Chapter 3 Flashcards
(64 cards)
Good data collection
A realistic and sound plan is needed to develop a study that is a good representation of the population
Three steps in designing a study
- Identify population of interest 2. Compile list of subjects 3. Decide sampling design
Note on identifying population of interest
Have to have the population match the study’s question
Sampling Units
Subjects of interest
Sampling Frame
List of subjects to sample from
Sample Design
Method of drawing samples from the sample frame
What makes a good Sampling Design?
Resulting sample is a good representative of the population and reflects characteristics of the population
Three types of Sample Designs
- Simple Random 2. Cluster 3. Stratified
Simple Random Sampling
Sample guided by equal chance, given a population of n subjects, each possible sample of that size (n) has the same chance of being selected
Fraternity example
Two of five officers set to go on trip, picked randomly from a hat. Possible samples of officers are C(5,2) = 10. Chance of selecting any one of samples is 1/10 and each officer appears 4/10 samples, each has a 4/10 = 2/5 chance of selection
Random Number Tables (Generators)
Number assigned to subjects in frame; random numbers of same length as above generated; subjects with numbers generated selected and process stopped when sample size is reached
Cluster Sampling
Population divided into large number of clusters and simple random sample of pre-specified number of clusters selected
Cluster Random Sample
All samples in the clusters chosen during the cluster sampling
Stratified Sampling
Population divided into separate groups (strata) and a simple random sample is selected from each
What you need for Stratified Sampling
Access to sampling frame and strata into which each subject belongs
Margin of Error
Potential error range in estimations
Sampling Fraction
Ratio of sample size n to population size N (n/N)
What if n/N is less than or equal to 0.05?
Margin of error is given by:
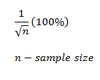
What if n/N is greater than or equal to 0.05?
We use finite population correction:
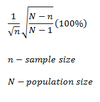
True proportion
Between the observed proportion ± margin of error
Bias
Responses from sample tend to favor parts of population and aren’t representative of the whole
Three types of Biases
- Sampling 2. Non-response 3. Response
Sampling Bias
Results from flaw in sampling method, especially if sample is non-random
Under-Coverage
Sampling frame that lacks representation from parts of the population



