Chapter 1: Foundations of Biochemistry Flashcards
(59 cards)
metabolites
- small organic molecules
- an intermediate or end product of metabolism
- intermediates in biosynthetic and degradative pathways
Molecular weight
- the mass of a molecule of a substance
- a.k.a molecular mass
- unit: atomic mass units (amu)
Molar mass
- the mass of one mole of a substance.
- units: grams per mole or g/mole
mole (mol)
- just a number
- 6.022x1023
- Avogadro’s number
macromolecules
- polymers with molecular weights above ∼5,000
- assembled from relatively simple precursors
- i.e. Proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, etc.
oligomers
a polymer whose molecules consist of relatively few repeating units
stereoisomers
- compounds with the same exact molecular formula and connectivity (chemical bonds) but they differ in the arrangement of atoms in three-dimensional space (configuration)
- simplest forms of stereoisomers are cis and trans isomers, both of which are created by the restricted rotation about a double bond or ring system
configuration
- the fixed spatial arrangement of atoms
- relative position of the atoms in a molecule
- does not change when the molecule twists into another conformation
- can be changed exclusively by cleaving and forming new chemical bonds
the fixed spatial arrangement of atoms. Interactions between biomolecules are invariably ______, requiring specific _______ in the interacting molecules.
- stereospecific
- configurations
Conformations
the set of possible shapes a molecule can have by means of rotation about single bonds
stereochemistry
the 3D relationships between atoms in a molecule
isomers
compounds with different physical and chemical properties but the same molecular formula
two types of stereoisomers
- enantiomers: mirror images
- diastereoisomers: non-mirrow images
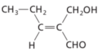
geometric isomer
each of two or more compounds which differ from each other in the arrangement of groups with respect to a double bond, ring, or other rigid structure.
when comparing compounds, if the bonds are the same, and there are double bonds or rings they are
geometric isomers
when comparing compounds, if the bonds are the same, and they are not superimposable, they are
stereoisomers
enantiomers
- compounds that are non-superimposable mirror images
- said to be chiral
chiral, asymmetric, stereogenic carbon atom, or stereocenter
a carbon w/4 different substituents
any molecule in which only one of its carbon atoms has 4 different groups attached will always be
chiral
max # of stereoisomers for a molecule with n chiral carbon is
\<= 2ⁿ n = # of chiral atoms
When a tetrahedral carbon has only three dissimilar groups (i.e., the same group occurs twice), only one configuration is possible and the molecule is _____, or _____
- symmetric
- achiral
racemix mixture / racemate
- when one enantiomer is combined w/the same amount of another
- solution does not rotate polarized light because the two compounds rotate the light equally in opposite directions
- displays different characteristics than a pure solution of either one
E and Z nomenclature
- Z = same side
- E = opposite sides
- Z & E are prefixes in parens, italicized, connecting to name with a hyphen: (Z)-4-Chloro-3-methil-2-betenoic acid
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog-Convention
priority of substituents for E and Z
- ↑ atomic # = ↑ priority
- if elements are isotopes of same element, the 1 w/↑ mass has ↑ priority
- unshared e- pair = lowest priority
- H has lowest priority