Ch. 1. Anatomy and organisation of the body Flashcards
Types of blood vessels
Arteries – carry blood away from heart Veins – return blood to the heart Capillaries – link arteries and veins
Abnormal immune mechanisms
undesirable responses of the immune system. Allergies as responses to antigens
Pelvic girdle:
two innominate bones and the sacrum
Types of blood cells
Erythrocytes – red blood cells – transport O2 and CO2 Leukocytes – white blood cells – protection of the body Platelets (thrombocytes) – cell fragments, play part in blood clotting
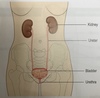
Urine
formed by kidneys. Consists of water and waste products (from protein breakdown – urea). Hormones from endocrine system influence kidneys to regulate water balance, blood pH. Bladder stores urine until it is excreted during micturition.
Capillaries
link arteries and veins – tiny blood vessels, very thin walls made of one layer of cells which enables exchange of substances between blood and body tissues
Survival of the species
depends on successful reproduction, involves fusion of male and female sex cell (sexual reproduction). Individuals with most advantageous genetic make-up are most likely to survive (natural selection, survival of the fittest)
Heart
involuntary muscular sac with four chambers, pumps blood round the body and maintains blood pressure. Beats 65-75 times per minute.
Lungs
pulmonary circulation, oxygen absorbed, and CO2 excreted Nitrogen in the air is not used by the body
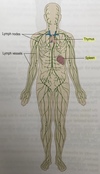
Lymphatic system organs
Spleen and thymus
Complications
other consequences that might arise if the disease progresses
Cranical cavity
contains the brain. It containes: Anteriorly – 1 frontal bone Laterally – 2 temporal bones Posteriorly – 1 occipital bone Superiorly – 2 parietal bones Inferiorly – 1 shenoid and 1 ethmoid bone and parts of frontal, temporal, and occipital bones
Three body planes
Median plane Frontal (coronal) plane Transverse plane


Thoracic cage functions
Protects thorax, heart, lungs, large blood vessels Forms joints between upper limbs and axial skeleton. The upper part of sternum (manubrium) articulates with the clavicles Intercostal muscle occupies spaces between the ribs Diaphragm is dome-shaped muscle that separates thoracic and abdominal cavities
Anatomy
Study of structure of the body and physical relationships between its parts
Alveoli
are surrounded by tiny capillaries, where the gas exchange between lungs and blood takes place
Special senses
stimulation of specialised receptors in sensory organs gives rise to sensation of sight, hearing, balance, smell, and taste.
Motor or efferent nerves
transmits signals from brain to effector organs (muscles and glands)
Urinary system ageing
Fewer nephrons, lower glomerular filtration rate Less able to regulate fluid balance
Thoracic cavity
in the upper part of the trunk, it containes: Anteriorly – sternum and coastal cartilages of the ribs Laterally – 12 pairs of ribs and intercostal muscles Posteriorly – structures forming root of the neck Inferiorly – diaphragm Main organs contained within: trachea, 2 bonchi, 2 lungs, heart, aorta, superior and inferior venae cavae, oesophagus, lymph vessels, lymph nodes The mediastinum – space between the lungs
Lymph nodes
filter lymph, removing microbes and other materials Site of formation and maturation of lymphocytes (white blood cells)
Special senses - Brain
initiates response with electrical impulses in motor (efferent) nerves to effector organs, muscles, and glands
causes of diseases:
Genetic abnormalities (inherites or acquired) Infection (by bacteria, viruses, microbes, parasites) Chemicals Ionising radiation Physical trauma Degeneration (excessive use or ageing)
What does blood consists of
consists of plasma and blood cells
Abdominal cavity
Largest body cavity, oval, its boundaries are: - Superiorly – the diaphragm - Anteriorly – muscles forming the anterior abdominal wall - Laterally – lower ribs and parts of muscles of the abdominal wall - Inferiorly – it is continuous with pelvic cavity Occupied by organs and glands of the digestive system (stomach, small intestine, most of large intestine, liver, gall bladder, bile ducts, and pancreas) Other structures (spleen, 2 kidneys and upper part of the ureters, 2 adrenal (suprarenal) glands)
Nerve communication
Communication along nerve fibres(cells) by electrical impulses, generated when nerve endings are stimulated
Epidermis
composed of several layers of cells that grow towards the surface from deepest layer. The skin surface consists of dead flattened cells that are constantly being rubbed off and replaced from below.


Communication systems
receive, collate, and respond to info that comes from the body (internally) or the environment (externally)


Peripheral nervous system
network of nerve fibres
Sensory or afferent nerves
transmit signals from body to the brain. The info is analysed and collated
Oxygen intake journey
Air passes through nasal cavity, the pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), the trachea, two bronchi (one bronchus per lung) and a large number of bronchial passages which end in alveoli (millions of tiny air sacs in each lung).
Digestive system
breaks down food so it can be absorbed into the circulation and then used by body cells. Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs.
Endocrine glands
detect and respond to levels of substances in blood by negative feedback mechanism
Vertebral column is split into 5 parts:
7 cervical (first one is called the atlas, forms a joint (articulates) with the skull) 12 thoracic (less movement possible than in the cervical and lumbar regions) 5 lumbar 1 sacrum (5 fused bones) 1 coccyx (4 fused bones)


Lymph vessels
with pores in the walls larger than in blood vessels
Systems
number of organs and tissues that contribute to one or more survival needs (digestive system)
Fertilisation
when female ovum fuses with spermatozoon. The fertilised ovum (zygote) then passes to uterus, embeds itself in the urine wall and grows to maturity during maturity (gestation) in 40 weeks.
Each lower limb
1 femur, 1 tibia, 1 fibula, 1 patella, 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsal bones, 14 phalanges


How many organs are in human body?
around 80
Tissues
formed by cells with similar structures and functions
Aetiology
causes of diseases:
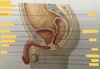
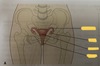
Pelvic cavity
- Superiorly – continous with the abdominal cavity - Anteriorly – pubic bones - Posteriorly – sacrum and coccyx - Laterally – innominate bones - Inferiorly – muscles of the pelvic floor Sigmoid colon, rectum, anus Some loops of the samll intestine Urinary bladder, lower parts of ureters and urethra Female reproductive organs – uterus, uterine tubes, ovaries, vagina Mele reproductive organs – prostate gland, seminal vesicles, spermatic cords, deferent ducts (vasa deferentia), ejaculatory ducts and the urethra
Pathogenesis
nature of the disease process and its effect on normal body functioning
What’s in plasma
90% water, substances dissolved or suspended in it (nutrients absorbed from alimentary canal, oxygen, chemicals e.g. hormones, waste materials)
Nerve cells
transmit electrical signs (nerve impulses)
Alimentary canal
9 m long tube, begins at the mouth and continues through pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum and anus


Transport systems
ensure all body cells are supplied with substances needed to support them (and waste excretion), (blood, cardiovascular system, lymphatic system)
Endocrine system
Discrete glands in different parts of the body, they secrete chemical messengers (hormones) to the blood, Slower than nervous system


Pathology
study of abnormalities



Special senses ageing
Ear – hair cells become damaged Eye – stiffening of the lens, cataracts (lens opacity) Taste and smell – diminishes Hearing impairment Glasses required for reading Bland taste, weaker smell
Cells
smallest independent units of living matter, often specialised (differentiated) to carry out a specific function
Accessory organs
salivary glands, pancreas, and liver. Salivary gland and pancreas produce and release digestive enzymes, while the liver secretes bile.
Nerves communicate by
releasing a chemical (neurotransmitter) into tiny gaps between them, Brain responds by sending impulses along motor (efferent) nerves to effector organ
Endocrine system ageing
Pancreatic islets – decline in function of B-cells Adrenal cortex – oestrogen deficiency More prone to type 2 diabetes, especially if overweight
Cardiovascular system ageing
Stiffening of blood vessels Reduction in cardiac function and efficiency Increased blood pressure, vessel rupture, and haemorrhage Reduction in cardiac output and reserve


Ageing
Kidney function begins to decline from 30 years of age Temperature regulation is less effective in infants and older adults Maximum efficiency is achieved during early adulthood Most organs are able to repair and replace their tissue with exception of brain and myocardium (heart muscle) Aging is associated with decreasing organ efficiency and increasing frailty At maturity many organs have functional reserve (spare capacity) which declines gradually, which allows for some decline before loss of function occurs Influenced by poverty, lifestyle choices (lack of exercise, smoking, alcohol misuse) Greying of hair and wrinkling of skin Increasing age is a risk factor for some diseases: cancer, coronary heart disease, dementia We have an ageing population, increasing life expectancy will have impact on healthcare Important to implement early interventions and prevention
Skin
forms a physical barrier against invasion by microbes, chemicals, and dehydration. Consists of two layers: epidermis and dermis.
Chemical energy
is essential fuel for cellular activity.
Spinal cord
lies within the bones of the spinal column
Protection of the body against name 4
external environment (skin); microbial infection (resistance and immunity); Body movement; Survival of the species (reproduction and transmission of inherited characteristics)

shoulder girdle
consists of clavicle and a scapula
Specific defence mechanisms
body generates specific (immune) response against anything foreign (antigens – pollen, bacteria, microbes, cancer cells). Following exposure, a lifelong immunity against the same antigen often develops.
Verbal communication
sound produced in the larynx when expired air from lungs passes through and vibrates the vocal cords. Speech produced by coordinated use of larynx, cheeks, tongue, and lower jaw)
Transverse plane
horizontal section dividing the body into upper and lower parts (can be at any level)
How much blood is in adults
5-6 liters
Nervous system ageing
Control of precise movement diminishes Conduction rate of nerve impulses decreases More prone to falls Poorer control (vasodilation, vasoconstriction)


Frontal (coronal) plane
divides the body longitudinally into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections

The Skeleton
Forms cavities and fossae (depressions or hollows) that protect some structures, forms the joints, gives attachment to muscles



Physiology
How the body systems work
Reproductive system ageing
Female menopause Cessation of female reproductive ability Reduced fertility in males
Metabolism
overall chemical reactions in all body cells. Sources of energy are mainly carbs and fats (when low, proteins can be used.). Can be split into anabolism and catabolism
Somatic (common) senses
pain, touch, heat, cold
Reproduction
essential to ensure the continuation of a species. Ova (eggs) are produced by two ovaries. One ovum is released at monthly intervals and travels towards uterus in the uterine tube.
Pathophysiology
considers how abnormalities affect body functions (often causing illness)
Faeces
waste materials from digestive system excreted during defaecation, indigestible food residue which cannot be absorbed and microbes.
Non-verbal communication
(nodding of the head) stimulated under voluntary (conscious) control
Carbon dioxide
waste product of cellular metabolism. Dissolves in body fluids to make an acid solution, must be secreted in appropriate amounts to maintain normal pH. Most excreted during expiration via lungs.
Tumours
when abnormal cells escape normal growth controls and proliferate. Rate of their production exceeds that of normal cell death causing mass to develop (-oma)
Thoracic cage
12 thoracic vertebrae 12 pairs of ribs 1 sternum or breast bone
Inflammation
tissue response to any tissue damage (trauma, infection), (-itis)
Lymph
tissue fluid (material drained from tissue spaces, including plasma proteins, bacteria or cell debris), transported along lymph vessels, returned to the bloodstream near the heart
Vertebral column
24 movable bones (vertebrae) plus the sacrum and coccyx. Bodies of bones are separated from each other by intervertebral discs consisting of fibrocartilage.
Digestive system ageing
Loss of teeth Peristalsis reduced Decline in liver mass Difficulty chewing Constipation Reduced liver metabolism
Muscoskeletal system ageing
Thinning of bone Stiffening of cartilage and other connective tissue Increased risk of fractures Stiffening of the joints Osteoporosis
External communication
(special senses, verbal and non-verbal communication)
Median plane
body divided longitudinally through the midline into left and right halves
Nutrients absorbed following digestion
promote body function, cell building, growth, and repair (water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and mineral salts)
Vertebral column functions
protects spinal cord, each vertebra has a hole (vertebral foramen), the foramina form a canal in which the spinal cord lies, adjacent vertebrae form openings (intervertebral foramina) which protect the spinal nerves as they pass from the spinal cord
upper limb
consists of: 1 humerus, 1 radius, 1 ulna, 8 carpal bones, 5 metacarpal bones, 14 phalanges
Ingestion functions
maintenance of water balance, fuel for energy production (carbohydrates and fats), provision of building blocks for synthesis of large and complex molecules needed by the body
Degeneration
ageing, or when structure deteriorate
Prognosis
likely outcome


Appendicular skeleton
consists of shoulder girdles and upper limbs, pelvic girdle and lower limbs Functions: voluntary movement, protection of blood vessels and nerves
Internal communication
(nervous system, endocrine system)
Reproductive cycle
consists of phases associated with hormone level changes involving endocrine system. One cycle takes 28 days. At ovulation an ovum is released from one of the ovaries mid cycle.


Resistance and Immunity ageing
Declines Increased risk of infection Long healing times
Thrombosis, embolism and infarction
effects and consequences of abnormal changes in the blood or blood vessel walls
Cavities of the body
Body organs are contained and protected within four cavities
Oxygen
Necessary for chemical reactions that result in release of energy from nutrients.
Spermatozoa
are produced in large numbers by the two testes situated in the scrotum. Spermatozoa pass from each testis through the deferent duct (vas deferens) to the urethra.
Non-specific defence mechanisms
protects against any invaders, skin, sticky mucus, antimicrobial substance (gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid which kills most ingested microbes). If microbes succeeded to enter the body, other non-specific defence mechanisms are activated (complement and inflammatory response).
When ovum is not fertilised
When ovum is not fertilised, it’s expelled along with uterine lining as bleeding (menstruation).
Dermis
has tiny sweat glands that have little canals or ducts leading to the surface, Hairs grow from follicles in dermis. Rich in sensory nerve endings. Regulates body temperature.


Organs
built of different types of tissues, evolved to carry out a specific function


Respiratory system ageing
Less mucus produced Stiffening of ribcage Decline in respiratory reflexes Increased infections Reduced respiratory minute volume
Hormones
stimulate glands or tissues, influencing metabolic etc activities, regulating body growth and maturation. Many other tissues secrete hormones as their secondary function
Skull
cranium (which contains the brain) and the face. Composed of several bones, which develop separately but fuse together as they mature. Protects delicate structures, enables breathing and eating.


