Back Flashcards
(18 cards)

Trendelenburg Test
- gluteus medius weakness
- if opposite drops

Beevor’s Sign
- patient performs crunch
- look for umbilicus to move
- segmental involvment of the nerves innervating the recturs abdominis

Valsalva Test
-space-occupying lesion (herniate ddisk, tumor, etc)
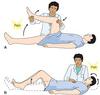
Kernig’s Test
lifting of leg
Brudzinski’s
- stretches dural sheath with neck flexion
- nerve root impingement
- irritation of meninges
- intervertebral disk or bony entrapment
SLR test
Straight Leg raise test
-sciatic nerve irritation
pn before 70 - disk involvement
pn before 30 - very reliable that findings are correct
modify: dorsiflex annkle and flex cervical spine - if no pn with this - cause is hamstring tightness not neurological

Well (Cross Straight Leg raise)
- SLR produces pain in opposite leg
- space occupying lesion (herniated disk)

Slump Test
- shoulder, neck, leg, ankle
- repeat on opposite side
- sciatic pain, impingement of dural lining, spinal cord or nerve roots

- patient extends spine and sidebends and rotates to affected side
- examiner gives over pressure
Quadrant Test
compression of intervertebral foramina (radiating pn)
facet joint pathology (local pn)
SI dysfunction (isolated at PSIS)
L1-S2 Sensory, Motor, Reflexes
L1-2 - hip flexion
L3 - knee extension
L4 - Dorsiflexion
L5 - Great Toe Extension
S1 - Eversion
S2 - Knee Flexion
Reflexes:
L2-L4: patellar
S1: Achilles

Femoral Nerve Stretch
prone with pillow under abdomen
knee is passivley flexed and hip extended
nerve root impingement of L2-L4

Tension Sign
90-90 position
-extend knee, palpate at tibial nerve in popliteal space
sciatic nerve irritation

Single Leg Stance Test
One leg - extend back
shear force on pars interarticularis
pain should be produced in opposite leg

SI compression and Distraction
Distraction - relieve pain
COmpression - reciprocate pain
SI pathology

FABER (Patrick’s Test)
flexion abduction external rotation
SI symptoms

Gaenslen’s Test
Supint - lies near edege of table - one leg hanging off - the other pulled back
-apply pressure to both legs
SI joint dysfunction
Long Sit Test
Patient is supine, hold at malleoli
Patient lifts hips off table - relaxes - moves into long sit position
longer to a shorter - anterior rotation of ilium
shorter to longer - posteior rotation of ilium
C1-T1
C1/C2: neck flexion
C3: neck lateral bending
C4: shoulder shrug
C5: Abduction
C6: Elbow flexion
C7: Elbow extension
C8: Oppostion
T1: Finger Abduction
Reflexes
C5: Biceps
C6: Brachioradialis
C7: Triceps
Most Lumbar/THoracic spince tests will indicate nerve root impingement. what tests will rule in disk involvement
Valsalva (space occupying lesion)
Milgram (space occuyping lesion)
SLR test (if pn before 70 hip flexion)
well cross SLR test (space occupying lesion)
femoral nerve stretch test (lumbar nerve root)
tension sign (sciatic nerve)


