Bridges - Endocrine Pancreas Flashcards
What is gluconeogenesis?
- Use of amino acids and fatty acids to generate glucose in the liver
- Stimulated by GLUCAGON
How does glucose uptake happen in different tissues?
-
Passive glucose uptake: brain, liver, kidneys
1. Higher concentration gradient outside the cell to a lower concentration inside the cell
2. In the liver, when you are making glucose, the opposite would be happening, i.e., spitting out glucose passively -
Stimulated glucose uptake: muscle, adipose (via GLUT-4 -> see attached image)
1. This is still PASSIVE transport -> you just need the transporter to enable this

What are the orders of fuel utilization in fasting and storage in the fed state?
- Energy production (fasting):
1. Creatine phosphate
2. Glycolysis
3. Glycogenolysis
4. Gluconeogenesis
5. Fat oxidation - Fuel storage (fed state):
1. Glucose uptake/oxidation
2. Glycogenesis
3. Lipogenesis
What are the responses to overfeeding?
- Most of this carbohydrate oxidation is going to occur in the muscle
- Liver is more for storage than for ATP generation

Why is this image so important?

- Both insulin and C-peptide packaged in IC vesicles, and released at the same time. If you had a defect in this enzyme, you would effectively be T1D
- If you want to know insulin production in someone taking exogenous insulin, you can measure the C PEPTIDE to see how much insulin they are making
What are the key pancreatic cells? What hormones do they release?
- Beta: insulin
- Alpha: glucagon
- Delta: somatostatin
- Ductal: exocrine

What are the functions of insulin?
- Promotes uptake of glucose from blood into muscle and adipose tissue
- Enhances synthesis of glycogen and TGs in liver, adipose, and muscle tissue
- INH gluconeogenesis from non-glucose precursors like amino acids and lipids
- Promotes glucose breakdown, and prevents lipid breakdown
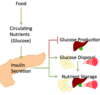
What causes insulin secretion (molecular pathway: iamge)?

What is this?

Pancreatic insulin with glucagon (red) and insulin (green) staining
What are the phases of insulin secretion?
- BIPHASIC
1. First phase: release of pre-packaged insulin
2. Second phase: need to make and release more insulin

How does insulin stimulate GLUT-4 translocation?
Akt

How does insulin promote glycogenesis?
- Allosteric activation
- Protein dephosphorylation: synthase (more active) and phosphorylase (less active)
How does insulin reduce gluconeogenesis?
- FBPase negatively regulated by F-2,6-BP
- PEPCK and G6Pase (first two enzymes) inhibited by insulin:
1. Allosterically
2. Protein phosphorylation
3. Transcriptionally repressed: Akt on FOXO (post-translational changes much faster than transcriptional ones)

How is glucagon released? What does it do?
- Secreted from alpha-cells of pancreas
- Released by low blood sugar levels
- Acts primarily on LIVER, not muscle or fat
1. Gluconeogenesis
What is the central transducer of glucagon signaling?
PKA: phosphorylates synthase (inactivating it) and phosphorylase kinase (which phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase, activating it)

How does glucagon promote gluconeogenesis in the short-term?
- Inactivation of phosphofructokinase-2, which normally generates the carbohydrate fructose-2,6,-bisphosphate, a positive regulator of glycolysis and a negative regulator of gluconeogenesis
1. Remember: insulin INC F-2,6-BP - The alleviation of this inhibition allows for promotion of the gluconeogenic metabolism

How does glucagon INC gluconeogenesis via transcription?
- More G6Pase, FBPase, and PEPCK

How are insulin and glucagon cleared by the body?
- Short 1/2 lives: Insulin 5 min, Glucagon 5-10 min
-
Insulin degradation: 80% in liver, kidney, and the rest in other tissues (target and non-target tissues)
1. Insulinase: insulin protease that may act when insulin-insulin receptor is internalized
2. Possible site of drugs to prolong insulin life, and make limited supply last longer - Glucagon degradation: most in liver (peripheral concentrations are low)
What does insulin do?
- Blocks gluconeogenesis
- Block glycogenolysis
- Promotes glycogenesis
- Enhances glucose uptake
- Promotes lipid storage
What does glucagon do?
- Promotes gluconeogenesis
- Promotes glycolysis
- Promotes glycogenolysis
- NOT really active in muscle and fat
What happens to glucose/insulin/glucagon after a meal?
- First: glucose goes up (food)
- Insulin INC in response to glucose
- Glucose levels drop
- Glucagon levels DEC as glucose levels are high, then INC as normoglycemia returns
How does the ANS regulate glucagon/insulin?
- SYM: INC glucagon, DEC insulin
- PARA: INC insulin, DEC glucagon

What factors are involved in long-term glucoregulation (graph)?
- As blood glucose drops, these changes are going to happen
- GH and cortisol are adaptations to chronic hypoglycemia (starvation)

What are the incretins? What do they do?
- Enhancers of insulin release (this is why the red curve is so much higher than the blue curve in the graph on the left) -> GUT
- Sensitize the beta cells to secrete more insulin
- DPP-4 degrades GLP-1 and GIP
1. What would it do to insulin and glucose? DEC insulin, INC glucose; also a drug target (e.g., Sitagliptin)



