Chapter 10: Flight Instruments, Displays Flashcards
Explain the function of the DISPLAYS SOURCE selector.

AUTO:
- allows DEU 1 to drive the captain’s outboard, captain’s inboard and upper display units while DEU 2 drives the first officer’s outboard, first officer’s inboard, and lower display units. Provides automatic switching from both DEUs to one DEU in case of single DEU failure.
ALL ON 1 or 2: (Used on the ground for maintenance purposes)
- selects either DEU 1 or DEU 2 to drive all 6 displays.
Explain the function of the DISPLAYS CONTROL PANEL Select Switch.

NORMAL:
- Left EFIS control panel controls captain’s displays and the right EFIS control panel controls first officer’s displays.
BOTH ON 1 or 2:
- both pilot’s displays are set to the selected pilot’s EFIS control panel.
Note: When in the NORMAL position, a DISPLAYS CONTROL PANEL annunciation illuminates below the altitude indication showing a failure of the associated EFIS control panel.
Describe the alert associated with a DEU failure.
DSPLY SOURCE (amber) on the lower left corner of the PFD.
Note: If a DEU fails, the remaining DEU automatically supplies data to all six displays. A single DEU failure will continue to supply each pilot with flight instrument information from independent sources. If the displays are automatically or manually switched to a single DEU source, a “DSPLY SOURCE” annunciation illuminates on both PFDs below the Airspeed Indicator.
Explain what the PLI indicates.

Indicates pitch limit (stick shaker activation for existing flight conditions).
Locate on the PFD, the selected MCP altitude, airspeed, heading and V/S.
Commanded information is displayed in magenta on the PFD. Selected MCP speed and altitude commands are displayed on the top of the altitude and airspeed tapes. Commanded heading is displayed on the compass and the commanded vertical speed is displayed to the right of the altitude tape on a tape and pointer.
Explain the meaning of the Max Speed Bar (red and black) on the airspeed tape.

Bottom of the bar indicates the maximum speed as limited by the lowest of the following:
- Vmo/Mmo.
- landing gear placard speed.
- flap placard speed.
Explain the meaning of the Min Speed Bar (red and black) on the airspeed tape.
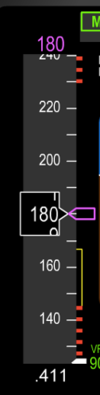
Top of bar indicates the speed at which stick shaker occurs.
Explain the meaning of the Speed Trend Vector.

Tip of green arrow indicates predicted airspeed in the next 10 seconds based on the current airspeed and acceleration or deceleration.
Explain the meaning of the Maximum Maneuver Speed Bar (amber) when flaps are not up.

When flaps are not up, bottom of the bar indicates flap limit placard speed for the next normal flap setting. The display logic is based on a normal flap setting sequence of 1, 5, 15, 30. The bar is removed when the flap lever is moved to the landing flap selected on the APPROACH REF page or when the flap lever is moved to flaps 40.
Explain the meaning of the Maximum Maneuver Speed Bar (amber) when flaps are up.

Bottom of the bar indicates the airspeed that provides a 1.3g maneuver margin to high speed buffet. May be displayed at high altitude with flaps up, at relatively high gross weights.
Explain the meaning of the Minimum Maneuver Speed Bar (amber) with the flaps extended.

Top of bar indicates minimum maneuver speed.
Recall the speed of the single white bug displayed during takeoff.

V2+15.
Note: The maneuver speed provides margin to stick shaker for an inadvertent 15 degree overshoot beyond the normal 25 degree angle of bank.
Explain when the single white bug is displayed during approach.

Single white bug is displayed after selection of VREF in the FMC.
Recall the speed of the single white bug during approach.

VREF +20.
Note: Displayed after selection of VREF. Indicates target airspeed in the event an engine is lost during approach.
Describe the PFD Radio Altitude display.

Displays current radio altitude on the bottom of the attitude indicator:
- displayed below 2500 feet AGL.
- box highlighted white for 10 seconds upon
descent below 2500 feet.
- turns amber when below radio altitude minimums.
Describe the Landing Altitude Indication (amber) at the bottom of the altitude tape.

- The cross hatched area indicates the FMC landing altitude for the destination runway or airport, or
- The landing altitude for departure runway or airport.
Describe the PFD Vertical Speed Indications.

Vertical Speed Pointer (white) – Indicates current vertical speed.
Selected Vertical Speed Bug (magenta) – Indicates the speed selected in the MCP vertical speed window with V/S pitch mode engaged.
Vertical speed (white) – Displays vertical speed when greater than 400 feet per minute. The display is located above the vertical speed indication when climbing and below when descending.
TCAS Vertical Speed Tape (red) – Tape turns red to indicate vertical speed values to avoid or exit during a TCAS resolution advisory. Vertical speed pointer is also red if it is within the vertical speed tape range.
Recall the location and purpose of the PFD Approach Reference indication.

- The Approach Reference indicator is displayed on the upper left-hand corner of the PFD.
- Displays the selected ILS/IAN identifier or frequency, approach front course, and ILS/DME/FMC distance and source annunciation.
Note: If the tuned ILS frequencies disagree, the frequency turns amber with an amber horizontal line through it. If the approach courses entered in the MCP disagree, the course turns amber with an amber horizontal line through it.
Explain the indications of a Resolution Advisory (RA) and where they are displayed.
- Aural directions such as “CLIMB, CLIMB” or “DESCEND, DESCEND”.
- Intruder aircraft symbol turns red, displayed on the ND in MAP, center MAP or VOR and APP modes.
- Avoidance maneuver area displayed in red on PFD.
- TCAS Vertical Speed Tape turns red to indicate vertical speed values to avoid or exit during a TCAS resolution advisory. Vertical speed pointer is red if it is within the vertical speed tape range.
Describe the slip/skid indicator.
Displaces beneath the bank pointer to indicate slip or skid:
- fills white at full scale deflection.
- turns amber if bank angle is 35 degrees or more; fills amber if the
slip/skid indication is also at full scale deflection.
Locate actual aircraft heading on the PFD and ND.

PFD – actual aircraft heading is under the white (inverted triangle) current heading pointer on the compass rose.
ND - actual aircraft heading is under the white (inverted triangle) current heading pointer on the outer edge of the compass rose (not in PLAN mode).
Describe where groundspeed and true airspeed are displayed.

Top left of ND when the EFIS selector is in the MAP, VOR, APP and PLAN modes.
Describe where wind direction and speed are displayed.

Top left of ND below GS / TAS.
Describe TCAS traffic displays and symbols.
TCAS Traffic Symbols – Indicates position of traffic targets. Displayed in MAP, center MAP, VOR and APP modes with TFC selected on the EFIS control panel.
Red Square – TCAS Resolution Advisory (RA).
Amber Circle – TCAS Traffic Advisory (TA).
White Diamond – TCAS Proximate traffic.
Arrow – Traffic climbing or descending at a rate greater than or equal to 500 fpm.
TRAFFIC – Displayed on the ND whenever a TCAS RA or TA is active, whether or not TFC is selected on the EFIS Control Panel.
OFFSCALE – Displayed whenever RA or TA traffic is outside ND range.












