Basic Tissue Types Flashcards
(51 cards)
Levels of Organization: cells interact to gorm, etc
Cells interact to form tissues, tissues interact to form organs and organ systems of the body
Body constructed of four basic tissues:
Epithelia. Connective Tissue. Muscle. Nerve.
Epithelial Tissue Function (4)
Forms barriers (between inside and outside world, and between compartments within body). Covers exposed body surfaces. Lines hollow organs, body cavities and ducts of glands. Forms glands.
Connective Tissue (4)
Links tissues and organs together. Provides structural and metabolic support for other tissues/organs. Stores energy as adipose tissue. Forms the immune system (cells produced by lymphatic tissue then migrate to connective tissue)
Epithelium is avascular?
it has no blood vessels, so exchange must happen in connective tissue aka structural and metabolic support
Muscle Tissue (3)
`Specialized for contraction. Generates force to produce motion of body parts, move substances through blood vessels and hollow organs. Maintains body temperature (heat loss from contraction)
Nervous tissue (2)
Receives, processes and integrates signals from within body and external environment. Generates and transmits impulses that control and integrate various functions of the body.
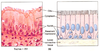
Characteristics of Epithelia (5)
Continuous, avascular, rest on basal lamina, little extracellular matrix, polarized.
Epithelia: continuous and avascular?
never begin or end; no blood vessels
Epithelia: rest on basal lamina?
basal lamina is a specialized layer of connective tissue, the epithelia binds to BL and other things in BL attach to what’s under
Epithelia: little extracellular matrix?
Extra = outside of cell. Cells secrete matrix that connect other cells to each other
Epithelia: polarized?
apical and basolateral surfaces differ - apical faces outside, there are junctions between cells. lateral + basal = basolateral
Tight junction
area where two cells are held so tightly together that things can’t really pass through - no diffusion: has to go THROUGH the cell
Types of Epithelia and Naming
different types serve different functions - named according to number of cells, 1 = simple 2+ = stratified. Shape of cells in outermost layer



Simple Squamous

Simple Cuboidal
Pseudostratified Columnar

Simple Columnar

Stratified Columnar

Stratified Squamous

Transitional
Simple Squamous Epithelium: properties, locations
Single layer of flat cells, very delicate so only found in places without a lot of force: lines body cavities, heart and blood vessels, and site of gas exchange in lungs