Biopsychology - Advanced Information Flashcards
What is the nervous system?
Specialised network of cells.
Primary internal communication system
Two Main Functions:
- Collect,process and respond to info and environment
- Coordinate working of different organs and cells in the body
Divided into CNS and PNS
Draw and label the subdidivisions of the nervous system
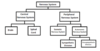
What is the CNS?
Made up of brain and spinal cord
What is the brain as part of the CNS?
- Centre of all concious awareness.
- Cerebral cortex (outer layer) highly develpoed and is what distinguishes higher mental functions from animals.
- Two hemispheres
What is the spinal cord as part of the CNS?
- Extension of the brain.
- Repsonsible for relflex actions
- Passes messages to and from brain and connects nerves to PNS
What is the PNS?
Transmits messages via millions of neurones to and from CNS.
What is the PNS divided into?
Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System (ANS & SNS)
What is the ANS?
- Involuntary system governs vital functions in body e.g. breathing, heart rate, digestion etc.
- Controls smoth muscles and glands.
- Control centre for this in brain stem
- Contains only motor pathways
- Subdivided into sympathetic and parasympathetic
What is the SNS?
- Under concious control.
- Controls muscle movement and recieves info from sensory receptors
- Controls skeletal muscles and movement .
- Control centres are in motor cortex.
- Contains sensory and motor pathways.
Describe the relationship of the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the ANS.
- Parasympathetic in opposition to sympathetic (actions are antagonistic)
- Acts as breaks and reduces activites of body that were increased by sympathetic branch
- ‘rest and digest’ response
What is the sympathertic branch responsible for?
- Increase HR
- Increases breathing rate
- Dilates pupils
- Inhibits digestion
- Inhibits saliva production
- Contracts rectum
What is the parasympthetic branch responsible for?
- Decrease HR
- Decreases breathing rate
- Constricts pupils
- Stimulates digestion
- Stimulates saliva production
- Relaxes rectum
What are neurons?
- Basic building blocks of nervous system - nerve cells that process and transmit messages through electrical and chemical impulses
- 100 billion neurons (80%) in brain
- Provide nervous system with its primary communication
Draw and label a typical neuron

What is the nucleus?
- Control centre of cell.
- Contains all chomosomal DNA
What is a dendrite?
- Receives nerve impulse/signal from adjacent neurons
What is an axon?
- Where the electrical signal passes along.
What is the myelin sheath?
- Insulate/protects axon from external influences that might effect transmission of nerve impulse down the axon.
What are the Nodes of Ranvier?
Speed up transmission of impulse by forcing it to ‘jump’
What are the terminal buttons?
- Send signals to an adjacent cell.
What is a sensory neuron?
- Carry messages from PNS to CNS
- Long dendrites
- Short axons
Draw and label a sensory neuron

What is relay neuron?
- Connect sensory neurons to motor or other relay neurons
- Short dendrites
- Short axons
Draw and label a relay neuron.









