Chapter 15: Odontogenic Cysts and Tumors Part III Flashcards
___ is a painless, nonulcerated, sessile gingival lesion, that is clinically determined to be one of the 3Ps (bump on the gum)
peripheral ameloblastoma
what is the average age of someone with a peripheral ameloblastoma?
50
where are peripheral ameloblastomas most commonly found?
mandibular posterior gingival mucosa
unlike intraosseous ameloblastomas, ___ have innocuous clinical behavior
peripheral ameloblastomas
what is the recurrence of peripehral ameloblastomas?
15%, and further excision has close to 0% recurrence

peripheral ameloblastoma
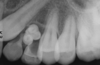
keep in mind that although this is in the anterior maxilla, most peripheral ameloblastomas are found in the posterior mandible
malignant ameloblastomas have histologic features of a ___, but shows metastatic deposits (what is the most common site for metastatic deposits?)
- conventional ameloblastoma
- lung most common site
ameloblastic carcinoma has ___ features and follows a markedly aggressive course
cytologic malignant
___ develops later in life than conventional ameloblastomas and malignant ameloblastomas
ameloblastic carcinoma
are ameloblastic carcinomas aggressive? what are the radiographic features?
- yes
- ill-defined margins and cortical destruction

ameloblastic carcinoma
adenomatoid odontogenic tumors occur in what age patient?
ages 10-20 (very uncommon in patients over the age of 30)
what are the common locations of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors? gender predilection?
- anterior maxilla
- F>M
most adenomatoid odontogenic tumors are what size? they may also rarely occur ___
- small
- peripherally
are adenomatoid odontogenic tumors symptomatic or asymptomatic? how are they discovered?
asymptomatic and discovered during xray to determine why a tooth hasn’t erupted
describe the radiographic features of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors
- 75% - tumor is circumscribed, unilocular RL involving the crown of an unerupted tooth
- most often canine
- RL often extends apically past the CEJ (helps differentiate from dentigerous cyst)
- lesion may contain fine, snowflake calcifications (can also help differentiate from dentigerous cyst)
- lesion may develop well-defined, unilocular RL between roots

what is the treatment of adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
tumor has a thick, fibrous capsule that makes enucleation easy
what is the recurrence and prognosis for adenomatoid odontogenic tumors?
- recurrence doens’t occur - lesion is completely benign, and aggressive behavior ahs not been documented
- prognosis is good

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
(you can see the snowflake calcifications)

adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors are also called ___
pindborg tumors
calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors occur around age ___
40
what is the common location of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumors? genetic predilection?
- posterior mandible
- M=F