Cellular pathology: Microscopy Flashcards
What is microscopy?
- Using microscopes to view objects/specimens that are not visible to the naked eye
What are the different parts of a microscope?
- Detector
- Objective (± immersion medium)
- Specimen (Cover glass)
- Light conditioning system (e.g. phase ring, Kohler illumination)
- Light source (Halogen, XBO)

When using a live specimen for microscopy, why do C02 and temperature need to be controlled?
- Because any change in ambient temperature lead to thermal extension or contraction in microscope objective and stage which chnages plane of focus
- Also prevents live specimen from dying under microscope
How can temperature and C02 be controlled during microscopy?
- You use an incubator box with a precision air heater that allows you to adjust temperature, and a controller which allows you to airflow and % C02
- Box also has openings which allow access to microscope

What problems can arise when trying to view something under a microscope for hours/days?
- Maintaining stability and viability of sample will be difficult
- Being able to see different parts of the sample over an extended period of time requires complex systems

What problems can arise when trying to view something under a microscope for seconds/minutes?
- Objectives may not have the quality to capture things that happen at high speeds
- Distinguishing the sample from the surronding when things move at speeds

What are the 3 elements of the “triangle of frustration” for microscopy?
- Temporal resolution - Amount of time to needed to capture a particular image
- Spatial resolution - No. of pixels used to construct a digital image
- Sensitivity - Ability to pick up image in lower light conditions

During microscopy there is usually a trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution when trying to capture an image, why is this?
- If you’re capturing something that happens really quickly on the microscope in order to capture the entire process you’ll need to sacrifice spatial resolution, bigger pixels and less detail but you’ll
- However, if you’re capturing something that’s still or not living you can have high spatial resolution, smaller pixels and high detail, but have low temporal resolution because you’re constantly capturing the same image

The objective of a microscope has a no. of different markings on it that denote different things. What are these markings and what do they mean?
- Magnification -
- Application
- Coverslip thickness (mm) - Maximum thickness of coverslip
- Immersion medium - Which medium this objective has been calibrated for
- Numerical aperture - The range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light

What affect does numerical aperture have on resolution?
- The aperture of the objective determines the resolution. The higher the numerical aperture the better the resolution power of the objective

Why does a higher numerical aperture result in a higher resolution power?
- Higher numerical aperture means the objective is able to accept more light it concentrates light in a specific way to give a ‘crisper’ image
Describe some specific characteristics of light microscopy
- Can be used to view samples ranging from tissues to cells.
- Light microscopes have rings and lenses that allow light from light source to be modified before it reaches sample

There are different techniques that can be used in light microscopy that change the way a smaple is viewed under a microscope. Name some of these techniques
- Bright-field - Simpliest technique, no filter required so full light reaches sample/objective
- DIC (Differential interference contrast) - Creates illusion of 3 dimensionality and enhances contrast between background and sample
- Phase contrast - Converts phase shifts in light passing through specimen into changes in brightness. Useful for tissue and cells that are changing shape.

What different things can light microscopy be used to view?
- Histology
- Cell morphology (phase contrast)
- Cell differentiation, cell migration (Time-lapse)
What is the advanatge of using light microscopy for histology?
- Allows you to view the whole tissue and shows you geographically what is happening in the tissue
What is the disdvanatge of using light microscopy for histology?
- It doesn’t give you enough detail on what each individual cell within a tissue is doing
How can you use light microscopy to see what each cell within a tissue is doing in more detail?
- You can use Immunohistochemistry
- It involves injecting antibodies into a particular tissue to locate where a specific protein, containing antigens for these antibodies, is located within the tissue
- Once the parts of the tissue that contain the protein have been identified you can use laser capture microdissection to seperate area with particular protein from area that doesn’t contain it

How can light microscopy be used to create a time-laspse effect when viewing live specimens?
- An incubator box is used to control CO2 and temperature to keep live specimen alive
- As the specimen moves around the stage of th microscope can alos move so that the specimen is being constantly captured by the microscope
- Alternatively, you can just capture the same part of the live specimen on diferent days to creat time-lapse effect
Briefly describe the structure of an electron microscope
- You have an electron source which produces electron beam - electron source replaces light source
- Electron microscope also has elctromagentic lense which modifies electron beam (similar to light conditioning system of light microscope)
- Electron microscope has viewing screen which allows you to view image of specimen

Why do images produced by electron microscopes have lighter and darker sections?
- Dark areas of image are where electrons have more difficulty passing through the specimen as it’s more dense in that area
- Lighter areas of image are where electrons have less difficulty passing through specimen as it’s les dense in that area

What are the 2 types of electron microscopy?
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
What is the difference in the mechansisms of transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy?
- In transmission electron microscopy a beam of electrons is transmitted through a speciment to produce an image
- In scanning electron micrsocopy electrons formed from interaction of electrons with atoms within specimen (secondary electrons) are also detected which allows for surface to be scanned and 3-D image to be produced

Briefly describe the mechanism of fluorescent microscopy
- Fluorescence light source emits light
- Fluorescence filter cube modifies light so only light at particular wavelength reaches specimen
- Specimen is modified so that when light reaches it reflects a particular wavelength of light back at oculars, a camera or a photomultiplier which produce digital image

What are the main differences between light microscope and fluorescent microscope?
- Light source is positioned differently on fluorescent microscope compared to light microscope
- fluorescent microscope contains fluorecence filter cube

What is fluorescence?
- The ability of certain types of molecules to absorb light, become excited and then generate and emit energy.

Can molecules constantly produce fluorescence?
- In a vaccum molecules can constantly fluoresce
- However, molecules in an environment can’t constantly fluoresce because eventually lead to the molecule getting destroyed due to energy loss
Explain the concept of the stokes shift
- The stokes shift is the difference between the wavelength of light that excites the molecule and the wavelength of light that’s emitted
- Wavelength of light that excites molecule always smaller than wavelength of light that’s emitted due to energy loss experienced by the molecule

What is the name of the process in which molecules that are able to fluoresce loose that ability?
- This process is called photobleaching
Explain how fluorescent proteins can be used for the live study of fluorescent tags in living cells/organisms
- Gene responsible for encoding fluorescent protein can be fused with gene that encodes preotein of interest. Genes can be placed in plasmid and introduced in cells via transfection.
- This results in cells producing fluorescent protein of interest when they express protein
- This process is called protein fusion

Explain how antibodies can be used or the live study of fluorescent tags in living cells/organisms
- Antibodies are normally able to recognise specific proteins (antigens)
- So specific antibodies for protein they can attach to a molecule that gives off colour (fluorophore).
Give an example of a fluorescent protein
- Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
Briefly describe the mechansim of confocal fluorescence microscopy
- Light source is a laser - allows you to control how light goes through specimen.
- light from laser is modified using dichroic mirrors before reaching specimen
- Light emitted from specimen is then detected using photomultiplier detector which produces digital image
- Also contains a detector pinhole aperture and a light source pinhole aperture
- These remove background light and allow you to see different levels of a specimen by controlling how far light travels through it
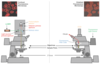
What are the advantages of using confocal fluorescence microscopy compared with widefield fluorescence microscopy?
- Higher z resolution and reduced out-of-focus blur make confocal images crisper and clearer
- Also allows for live imaging
What are the disadvantages of using confocal fluorescence microscopy compared with widefield fluorescence microscopy?
- Only a small volume can be visualised by confocal microscopes at once
- Bigger volumes more time consuming, as more sampling and image reassembling is needed


