Approach to Reproductive Topics Flashcards
Which of the following is the development of breast tissue due to estroegn from the ovaries?
A. Adrenarche
B. Gonadarche
C. Menarche
D. Spermarche
E. Thelarche
Thelarche

Puberty in females begins between what ages?
Puberty in males begins between what ages?
Females: 10-14
Males: 11-16
NOTE: menarche in females starts around 2-3 years after beginning puberty
What things are included when taking a menstrual history?
- age of menarche, duration, flow and cycle length
- Last menstrual period (LMP)
What 5 things are recorded when taking a gynecologic history?
- Breast history
- last mammogram (if applicable)
- previous GYN surgery
- history of infertility
- last pap smear
BE familiar with these Tanner stages

Oh boy
Women should get their pap smear starting at 21 years of age until 65 years of age. A woman with an abnormal pap smear would need to get a Pap how often?
A. once per month
B. yearly
C. every 3 years
D. every 5 years
yearly
Women should get their pap smear starting at 21 years of age until 65 years of age. How often should a woman with consecutively normal pap smear with negative HPV testing get assessed?
A. once per month
B. yearly
C. every 3 years
D. every 5 years
every 5 years
At what Tanner stage would a boy be at if you note enlargement of the testes and scrotum, with scrottal skin redness and texture changes?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 2
At what Tanner stage would a boy be at if you note darkening of the scrotal skin?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 4
NOTE: stage 5 is adult genitalia
At what Tanner stage would a girl be at if you note further enlargement of breast and areola, with no separation of their contour?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 3
At what Tanner stage would a girl be at if you note the areola and papilla form a secondary mound above level of breast?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 4
At what Tanner stage would a boy or girl be at if you note sparse growth of long, slightly pigmented hair, straight or curled, at base of penis or along labia?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 2
At what Tanner stage would a boy or girl be at if you note darker, coarser, or more curled hair spreading sparsely over junction of the pubes?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
E. Stage 5
Stage 3
In which of the following scenarios is a pap smear no longer necessary?
A. Consecutive normal pap smears for 40 years straight since 21
B. Following a Hysterectomy for noncancerous reasons
C. Following a Hysterectomy for cervical cancer
D. Women have to get pap smears forever until they die
Following a Hysterectomy for noncancerous reasons
While both pelvic exam and pap smear require insertion of the speculum. A pap smear only looks to obtain samples of cervical cells as well as look at the cervix. while a pelvic exam includes what?
- examining internal and external genitalia
- check for cervical motion tenderness
- obtain swabs for STIs
T/F: When performing a pelvic exam, first visually inspect, then perform bimanual exam, then obstain swab samples if indicated
True
What are some broad based DDx associated with Pelvic pain?
GU:
GYN:
GI:
GU: STI, UTI
GYN: Ectopic pregnancy, ruptured ovarian cyst
GI: appendicitis, constipation, IBS
What is the classical presentation of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
A. Abdominal or pelvic pain with vaginal bleeding
B. Other pregnancy related symptoms (naeusea, breast tenderness)
C. polyuria and polydipsia
D. All but C
All but C
A female that presents with any symptoms that go under ectopic pregnancy should ALWAYS be evaluated with what?
Urine pregnancy
(maybe: speculum exam, and with confirmed pregnancy transvaginal ultrasonography)
When a UTI is suspected, what specialty test is a good idea to perform?
A. McBurney’s Point Tenderness
B. Rebound Tenderness
C. McMurray’s
D. Lloyd’s Punch
Lloyd’s Punch (check for costovertebral angle tenderness)
Which of the following is true of Prostate Exams, Testicular Exams, and Prostate Specific Antigen?
A. Should always be performed routinely
B. Should be performed once every 2-3 years
C. Only performed based on patient signs and symptoms from history
D. Should be performed everytime they see a health professional. Every time.
Only performed based on patient signs and symptoms from history
Which of the following hernias is most common in men older than 40, with hernia located above inguinal ligament clos to the pubic tubercle?
A. Femoral Hernia
B. Indirect Hernia
C. Direct Hernia
D. All of the above
Direct Hernia

All of the following are risk factors for STIs, EXCEPT?
A. New partner in the past 90 days
B. Multiple sex partners or a partner who has multiple partners
C. Sex with partners recently treated for an STI
D. Sex Worker
A. New partner in the past 90 days
Correct: New partner in the past 60 days (2 months)
Alll of the following are bacterial STIs, except for which of the following? (Bonus: what are they)
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Herpes Simplex-2
D. HPV
E. Syphilis
F. Trichomoniasis
C. Herpes Simplex-2 (virus)
D. HPV (virus)
F. Trichomoniasis (protazoan)
Which of the following is a gram negative bacteria that classically presents in males with discharge and dysuria, and pelvic pain or mucpurulen vaginal discharge in females? (warning pictures ahead)
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
Gonorrhea

Which of the following STIs calssically presents with genital warts, and has strains that can lead to cancer in both the oropharyngeal region or lower genital tract?
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
HPV

Which of the following STIs classically presents in most males as asymptomatic, but in females causes a foul smelling thin vaginal discharge, puritus, and dysuria?
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
Trichomonasis
NOTE: Wet mount, or NAATs(nucleic acid amplification test) is used to diagnose

Which of the following STIs classically presents in singles or clusters of vesicles on the genitalia, and may be accompanied by burning, tingling, or pain prior to the vesicles appearing?
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes (virus)
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
Genital Herpes (virus)
NOTE: Complications include meningitis, PID, hepatitis, increase risk of HIV due to open sores
- diagnosed with serologic test or PCR

Which of the following STIs classically in 4 stages: Painless ulcer (chancre) > Joint pain and fatigue > asymptomatic latent phase > neurologic isses (confusion, head ache, vision loss)
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes (virus)
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
Syphilis
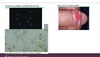
Which of the following STIs is a gram negative bacteria that is often asymptomatic, but can present in males with penile discharge, prurtitus (itch), and dysuria; and vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding or pain during intercourse (dyspareunia), and dysuria?
A. Chlamydia
B. Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis
D. Genital Herpes (virus)
E. Trichomonasis
F. HPV
Chlamydia
NOTE: complications include PID if untreated and fertility issues
- NAATs on endocervical, urethral, vaginal, pharyngeal, rectal, or urine samples to diagnose
What is the most common area of precancerous lesions and cancers to form, and is why this area must be checked during a pap smear?
ectocervix-endocervix-transitional zone/squamocolumnar junction (SCJ)


