Cell Adaptation Flashcards
Occurs when the cell homeostasis is distorted by stresses or pathologic stimuli
Cell adaptation
Tendency to stability in the normal body states of the organism; it is the ability to maintain equilibrium by adjusting its physiological processes
Homeostasis
True or False: Cell Adaptation is a reversible change
TRUE
True or False: In cell adaptation, cells preserve viability and function
TRUE
What are the principle responses of adaptation?
- Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3. Hyperplasia 4. Metaplasia 5. Dysplasia
Decrease in size abd/or number of the cells and their metabolic activity after normal growth has been reached.
Cells are not dead.

Atrophy

Atrophy is a _____ in protein synthesis and an ______ in protein degradation in cells
Atrophy is a decrease in protein synthesis and an increase in protein degradation of cells
Causes of Atrophy
- Decrease work load
- Denervation
- Decreased blood spply or oxygen
- Inadequate nutrition
- Loss of endocrine stimulation
- Aging
- Muscle disuse in a limb that is in a cast
- Sedentary
- Atrophy of adrenal cortex by reduction of ACTH stimulation [steroid therapy]
- Atrophy in tissues adjacent to a tumor due to pressure an compromised blood supply
Examples of Atrophy
Identify
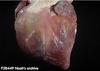
Serous Atrophy of fat
Increased size of cells and their functions
- synthesis of more organelles and structural proteins: bigger cells
Hypertrophy
Where is hypertrophy more common?
In cells with little replication
[stable or permanent cells: cardiomyocytes, neurons]
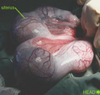
Hypertrophic pregnant uterus
9example of physiologic hypertrophy]
Examples of Pathologic Hypertrophy
Cardiac hypertrophy from hypertension or aortic valve disease
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
the shape of the heart becomes globulus





