Block 2 Dr. Burns Flashcards
Sickle Cell Disease (Case II)
- Low Hemoglobin
- High Reticulocytes
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Blood Film (a) Show sickled erythrocytes.
- Bony infarctions can cause unequal finger length
Prognosis:
- High Likelihood of crises necessitating hospital admission, transfussion, prophylactic penicillin
Facts:
- 1 in 365 African americans
- 1 in 16, 300 Hispanic Americans
- Autosmal Recessive
- Caused by a A -> T transversion in the HBB encoding B-Globin
- Amino Acid 6: Glutamic Acid (E) -> Valine (V) . E6V
- Results in abnormal hemoglobin (HbS)
- Normal adult Hemoglobin in HbA
- Results in abnormal hemoglobin (HbS)
Clinical Presentation:
- Presents within first 2 years
- Severe Hemolysis
- Crises lastin 5 to 7 days
- Hemolytic Anemia, failure to thrive, ,splenomegaly
- Painful swelling of hands/feet ( occlusion of Capillaries.
- Repeated Infections
- Infection is a major cause of Death.
Treatments:
- Hydroxyurea
- Supporting including O2 Transfussion, Penicillin
Co-Occurrence of the Sickle Cell Allele and Malaria
The Sickle Cell allele provides protection to newborn babies and young todlers agains malaria. Approximatelly 90 % of newborns die of maleria, but the sickle cell allele protect them from the parasite malaria.
Sickle Cell Trait
- Heterozygotes (ie. Carries)
- Trait: generally healthy but may be symptomatic under stressful conditions
- 8- 10% African Americans
- ~ 25% in West Africa.
- Individuals do generally have a sub-clinical anemia that can be detected in a complete blood count (CBC)

Restriction Endonucleases.
DNA Nucleases
- Digest DNA
- Cleave Phosphodiester bondes between nucleoties.
- Exonucleases digest from an end
- Endonucleases digest at an internal site.
Restriction Endonucleases
Restrictions Enzymes
- Recognize a specific DNA sequence and cleave a phosphodiester bond in both strands within that sequence.
-
Highly Specific.
- Always cleaves at the same Short DNA sequence.
- Only cleaves within that 4-8 bp sequence.
- Biological Role in bacterias as a component of the restriction/ Modification system.
- A Bacterial defence mechanism against bacteriophage

Restriction Endonucleases
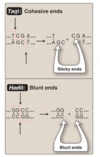
Sticky Ends/Cohesive Endes.
- The restriction enzyme produces a staggered cut generating a 3’ or 5’ single-stranded overhang
- The overhangs can anneal with the complimentary overhang from another end (They are Sticky)
Blunt Ends:
- The restriction enzyme cuts both strands at the same position so no overhang is generated.
Restriction Fragments.
Electrophoresis
- Digestion of a DNA sample with a restriction enyme
- Separation by gel electrophoresis
- Staining of DNA with a RED fluorescent dye.

The Sickle Cell Mutation Alters……
A restriction Site
- Wild-type allele (BA ) contains an MstII recognition frequence
- Mutant allele (BS) does’nt
- So we can use MstII to distinguish the alleles
- This could be the basis for a genetic test to genotype individuals and make a diagnosis.

Hybridization Assays
A Nucleic acid probe of know sequence is used to detect the specific complementary sequence within a complex sample of target nucleic acid.

Hybridization Stringency
- Stringency: the degree to which non complementary sequences are tolerated during hybridization.
- The higher the stringency the fewer mismatches will be tolerated.
- Some applications require high stringency.
- E.g. Detecting a point mutation, a “ perfect match” is necessary.
- Others require a low stringency
- E.g. Identifying multiple genes in a gene family, “ mismatches” are tolerated.
- Stringency is determined by hybridization conditions:
- Temperature
- Salt concentration
- Denaturing Agents (Formamide)
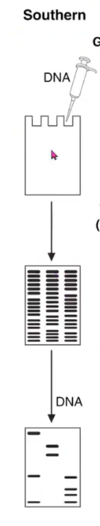
Southern Blootting
- DNA target separated by gel electrophoresis
- Transferred onto membrane
- Detection of the DNA target using complementary DNA probe
Northern Blotting
- RNA target separated by gel electrophoresis
- Transferred onto membrane
- Detection of the RNA target using complementary DNA probe.

Western Blotting;
- Protein target separated by gel electrophoresis
- Transferred onto membrane
- Detection of the protein target using antibodies agains protein.



