Ch 10-Photosynthesis Flashcards
Explain the significance of photosynthesis to other living organisms
Photosynthesis is important to lving organismas because it is the number one source of oxygen in the atosphere. without photosynthesis, the carbon cycle could not occur, oxygen-requiring life would not survive and plants would die.

Describe the main structures involved in photosynthesis
Chloroplast
- found mainly in cells of mesophyll-interior tissue of the leaf
- outer and inner membrane
- stroma
- thylakoids
- grana or granum
Thylakoids
- internal compartment-thylakoid space-surrounded by thylakoid membranes
- chlorophyll resides in thylakoid membrane
- Stroma
Identify the substrates and products of photosynthesis
Substates
- Sunlight
- carbon dioxide
- water
Products
- Oxygen
- glucose
Explain how plant absorb energy from sunlight
light energy the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb the light. In plants, pigment molecules absorb only visible light for photosynthesis. The Visible light seen by humans as white light actually exists in a rainbow of colors.
Describe how and where photosynthesis takes place within a plant
Takes place in the mesophyll of the leaves, inside the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain disc-shaped structures called thylakoids, which ccontain the pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs certain portions of the visible spectrum and catures energy from sunlight.
List different photosynthetic pigments and describe their roles
- CHLOROPHYLL a
- key light-capturing pigment
- CHLOROPHYLL b
- accessory pigment
- Carotenoids
- accessory pigment
Describe photosystems
are complex arrangments of chlorophyll a with pigments, including clorophyll b, xanthophylls and carotenoids, which capture light energy to energize an electron removed from a water molecule. in plants, photosystems are located in the thykaloid membrane with in the chloroplast.
Describe different types of electron flow during light dependent reaction.
- Linear electron flow
- Primary pathway
- Involves both photosystems
- produces atp, nadph, and oxygen
- Cyclic electron flow
- involves only ps1
- produces only atp
- no oxygen releaseed
- found in purple sulfur bacteria
Describe the Calvin cycle
- Carbon fixation
- catalyzed by rubisco
- Reduction
- Regeneration of CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
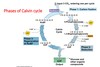
Define Carbon Fixation
The process by which photosynthetic organisms such as plants turn inorganis carbon into organic compounds
Explain Photorespiration
a respiratory process in many higher plants by which they take up oxygen in the light and give out some carbon dioxide, contrary to the general pattern of photosynthesis
Describe alternative mechanism of carbon fixation with examples
- C3 plants
- example- most of the plants
- C4 plants
- Minimize photorespiration by incorporating CO2 into 4-Carbon compounds, Catalyzed by enzyme PEP carboxylase
- ex-sugarcane
- Minimize photorespiration by incorporating CO2 into 4-Carbon compounds, Catalyzed by enzyme PEP carboxylase
- CAM plants (Crassulacean acid metabolism)
- Open stroma at night, incorporate CO2 into organic acids, stored in vacuoles
- ex- pineapple, succulent plants
- Open stroma at night, incorporate CO2 into organic acids, stored in vacuoles

