Cellular Pathology: Ultrasonagraphy Flashcards
What is ultrasound?
- Sound waves with frequencies higher than the human audible range with the upper limit for this being around 20kHz

Explain the concept of the pulse echo principal
- The ultrasound probe has 2 main functions, to first emit a sound wave and then to receive the echoes from the original reflected wave which is used to produce an image
- Ultrasound waves are produced in pulses because the probe can’t emit and receive echoes at the same time

What happens to an ultrasound wave when it reaches a tissue boundary?
- Whenever the ultrasound wave passes through a tissue boundary it can be reflected or will pass through and continue propogating.
How does the density of a tissue affect how it reflects an ultrasound wave?
- Adjacent tissues with varying densities will reflect more of the sound wave, adjacent tissues with similar densities will reflect less
Why does fluid show up dark on an ultrasound image?
- There isn’t a lot of matter within fluid for the ultrasound waves to reflect off of so most of the waves travel through the fluid
- This results in a low amplitude which leads to a dark area being created on the ultrasound image

Why does bone/gas show up as light on an ultrasound image?
- Bone and gas are quite dense, there’s a lot of matter for the ultrasound waves to reflect off, so most of the waves are reflected back
- This results in a high amplitude which leads to a light area being created on the ultrasound image
What are some of the clinical applications of ultrasounds?
- Obstetrics (childbirth/midwifery)
- Gynaecology
- Abdominal
- Urinary
- Trauma - POCUS (point of care ultrasound)
- Cardiology

What are some of the advantages of ultrasound compared to other types of clincal imaging?
- No ionising radation
- Usually non invasive
- No documented side effect in humans
- Widely Accessible
- “real time” imaging
What are some of the disadvantages of ultrasound compared to other types of clincal imaging?
- Ultrasound image quality is highly dependant on patient habitus
- Effectiveness and accuracy are highly operator dependant
- Training is more resource intensive for departments compared to other departments
What is a potential risk of using ultrasound?
- Ultrasound can heat the tissue under the area where you are scanning
What is the major advantage of Ultrasound over X-ray/CT in obstetric Imaging?
- No ionising radiation is used
What are the 2 main obsteric ultrasound scans that are offered to preganant women in the UK?
- 12 week scan
- 20 week scan
What features of a foetus are detected during the 12 week scan?
- ‘Viability’
- Number of foetus’
- Gross anatomy of foetus
- Detectable major abnormalities
- Gives an accurate gestational age of the foetus.
What are some of the major foetal abnormalities that can be detected during the 12 week scan?
- Anencephaly - The absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp
- Omphalocele/Exomphalos - The intestines, liver and occasionally other organs remain outside of the abdomen in a sac
- Body stalk defect - The abdominal organs develop outside the abdominal cavity and remain attached directly to the placenta
- Cystic hygroma - A collection fluid-filled sacs known as cysts that result from a malformation in the lymphatic system

What are some other major abnormalities that can be detected during the 12 week scan?
- Blighted Ovum/Missed Miscarriage
- Molar pregnancy - Occurs when a non-viable fertilized egg implants in the uterus
What happens to the risk of miscarriage during a pregnancy as it approaches 12 weeks and goes beyond this time?
- The risk of miscarriage becomes extremely low

What is the overall frequency of down syndrome?
- About 3 per 2000 births.
What hapens to the frequency of down syndrome in a baby as the age of the mother increases?
- Frequency of down syndrome also increases
- Mother aged 20 has a 1:1500 chnace of birthing a baby with down syndrome while a mother aged 45 has a 1:50 chnace of birthing a baby with down syndrome
Explain how downs syndrome is screened for during the 12 week scan
- Fetal nuchal translucency (NT) screening uses ultrasound to measure the size of the nuchal pad at the nape of the fetal neck.
- This can is combined with a blood test

Explain how non-invasive prenatal testing will be able to test for down’s syndrome in the future
- Non-invasive prenatal test involves taking a blood sample from the mother
- This blood smaple is then used to detect presence of free-flowing foetal DNA within the maternal bloodstream
- This foetal DNA is then analysed to see if there are any genetic abnormalities such as downs syndrome

What things are detected/checked during the 20 week scan?
-
Abnormalities that:
- May indicate the baby has a life-limiting condition
- May benefit from antenatal treatment
- May require early intervention following delivery
- Placenta localisation
- Fetal Biometry -
- Fibroid Monitoring
- Liquor (amniotic fluid) Assessment
What measurements of the foetus are taken during the 20 week scan?
- Circumference of top of head
- Femur length
- Abdominal circumference
- Estimate of Weight - Femur lenght and abdominal circumference used to calculate estimate
What foetal abnormnalities can be identified during the 20 week scan?
- Spina bifida - Incomplete formation of the spine/spinal cord which creates a gap in the spine. Some spinal nerves can protrude through the gap creating a cyst.
- Achondroplasia - Genetic disorder that results in dwarfism
- Talipes (Club Foot)
- Low lying placenta (placenta previa)

How can looking at the brain during an ultrasound be used to diagnose spina bifida?
- If you identify a mishaped cerebellum (banana sign) then foetus may have spina bifida - cerebellum mishaped because it’s pulled down due to whole spinal cord also being pulled down
- Idents (lemon signs) in the head of the foetus are caused as a result of extra force pulling down on the head

What are some features of achondroplasia in a foetus?
- Frontal bossing
- Shorter long bones
- Thickened soft tissue surrounding the long bones
- Bowing (bending) of long bones

How can low lying placenta be diagnosed during the 20 week scan?
- Measure the distance from the lowest edge of the placenta to the internal OS of the cervix.
- If the placenta is within 2.5cm of the cervix then future scans are required.

What procedure may need to occur if the low lying placenta doesn’t raise closer to the due date?
- C-Section may be required
What are some of the resons why a baby may be born with club foot?
- Mechanical reasons - Baby may be in odd position, may not be a lot of fluid around the foot so it gets trapped in that position which wekaens tendons around ankle
- Chromosomal reasons - May be linked to downs syndrome, trisomy 13

How can talipes (club foort) be treated?
- Ponseti Method - Over a no. of years foot is gradually manipulatedf so it ends up in normal position. Brace/cast is placed on the baby’s foot after each round of manipulation
What other abnormalities can be diagnosed during the 20 week scan?
- Anhydramnios/Oligohydramnios - Lack of amniotic fluid
- Polyhydramnios - Excess amniotic fluid

What is one of the main causes of polyhyramnios?
- Gestational diabetes
What is the umbilical artery doppler assessment?
- A test that can be used to highlight the affects of pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)

What are some reasons why a woman may be referred to a early pregnancy (EPU) clinic?
- Lower abdominal/pelvic pain
- Bleeding
- Confirmed history of recurrent miscarriage and
- Previous obstetric history issues
In the case of an emergency at any point during a pregnancy, the woman needs to be checked for ectopic pregnancy, what is ectopic pregnancy?
- When a fertilised egg implants outside of the uterine cavity
What symptoms are associated with ectopic pregnancy and what can cause it?
- Symptoms: Severe pain and bleeding
- Causes: Tubal damage (from surgery, PIDS, endometriosis)

During an ultrasound scan how can you tell if a set of twins are dichrorionic (have seperate inner sacs) or monochorionic (share the same inner sac)?
- Dichorionic twins can be identified by the presence of lambda sign
- Monochorionic twins can be identified by the presence of the T sign

Although 3D/4D ultrasound scans don’t have much diagnostic value what can they be sued for in terms of diagnosis?
- They can be used to give parents a better visualisation of what cleft lip will look like

Name some of the interventional procedures that are ultrasound-guided?
- CVS (chorionic villus smapling) - take a sample of the placenta
- Amniocentisis - take a sample of the amniotic fluid

What are fibroids?
- Masses of benign fibrous tissue that develop around the uterus and grow until the blood supply they receive can no longer support further growth.
- Some can get very large and require surgical interventions

Ultrasound scans can be used to diagnose the cause of post menopausal bleeding. What are some of the causes of post menopausal bleeding?
- Uterine polyps - Growths from the inner wall of the uterus which extend throughout the cavity and into the cervix and vagina. Usually benign but on rare occasion some can turn cancerous.
- Endometrial cancer
- Ovarian cancer

What organs are usually scanned during an abdominal ultrasound scan?
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Abdominal aorta
- Pancreas
- Spleen
- Gallbladder / Biliary Tree
Aortic screens can be conducted as part of an abdominal scan. What are aortic screens used to diagnose?
- Used to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysim
When is an abdominal aorta considered aneurysmal?
- When it reaches 3cm in AP diameter

How can aortic aneuryism be treated?
- A stent (metal mesh) can be placed around the area of aneuryism which help support the aorta in that area
- These stents have tubes (limbs) which allow for blood to continue to flow

What other conditions can an abdominal ultrasound scan be used to diagnose?
- Cirrhosis of the liver/ascites
- Gallstones
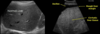
What are gallstones and what are they caused by?
- Gallstones are small stones composed of bile components that form in the gallbladder
- Caused by an imbalance in the chemical make up within the bile in the Gallbladder (high cholesterol / bilirubin)

What conditions can a urinary ultrasound scan be sued to diagnose?
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Enlarged prostate
- Ectopic kidney
- Renal calculi (Kidney stones)

What conditions can a testicular ultrasound scan be sued to diagnose?
- Varicocele
- Hydrocele
- Testicular cancer
- Simple cyst

Why is ultrasound especially useful for breast scans for women under the age of 35?
- Under the age of 35 breast tissue tends to be denser, leading to difficulty with diagnosing the nature of breast lumps on mammograms
- This is because differentiation between solid and fluid filled areas is relatively poor
- Ultrasound can make the differentiation at an improved rate (about 30% increased)
What vascular conditions can a testicular ultrasound scan be used to diagnose?
- Ultrasound used to exclude or confirm the presence of a deep vein thrombosis in cases of pain and swelling in the lower limbs
How can ultrasound be used to diagnose deep vein thrombosis?
- A technique called colour flow doppler is used to check the blood flow in particular lower limb arteries/veins such as the femoral vein
- If the vein/artery shows up as black then it means that it’s completely occluded as it means there’s no blood flowing in that region

What are some applications of Musculo-Skeletal Ultrasound (MSK)?
- Can be used to identify:
- Muscle/tendon tears
- Inflammation
- Nerve Entrapments
- Soft tissue lumps
- Cysts
- Hernias
FAST (Focused Assessment with Sonography of Trauma) is conducted as a part of POCUS (point of care ultrasound) what is FAST?
- FAST is is an ultrasound scan protocol undertaken at the time of presentation of a trauma patient.
- It involves using ultrasound to scan the chest, as well as the top, side and bottom of the abdomen and look for the presence of free fluid (e.g. blood) around the liver, kidneys or heart