Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Flashcards
(22 cards)
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
part of the nervous system that controls the internal (visceral) organs of the body (i.e. the viscera)
not normally under conscious control
- bladder control, crying
3 main divisions of the ANS:
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS)
- Enteric Nervous System (ENS - the gut)
ANS function
primary role is to maintain homeostasis
SNS and PSNS work together to maintain homeostasis
it helps regulate:
- heart rate
- blood pressure
- body temperature
- gastrointestinal and bladder motility
- gland secretions (hormones, sweat)
- regulates blood glucose levels
- sexual function
ANS organization visual receptors
homeostasis is the relatively constant condition of the internal environment of the body
sensory receptors monitor internal environment/organs

ANS organization sensory afferent fibers
these receptors send signals back to CNS through sensory afferent fibers

ANS organization integration centers
CNS integration centre interprets signals and activates hypothalamus

ANS organization hypothalamus
hypothalamus master controller of ANS
ANS organization SNS & PSNS
output through branches of the ANS:
- sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
- parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)

ANS organization smooth/cardiac muscle glands
the ANS exerts its actions by controlling target organs (effectors):
- smooth muscle in blood vessels, digestive tract
- specialized cardiac tissue and cardiac muscle
- glands; salivary, sweet, adrenal gland, etc.
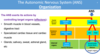
ANS peripheral efferent nerves

general characteristics of peripheral (efferent) nerves
- preganglionic neurons (cell body in CNS, terminates on ganglion)
- ganglion
- postganglionic neurons (cell body in ganglion, terminates on target tissue)
- target tissue/organ)

somatic and autonomic motor system

pathways of peripheral (efferent) nerves
a) parasympathetic pathway
b) sympathetic pathway
c) adrenal sympathetic pathway

PSNS vs SNS - anatomical differences
both contain:
- preganglion neurons
- ganglion
- postganglionic neurons
- target tissue/organ
differences:
- location of ganglion
- length of preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron
- types of neurotransmitters released
parasympathetic: long pre-ganglionic neuron (Ach); short post-ganglionic neuron (Ach)
sympathetic: short pre-ganglionic neuron (Ach); long post-ganglionic neuron (NE)

adrenal sympathetic pathway
there is only one SNS preganglionic neuron to adrenal gland
adrenal gland secretes epinephrine (adrenaline) with a little norepinephrine

innervation of SNS and PNS

innervation of upper body, heart and lungs (SNS)
fight or flight

more light entering eye
thick mucus
increases blood output by the heart
move air in & out of lungs easily
innervation of digestion (SNS)
fight or flight

shut down digestion
innervation of adrenal glands, kidneys and bladder (SNS)
fight or flight

releases epinephrine (adrenaline)
holds in urine
innervation of adrenal glands, kidneys and bladder (PSNS)
rest and digest

no PSNS innervation for the kidney
contracts bladder
innervation of upper body, heart and lungs (PSNS)
rest and digest

less light entering eye
watery saliva and enzymes for digestion
decreases blood output from heart
innervation of digestion (PSNS)
rest and digest
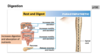
increases digestion and absorption of nutrients
innervation reproductive organs (PSNS & SNS)
sexual activity

sexual responses are mediated by the coordinated activity of both SNS and PSNS


