Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Visual System Flashcards
(36 cards)
laminar organization of the retina
- photo receptors
- rods and cones
- horizontal
- bipolar
- amacrine
- ganglion cells

layers of the retina
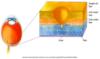
Retinal output to __________
CNS
how do photo receptors in the retina work?
- Hyperpolarize when stimulated by light
- Depolarize when exposed to dark or shadow
- Release neurotransmitter (glutamate) when DEPOLARIZED (i.e., exposed to dark such as shadow)
- COUNTER INTUITIVE: Photo Receptors release more glutamate by dark than by light

regional differences in retinal structure
Periphery of Retina:
- Higher ratio of rods to cones
- Higher ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells
- More sensitive to light

When center receptors are depolarized (dark) the Bipolar Cell is __________ via horizontal cell connections.
hyperpolarized

Photo Receptors, Horizontal Cells and Bipolar Cells:
The Big Picture

what are ganglion cells?
- Ganglion Cells Receive input from Bipolar cells
- Connected laterally by Amacrine cells (similar to horizontal cells)
- Ganglion Cells have a similar Center-Surround organization as Bipolar Cells
- On-Center Off-surround or Off-Center On-surround
- Uniform illumination: surround cancels out signal from center and averages out signal
- Ganglion Cells are Responsive to differences in illumination at EDGES

__________ is only electromagnetic radiation that we can see.
- Wavelength/frequency, amplitude
- Hot colors: Orange, red
- Cool colors: blue, violet

Color is constructed in the __________.
mind
Do rods or cones see color?
cones
- Color is perceived through mixing of signals from 3 cone types: blue, green, and red cones
- Each type has a special spectral sensitivity
- Young-Helmholtz trichromacy theory of color vision

how do we see all the colors?
Opponent Process Theory of Color Vision was developed to account for G-R B-Y oppositions

how do color opponent ganglion cells work?
[AFTER EFFECT: When one color is saturated the surround opposition color is activated and leads to perception of the opposite color]

three types of LGN cells
- P-type X ganglion cells (parvocellular [small])
- M-type Y ganglion cells (magnocellular [big])
- W ganglion cells (koniocellular [tiny])

P-type ganglion cells
- Parvocellular = “small”
- Form & color
- Narrow band
- Selective response to wavelength and fine detail
- Sustained response
M-type Y ganglion cells
- Magnocellular = “big”
- Gross features & movement
- Broad band: Optimal response to large objects and rapid changes in stimulus
- Transient response
W ganglion cells
- Koniocellular = “dust/tiny”
- Color
- Visual Attention
retinofugal projection

Visual Pathways - Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
(parts of the brain)
- Primary projections to the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) in the Thalamus prior to visual cortex
- geniculate = “elbow”

Visual Pathways - Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
(visual field)

non-thalamic targets of the optic tract
- Hypothalamus: Biological rhythms, including sleep and wakefulness
- Pretectum: Determines pupil size; certain types of eye movement
- Superior Colliculus: Orients the eyes in response to new stimuli

possible problems in
primary area of the visual cortex
(unimodal)
- Cortical blindness
- Anton’s syndrome (denial of blindness)
- Blindsight (unconscious perception)
- Anopia Hemianopia (visual field deficit)
- Scotomas
possible problems in
secondary area of the visual cortex
(unimodal)
- Visual agnosias
- Object agnosia
- Apperceptive: Disruption of basic processes; cannot discriminate or copy simple forms, such as a square or triangle
- Associative: Can perceive and copy an object, but cannot discern meaning (what is it?)
- Integrative: Similar to associative but difficult with details & wholes
- Prosopagnosia
- Color agnosia (achromatopsia)
- Object agnosia
- Akinetopsia– deficit in motion processing
- Dorsal simultaneous agnosia: Can copy objects in a piecemeal fashion but cannot integrate parts of objects into a whole, especially with many parts\
- Optic ataxia: Deficit in visually-guided reaching
- Ocular apraxia: Cannot shift gaze at will with shifts of attention
possible problems in
tertiary area of visual cortex
(multimodal)
- Object anomia; color anomia
- Alexia (word blindness)
- Disruption of body orientation in extrapersonal space based on visual cues
- Constructional apraxia (based on visual cues) & dressing apraxia
- Disruption of geographic knowledge including environmental agnosia












