Aneurysms Flashcards
(15 cards)
What is the definition of an aneurysm?
Abnormal dilatation of a blood vessel more than 50% of its normal diameter
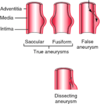
What is the definition of a true aneurysm?
Dilatation of a blood vessel involving all layers of the wall and is more than 50% of its normal diameter
What are the types of true aneurysm?
Fusiform e.g. AAA
Saccular e.g. Berry aneurysm

What is the definition of a false aneurysm?
A collection of blood around the vessel wall that communicates with the vessel lumen
What is the aetiology of a false aneurysm?
Usually iatrogenic e.g. puncture, cannulation
What is the definition of aortic dissection?
Vessel dilatation caused by blood splaying apart the media to form a channel within the vessel wall
What are some causes of aneurysms?
Congenital:
- AD PKD: Berry aneurysms
- Connective tissue disorders: e.g. Marfans, Ehlers-Danlos
Acquired:
- Atherosclerosis
- Trauma e.g. penetrating trauma
- Inflammatory: Takayasu’s aortitis, HSP
- Infection: Tertiary syphilis, salmonella typhi
What are complications of aneurysms?
- Rupture
- Thrombosis
- Distal embolisation
- Pressure: DVT, oesophagus, nutcracker syndrome
- Fistula: IVC, intestine
What aneurysms require monitoring?
Those 4-5.5cm (over 5.5 require repair)
Which aneurysms should be repaired?
Symptomatic: Back pain, tenderness to palpation, distal embolic events, ruptured/leaking
Asymptomatic: 5.5cm+ or those increasing in diameter by 1cm or more
Why is it recommended to repair aneurysms 5.5cm+?
At this size the risk of rupture increases exponentially- 10% at 5.5cm, increasing with increasing size
What is a false aneurysm?
A collection of blood around a vessel wall that communicates with the lumen (i.e. a pulsating haematoma)
Formation of fibrous tissue around the haematoma forms a false sac which communicates with the vessel lumen
What is the difference between a true and false aneurysm?
A true aneurysm involves all layers of the arterial wall
What is the aetiology of a false aneurysm?
Following a laceration/puncture to vessel wall
Usually iatrogenic or traumatic e.g. common femoral following puncture for radiological procedure
How do you manage a false aneurysm?
Non-surgical:
- US compression
- Thrombin injection
Surgical repair


