BODY Flashcards
quadrate lobe
segment IV
caudate lobe
segment 1
hot quadrate sign
SVC obstruction
hot spot in segment 1
Budd-Chiari
dorsal pancreatic duct
Santorini
ventral pancreatic duct
Wirsung
entrance air kerma for abdominal radiograph
3 mGy
MC duodenal malignancy
adenocarcinoma

HIV cholangiopathy papillary stenosis
4 phases of renal contrast
- non-contrast
- corticomedullary
- nephrographic
- excretory (pyelographic)

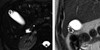
pancreas divisum
- main pancreatic duct (solid arrow, Santorini) drains into minor papilla
- CBD and smaller ventral duct (Wirsung, curved arrow) drain inferiorly into major papilla
caudate lobe hypertrophy
- Budd Chiari
- PSC
- PBC

- clover leaf sign
- healed peptic ulcer of duodenal bulb
MC locations of GIST
stomach > duodenum > anorectum
median survival after successful surgical resection of pancreatic cancer
1.5 years

septate uterus
- horizontal/normal uterine fundal contour

bicornuate uterus
- heart-shaped fundus, with indentation of outer contour
MC associated abnormality with Mullerian Duct Anomalies
- ipsilateral renal agenesis

goblet sign
- urothelial neoplasm
MC MDA
septate uterus
Zuckerkandl fascia
posterior perirenal fascia
Gerota fascia
anterior perirenal fascia
epiphrenic diverticula usually occur on which side?
right

cone shaped cecum
- Entamoeba histolytica