Antomical Regions and Directional References Flashcards
Two methods of dividing abdominal region
abdominopelvic quadrants (4) abdominopelvic regions (9)
Abdominopelvic Quadrants - how to divide, use
one horizontal and one vertical line that intersect at the umbilicus/navel - useful for description of aches, pains, injuries
RUQ
right lobe liver, gallbladder, right kidney, stomach, small and large intestine
RLQ
Cecum, appendix, small and large intestine, reproductive organs, right ureter
LUQ
left lobe liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, small and large intestine
LLQ
majority of small intestine, large intestine, reproductive organs, left ureter
9 Abdominal Regions
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right inguinal, hypogastric, left inguinal
Thoracic Cavity (3)
two pleural cavity (lungs) pericardial cavity (heart)
diagphragm
dome shaped muscular sheet, separates superior thoracic cavity and inferior abdominopelvic cavity
body cavities
internal chambers where vital organs are suspended: protection from accidental shocks, cushions them
9 abdominal Regions (picture)





Anterior/Ventral
front/before/belly side: navel is on anterior/ventral surface
Posterior/Dorsal
back/behind - shoulder blade aka scapula is on posterior/dorsal side of body
cranial/cephalic vs. caudal
toward the head vs. toward the tail
superior vs. inferior
above (aka towards head) vs below (aka towards feet
Medial vs. Lateral
toward midline vs away from midline
proximal vs. distal
toward an attached base vs away (thigh is proximal to the foot, fingers and distal to the wrist)
Transverse/Horixonal/Cross-sectional Plane - transversely or horizontally
perpendicular to long axis: separates superior and inferior
Frontal or Coronal plane - frontally, coronally
extends from side to side, divides body into anterior and posterior
Sagittal Plane - Sagittally
extendes from anterior to posterior, divides body into left and right halves
Midsagittal vs parasagittal
mid: passes through midline, divides body in half (left and right)
para: misses midline, separates right and left unequally
oblique plane
not orthoganal - at an angle


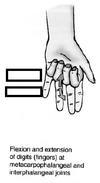
Flexion vs Extension
Flexion: making angle smaller OR moving anteriorally. Extension: making angle bigger or moving posteriorally.









Circumduction

Opposition and Reposition

Retrusion, Protrusion. Elevation and Depression.
Retrusion: posterior, in, rotrustion: anterior, push out. Elevation up, depression down.
Inversion and Eversion

Supination and pronation



