Attitudes and persuasion Flashcards
Who’s the fundamental debate in attitudes between and what do they say?
Cognitive (attitudes and persuasion fundamentally cognitie) vs discursive (focus on attitudes as discursive and examine rhetoric of persuasion in everyday persuasive attempts)
Describe debates in cognitive perspective
How can we measure it? - Explicit measures: Thurstone/Likert scale / semantic differences / (people might hide their attitudes though) - or implicit association test What cognitive processes are involved? How do we explain the sometimes low correspondence with actual behaviour?
Describe Thurstone scale
Various statements (with degrees of agreeing with one or the other side of argument) - choose the one you agree with Problem: researcher defines attitudes
Describe Semantic differential
Have a statement (eg Chinas actions in Tibet has been) and then a line with to extremes in each end (eg good———-bad) - asked to choose where on the line you stand Problem: Double definition of neutral category (ie is tutor kind——wise - what is the middle?)
Describe likert scale
Statement and a line with agre—-disagree. Choose where you stand. Problem: Are people honest? Does it relate to behaviour?
Describe implicit association test
(think the men vs woman over kitchen vs work) Problem: Big leap from associations to attitudes
Describe Fishbein and Ajzen’s theory of reasoned action
Attitudes towards behaviour AND subjective norm –> Behavioural intention –> Behvaiour
Describe Ajzen’s theory of planned behaviour
Perceived control eg *I would love to stop smoking, but I am so stressed at the moment’
Problem: What about habit?
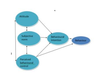
Heider’s balance theory (Concistency theory 1)
Our attitudes towards someone can be changed if they have a positive attutide to somethig we have a negative attitude towards et vice verca (think vegetarian dates hunter)

Festinger’s dissonance theory (Consistency theory 2)
We have inner drive that hold attitudes in harmony and avoid disharmony (dissonance)
Cognitive Dissonance = situation with conflicting attitudes cause discomfort and leads to change in one of the attitudes to restore balance (example smokers change beliefs in order to keep smoking)
Describe ingredients of persuasion
Who (source) says what (message) to whom (audience)
Source factors: Credibility, expertise, trustworthness, attractiveness, similarity
Message factors: numbers of arguments (more the mor certain), strength of arguments
Audience factors: Intelligence and self-esteem
Describe the elaboration likelihood model
High personal consequence –> central route –> attitude change determined by argument quality no signifacent effect of source expertise
Low personal consequence –> periphical route –> Attitude change determined by source expertise
Describe debates in discursive perspective
How can we rethink attitudes as discursive work?
What constructions are working in persuasive talk and how is it positioned as true?
Issues: variables (as attractivness and credibility) often work at same time, experiments consequences differ from real life
–> attitudes interactionally deployed rather than static
–> what’s going on in the head not focused on, instead focus on language activity


