Cell identification (Blood Smear) Flashcards
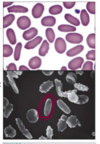
Identify the cells in this smear.
List the function of them.
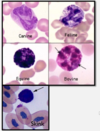
Basophils
- These are rare to find in circulation in a healthy animals.
Major Function: hypersensitivity, balance eosinophil reactions.
Identify the cell in this smear
List the major function, and any notable identifying features

Eosinophil
Major function- response to allergens, parasites, hypersensitivity.
Granulocyte with orange-red-pink staining granules; often round but more elongate in cats.
sighthounds have faded “grey eosinophils” (Do not confuse with toxic neutrophils)
Identify the cell in this smear.
List the major function, and any key identifying features

Heterophil
The cytoplasm contains numerous red-orange oval, needle, or rice-shaped granules.
In Birds and Reptiles, have these rather than neutrophils
These cells lack myeloperoxidase (breaks down exudate). This explains why birds have more of a caseous exudate in infections
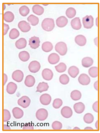
Identify the cell in this smear.
List the major function, and any key identifying features

Lymphocyte
Major function: immunogenic.
This is the predominant leukocyte in:
- adult ruminants (primary cell)
- some bird and reptile species.
Identification- thin rim of blue cytoplasm
Identify the cell in this smear.
List the major function, and any key identifying features

Monocyte
Major function: 2nd line of defense for infections, immunogenic
Typically a large cell witih cytoplasm that is blue to blue-gray,
** often vacuoles form in EDTA**
- Can be difficult to differentiate from immature neutrophils
Identify the cell in this smear.
List the major function, and any key identifying features

Immature Neutrophil
Major function: first line of defense against pathogenic bacteria.
Identification: the more basophilic staining cytoplasm= more RNA
-this is the most common leukocyte in healthy dogs, cats, horses, primates
The more common immature neutrophils are, is indicative of how intense the tissue demand is.
Identify this cell
List the major functions as well as any key identifying features

Mature neutrophil
Function: first line of defense against pathogenic bacteria.
This is the most numerous leukocyte in healthy dogs, cats, horses, primates.
Incraesed WBC on a smear
Leukocytosis
Decreased WBC concentration on Smear
Leukopenia
What are granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
these have segmented nucleus
Leukocytes with cytoplasmic granules may or may not be visible
What is Pelger-Huet Anomally

This is an inherited blood condition, where the nuclei of several types of white blood cells have hyposegmentation with band or peanut shape with mature nuclear chromatin
- the image here is from a neutrophil affected by this condition
- Can be mistaken for bands leading to misdiagnosis of inflammation and/or infection
Seen in Australian Shepherds, foxhounds, Samoyeds and mixed breed dogs
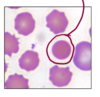
Identify this cell type
List any key identifying features as well as additional important information

These cells with the long arrow are aggregate reticulocytes.
These cells correspond to polychromatophils on blood smear stained with Wright’s type stain.
These cells are found in circulation in response to a regenerative anemia.
List the name of this cell on a smear
Include the major function, or any key features of this cell type

Punctate Reticulocyte
These cells persist in circulation for several weeks-> therefore not a good indicator of current regenerative response
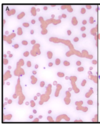
Identify the features of this cell on a smear
list the key functions, or conditions it is seen in
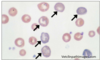
Basophilic Stippling
- Spontaneous aggregation of ribosomal RNA in RBC cytoplasm
This may be seen with:
- regeneration (especially in ruminants)
- Lead poisioning (also would expect an increased number of nucleated RBC)
Identify the type of cell on the smear
Include any major functions, or conditions associated with this type of cell.

Echinocytes (“Crenated Cell” or “Burr cells”)
These are spiculated RBC with evenly distributed, short projections
Artifactual causes: Excess EDTA, RBC dehydration, Increased pH, Aged blood
Disease processes: Electrolyte depletion from sweating diarrhea etc. Renal Disease, PK deficiency, snake envenomation
-Most commonly artifactual, but it is worth noting