Basic Microscopy and Histology Flashcards
How are stratified epithelia named?
According to the cells at its apical surface
Areolar tissue contains multiple cell types including _________ and ________, and it includes ________, ________, and _______ fibers.
Fibroblasts
Macrophages
Elastic
Collagen
Reticular
What are the two major cell types of the nervous system?
Neurons, neuroglia
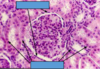
Identify letter n.

Fibroblast
What type of tissue and class is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, blood
Description: RBC and WBC in plasma matrix
Location: Blood vessels (Gas, nutrient, waste transport)
How are epithelial tissues classified on the basis of cell shape?
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar
What are the three subtypes of loose connective tissue?
Areolar, adiose, and reticularis
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, dense, regular
Description: Primarily collagen fibers in parallel where fibroblasts are the major cell type
Location: Tendons, ligaments (Muscle attachment to bone or other muscle, tensile stress resistance when pulled in one direction)
Reticular tissue contains ________ cells and a network of _________ fibers.
Retricular
Reticular
What is the ground substance of blood?
Plasma
Cartilage contains _____% water
80
What do we mean by polarity?
Epithelial tissue has an apical (environment-facing) and a basal (internal-facing) side
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, dense, irregular
Description: Irregularly arranged collagen fibers where fibroblast is the major cell type
Location: Skin dermis, digestive tract submucosa (structural strength, tensile strength resistance in all directions)
What type of tissue and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Muscle, smooth
Description: Spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei with no striations, arranged in sheets
Location: Walls of hollow organs (propulsion, involuntary control)
What occurs prior to microscopic examination?
Tissues are fixed, sectioned, and stained
What are the primary components of the neuon?
The soma (cell body), the dendrites, and the nerve fiber (axon)
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, cartilage, elastic
Description: Similar to hyaline cartilage but contains more elastic fibers in matrix
Location: External ear, epiglottis (shape maintenance, great flexibility)
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Transitional epithelium
Description: Several cell layers that resembles stratified squamous or cuboidal with apical cells dome-liked or squamous-like depending upon degree of stretch
Location: Urinary bladder (stretch, distention)
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Simple columnar epithelium
Description: A single layer of tall cells with round-to-oval nuclei located at the base of the cell and some cells bear cilia
Location: Digestive tract (absorption and secretion; ciliated types propel mucus)
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, cartilage, hyaline
Description: Firm matrix produced by chondrocytes with mature chondrocytes in the lacunae
Location: Cartilage in nose, trachae, and larynx (support and reinforcement, resiliant cushioning, compressive stress resistance)
What tissue type is this?
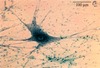
Nervous, neuron
What type of tissue and class is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, bone
Description: Hard, calcified matrix with many collagen fibers and osteocytes lie in lacunae
Location: Bone (support, protection, muscle lever, blood cell production)
What type of tissue type and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Muscle, cardiac
Description: Cells are branched, lightly striated, and uninucleated, joined by intercalcated discs that may not be visible
Location: Walls of heart (blood circulation)
What are the three subtypes of cartilage?
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
What are the four functions of connective tissue?
(1) Binding and support, (2) protection, (3) insulation, and (4) transportation
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?
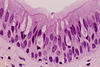
Type: Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Description: A single layer of cells with differing heights and nuclei at different levels; some bear cilia
Location: Trachea (secretion of mucus and propulsion of mucus via ciliary action)
What is this tissue type? Where is it found?
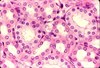
Type: Simple cuboidal epithelium
Description: A single layer of cube-like cells with spherical-shaped central nuclei
Location: Kidney tubules (secretion, absorption)
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Stratified squamous epithelium (non-kerantinized)
Description: Several cell layers with basal cells are cuboidal or columnar with metabolic activity and apical cells are flattened
Location: Esophagus, mouth (protection of underlying tissues)
What are the four primary tissue types?
Epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscle
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, loose, adipose
Description: Very sparse matrix and closely packed adipocytes have nuclei pushed to the side by a large lipid droplet
Location: Under skin; around kidneys, eyeballs; within abdomen; around breasts (fuel, insulation, protection, support)
The most abudant and widely distributed type of tissue is…?
Connective tissue
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Simple squamous epithelium
Description: A single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
Location: Alveoli in the lungs (diffusion and filtration)
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
What are the functions of muscle tissue?
Body movement production, contraction
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, loose, areolar
Description: Gel-like matrix with with 3 fiber types includes fibroblasts and some WBC
Location: Widely distributed under epithelia (wraps and cushions tissues, phagocytize bacteria, holds and conveys tissue fluid)
What is this tissue type? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
Description:
Location: Epidermis
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
To cover the external body, to line inner cavities and tubules, and to function in protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception
What are the two types of bone tissue?
Spongy and compact
What is histology?
The study of tissues
What is A? What is B?

A: Vein
B: Artery
The primary cell type of growing cartilage is the _________, and the primary cell type of mature cartilage is the ________.
Chondroblast
Chondrocycte
From what do connective tissues derive?
Mesenchyme (embryonic connective tissue)
What tissue type and subtype is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?
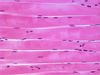
Type: Muscle, skeletal
Description: Cells are long, cylindrical, multinucleated, and striated
Location: Skeletal muscle (Voluntary movement, locomotion, environmental manipulation, facial expression)
What are the primary cell types of blood?
Erthyrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
How are epithelial tissues classified on the basis of cell layer?
Simple and stratified
What do neurons do?
Generate and conduct nerve impulses
The primary cell types of growing bone are the ________ and those of mature bone are the _________.
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
What do neuroglia do?
Protect, support, and insulate the neurons?
What are the four classes of connective tissue?
(1) Connective proper (loose and dense), (2) cartilage, (3) bone tissue, and (4) blood
What is the main cell type of the nervous system?
Neuron
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, cartilage, fibrocartilage
Description: Similar to hyaline cartilage but with more thick collagen fibers and less firm matrix
Location: Intervertabral discs, knee discs (tensile strength, shock compression resistance)
What type of tissue, class, and sub-type is this? What are its characteristics? Where is it located?

Type: Connective, loose, reticular
Description: Network of reticular fibers in loose ground substance
Location: Lymphoid organs (i.e., lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen) (soft internal skeleton, support of other cell types)
What organ is this tissue from? What type of tissue is it composed of?

Kidney
Simple cuboidal epithelium
What tissue type is this?

Connective tissue - areolar tissue
What two tissue types are located in this picture?

Simple squamous epithelium
Simple cubodial epithelium
Where in the body would you find these tissues?
Simple squamous epithelium - the Bowman’s capsule of the kidney
Simple cuboidal epithelium - distal and proximal tubules of the kidney
What type of tissue type is this?

Simple cuboidal epithelium
Where would you find this tissue in the body?

Forms the kidney tubules and collecting ducts, the ducts and secretory portions of many glands, and the surface of the ovary
What tissue type is presented in these pictures?
Where would you find these tissues in the body?

Simple columnar epitelium (non-ciliated)
Digestive tract from stomach and anal canal; the gallbladder; portions of the uterus and uterine tubes; excretory ducts of some glands
Make sure you can identify the following in areolar tissue.
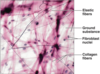
You should be able to identify an erthryocyte from a lymphocyte.

Pay close attention to the morphological differences between elastic, hyaline, and fibrocartilage cartilage types.



