifying or assaying the protein of interest in the presence of other proteins. Purification can be monitored by assaying _____ _____
- specific activity
pI is the pH at which the net charge is
zero
pH = pKa at the _____-_____ point of each substance. most of the base is consumed at the rate of about _____ pH unit on either _____ of this value. In this range, the change in pH is w/moles of base added is _____; thus this is the best _____ _____
- half neutralization
- one
- side
- minimal
- buffering range

Lecture
Most proteins are very soluble at high pH, where all of their molecules are _____ charged. The protein is _____.
- negatively
- deprotanated
Lecture
The lowest solubility occurs at the
- isoelectric point
Lecture
At low pH, proteins are soluble becase of their _____ charge. The protein is _____.
- positive
- protonated
Lecture
A the ______ point, where the protein has no net-charge its molecules retain regions of _____ and _____ charge on their surface, resulting in _____ and _____
- isoelectric
- positive
- negative
- aggregation
- precipitation
Lecture
ionic strength of a solution is a
measure of the concentration of ions in that solution
Lecture
ionic strength formula
Example: 0.04 M (NH4)2SO4
[NH4+] = 0.08 M
[SO4] = 0.04 M
Example: 0.04 M (NH4)2SO4
- µ
- = (1/2) {0.08 × (+1)2 + 0.04 x (-2)2}
- = (1/2) {0.08 + 0.16} = 0.24 M
- 1/2: takes into accounts both ions are, cation & anion
- c: concentration in molar units (mol/L)
- z: charge of each ions
- i.e. if the ions is sulfate (SO 42-) then z = 2
- multivalent ion has a bigger contribution

Lecture
ionic strength formula
- calculate the sum of the molar concentration of each ion multiplied by the valence squared
- 1/2: takes into accounts both ions are, cation & anion
- c: concentration in molar units (mol/L)
- z: charge of each ions
- i.e. if the ions is sulfate (SO 42-) then z = 2
- multivalent ion has a bigger contribution
- determines the strength of buffer solutions that should have concentrations similar to the found in nature

primary structure
- a sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and includes any disulfide bonds
- most important element of primary structure is the sequence of amino acid residues.

secondary structure

- arises from the hydrogen bonds formed between atoms of the polypeptide backbone (primary structure)
- The hydrogen bonds can form between the partially negative oxygen atom and the partially positive nitrogen atom
- Most proteins have segments of their polypeptide chains that are either coiled or folded in patterns that contribute to the protein’s shape
- Many of these coils and folds repeat so often that they have been given names
- Two folds that are extremely common in biochemistry are the alpha-helix and the beta-pleated sheet.

Tertiary structure
- is the three-dimensional shape of the protein formed by the interactions of the side chains of the various amino acids
- hydrophobic interaction plays a major role in the correct folding of a protein
- As a polypeptide folds, amino acids with nonpolar side chains usually cluster at the core of the protein, staying away from water
- Once the nonpolar amino acids have formed the nonpolar core of the protein, weak van der Waals forces stabilize the protein
- hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions between the polar, charged amino acids contribute to the tertiary structure
- These are all weak interactions w/cumulative effect that helps give proteins their unique shape
- Disulfide bridges, covalent bonds formed between two cysteine residues, further reinforce the shape of a protein
Disulfide bridges form when
the sulfhydryl groups of two cysteine residues come into close contact because of protein folding
quartinary structure
- Some proteins are made up of more than one amino acid chain, giving them a quaternary structure
- These multi-chain proteins are held together with the same forces as the tertiary structure of individual protein chains
- hydrophobic
- hydrophillic
- positive/negative and cysteine interactions
the _____ _____ of a protein determines how it folds up into its unique three-dimensional structure, and this in turn determines the _____ of the protein
- primary structure
- function
Breaking disulfide bonds in proteins
reduction by dithiothreitol


Breaking disulfide bonds in proteins
oxidation by performic acid


sulfhydryl
- a functional group consisting of a sulfur bonded to a hydrogen atom
- also called a thiol
- ,nomenclature jof “-thiol” as a suffix and “mercapto-“ or “sulfanyl” as a prefix
- play an important role biochemistry, as disulfide bonds connect necessary amino acids together for functional purpose in secondary, tertiary, or quaternary proteins structures.
Mass spectrometry can provide a highly accurate measure of the _____ _____ of a protein, but can also provide the _____ of multiple short polypeptide segments (20 to 30 amino acid residues) in a protein sample quite rapidly.
- molecular weight
- sequences
analytes
Molecules to be analyzed
The accurately measured _____ _____ of a protein is critical to its identification. Once the mass of a protein is accurately known, _____ ______ is a convenient and accurate method for detecting changes in mass due to the presence of bound cofactors, bound metal ions, covalent modifications, and so on.
- molecular mass
- mass spectrometry
There are three ways to obtain a peptide
- purification from tissue, a task often made difficult by the vanishingly low concentrations of some peptides
- genetic engineering
- direct chemical synthesis
The complexity of proteins makes the traditional synthetic approaches of organic chemistry impractical for peptides with more than _____ or _____ amino acid residues. One problem is the difficulty of _____ the product after each step
- four or five
- purifying
For a given protein, the amino acid residues essential for the activity of the protein are _____ over evolutionary time. The residues that are less important to function may _____ over time—and these _____ ______ can provide the information to trace evolution
- conserved
- vary
- variable residues
Amino acid substitutions are not always _____, however. At some positions in the_____ _____ the need to maintain protein function may mean that only _____ _____ _____ substitutions can be tolerated. Some proteins have more variable_____ ______ _____ than others. For these and other reasons, different proteins can evolve at _____ _____
- random
- primary structure
- particular amino acid
- amino acid residues
- different rates
Amino acid sequences are deduced by fragmenting polypeptides into smaller peptides with reagents known to cleave specific _____ _____; determining the amino acid sequence of each fragment by the automated _____ _____ _____; then ordering the peptide fragments by finding sequence overlaps between fragments generated by different reagents. A protein sequence can also be deduced from the nucleotide sequence of its corresponding gene in DNA, or by _____ _____
- peptide bonds
- Edman degradation procedure
- mass spectrometry
Short proteins and peptides (up to about _____ residues) can be chemically synthesized. The peptide is built up, one a_____ _____ _____ at a time, while tethered to a _____ ______.
- 100
- mino acid residue
- solid support


